The Earth`s structure
... It is the layer on which we live as the continents and the oceans rest on it. It is made of solid material and floats on the Mantle. Its thickness varies depending upon the type of materials of which it is made. Therefore Oceanic crust is about 6 to 11km thick, while Continental crust is about 30 km ...
... It is the layer on which we live as the continents and the oceans rest on it. It is made of solid material and floats on the Mantle. Its thickness varies depending upon the type of materials of which it is made. Therefore Oceanic crust is about 6 to 11km thick, while Continental crust is about 30 km ...
Unit 1:
... ordering of rock layers (relative dating and radioactive dating). Week 3: Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics: 8.L.4.1: Summarize the use of evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy to form the basis for biological classification systems and the theory of evolution. Week 4 ...
... ordering of rock layers (relative dating and radioactive dating). Week 3: Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics: 8.L.4.1: Summarize the use of evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy to form the basis for biological classification systems and the theory of evolution. Week 4 ...
Are the continents moving? What are plate tectonics?
... had once been joined, and over time had drifted apart. Pangaea was a supercontinent that included all the world's landmasses in the late Paleozoic and, according to the theory of plate tectonics. ...
... had once been joined, and over time had drifted apart. Pangaea was a supercontinent that included all the world's landmasses in the late Paleozoic and, according to the theory of plate tectonics. ...
BR field trip - Marshall University
... “Lynchburg Formation” (mostly known as the Ashe and Alligator Back formations) and its stratigraphic equivalent??? the Mount Rogers and Konnarock Formations (Late Proterozoic). The latter two formations represent acidic and basic volcanic and pyroclastic rocks (Mt. Rogers) and glacial deposits (Konn ...
... “Lynchburg Formation” (mostly known as the Ashe and Alligator Back formations) and its stratigraphic equivalent??? the Mount Rogers and Konnarock Formations (Late Proterozoic). The latter two formations represent acidic and basic volcanic and pyroclastic rocks (Mt. Rogers) and glacial deposits (Konn ...
No Slide Title
... How are the ocean basins formed? How permanent are these features? What is the age of the ocean floor? What’s the age of the continents? Why are the ocean basins deep and the continents high? ...
... How are the ocean basins formed? How permanent are these features? What is the age of the ocean floor? What’s the age of the continents? Why are the ocean basins deep and the continents high? ...
Plate tectonics
... nickel and iron. Outer part is liquid and inner part is solid. 4000 – 4700 o C The average density of the Earth is much higher than the crust, so the inner core must be very dense ...
... nickel and iron. Outer part is liquid and inner part is solid. 4000 – 4700 o C The average density of the Earth is much higher than the crust, so the inner core must be very dense ...
PPT link ch 14
... depend on stripping ratio • Large land area can be involved, especially for coal and bauxite. Results of Mining utube ...
... depend on stripping ratio • Large land area can be involved, especially for coal and bauxite. Results of Mining utube ...
Geology 13/14 (RTF 44kB)
... GL3301 Sedimentary Petrology: from sediment to rock TBA 5 credits This module deals with how sediment is produced at the Earth’s surface and then becomes rock and how the information preserved in these sedimentary rocks can be related to the physical, chemical and biological processes that occurred ...
... GL3301 Sedimentary Petrology: from sediment to rock TBA 5 credits This module deals with how sediment is produced at the Earth’s surface and then becomes rock and how the information preserved in these sedimentary rocks can be related to the physical, chemical and biological processes that occurred ...
Homework Assignment #3: Igneous Processes and
... down. The same is true in rock (only even more so because rock is denser than water). So, as long as magma is deep within the earth, it is under great pressure and the gas it contains remains dissolved. However, when that magma rises up toward the surface, the pressure on it decreases. The gas can n ...
... down. The same is true in rock (only even more so because rock is denser than water). So, as long as magma is deep within the earth, it is under great pressure and the gas it contains remains dissolved. However, when that magma rises up toward the surface, the pressure on it decreases. The gas can n ...
Important Vocabulary Terms: Match them with definitions below
... Answer the following using the above Mohs Hardness Scale. I scratch a mineral with my fingernail, which mineral or minerals can it be? Talc or Gypsum Which tool can scratch Fluorite but not Apatite? Nail Which minerals could scratch steel? Quartz, Topaz, Corundum, and Diamond If I wanted to engrave ...
... Answer the following using the above Mohs Hardness Scale. I scratch a mineral with my fingernail, which mineral or minerals can it be? Talc or Gypsum Which tool can scratch Fluorite but not Apatite? Nail Which minerals could scratch steel? Quartz, Topaz, Corundum, and Diamond If I wanted to engrave ...
Plate tectonics/boundaries
... Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. ______ 1. A break in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other is called a a. plate. b. layer. c. boundary. d. fault. ______ 2. Continental crust consists mainly of the rock a. nickel. b. basalt c. mantle. d. granite. _____ ...
... Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. ______ 1. A break in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other is called a a. plate. b. layer. c. boundary. d. fault. ______ 2. Continental crust consists mainly of the rock a. nickel. b. basalt c. mantle. d. granite. _____ ...
Earth Changes
... But mostly we just get on out and take a look.” Geologists, seismologists, paleontologists too, Doing the rock science bugaloo! The igneous rock bubbles up from the ground, Sedimentary rock falls and settles on down. When it gets low enough, with some pressure and heat, A changed metamorphic rock yo ...
... But mostly we just get on out and take a look.” Geologists, seismologists, paleontologists too, Doing the rock science bugaloo! The igneous rock bubbles up from the ground, Sedimentary rock falls and settles on down. When it gets low enough, with some pressure and heat, A changed metamorphic rock yo ...
Plate Tectonic, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes Test Review
... Layers based on composition: a. Describe each layer: i. __Crust____________- the thinnest layer. We live on it. Made up of two types: continental (less dense/granite) and oceanic (more dense/ basalt). Lighter minerals (silicates) ii. ___Mantle_________- Magnesium and iron. Makes up most of Earth’s m ...
... Layers based on composition: a. Describe each layer: i. __Crust____________- the thinnest layer. We live on it. Made up of two types: continental (less dense/granite) and oceanic (more dense/ basalt). Lighter minerals (silicates) ii. ___Mantle_________- Magnesium and iron. Makes up most of Earth’s m ...
geologic highlights of southeastern arizona and vicinity
... crust. Thick deposits of limestone, mudstone (shale) and sandstone form in these marine and tidal/beach environments. Paleozoic marine sedimentary rocks from this time are now exposed throughout Arizona, notably in the Grand Canyon and Whetstone Mountains. The first abundant fossils of marine life w ...
... crust. Thick deposits of limestone, mudstone (shale) and sandstone form in these marine and tidal/beach environments. Paleozoic marine sedimentary rocks from this time are now exposed throughout Arizona, notably in the Grand Canyon and Whetstone Mountains. The first abundant fossils of marine life w ...
Topic 2 notes - WordPress.com
... Note that state symbols are added to each substance: o s – solid o g – gas o l – pure liquid (e.g water) o aq – aqueous solution…formed when substances dissolve in water (e.g sodium hydroxide) Mass is conserved in chemical reactions: Atoms are NOT made or destroyed in a chemical reaction. They are o ...
... Note that state symbols are added to each substance: o s – solid o g – gas o l – pure liquid (e.g water) o aq – aqueous solution…formed when substances dissolve in water (e.g sodium hydroxide) Mass is conserved in chemical reactions: Atoms are NOT made or destroyed in a chemical reaction. They are o ...
C1 – Topic 2 notes - ARK Elvin Academy
... Note that state symbols are added to each substance: o s – solid o g – gas o l – pure liquid (e.g water) o aq – aqueous solution…formed when substances dissolve in water (e.g sodium hydroxide) Mass is conserved in chemical reactions: Atoms are NOT made or destroyed in a chemical reaction. They are o ...
... Note that state symbols are added to each substance: o s – solid o g – gas o l – pure liquid (e.g water) o aq – aqueous solution…formed when substances dissolve in water (e.g sodium hydroxide) Mass is conserved in chemical reactions: Atoms are NOT made or destroyed in a chemical reaction. They are o ...
File
... d. Hot magma rises through the boundary at the mid-ocean ranges, creating new rock and pushing apart the plates 13. The oldest oceanic crust would be found in which location? a. At the edge of a continent b. Half way between a ridge and a trench c. At a mid-ocean ridge d. At a deep sea trench 14. Wh ...
... d. Hot magma rises through the boundary at the mid-ocean ranges, creating new rock and pushing apart the plates 13. The oldest oceanic crust would be found in which location? a. At the edge of a continent b. Half way between a ridge and a trench c. At a mid-ocean ridge d. At a deep sea trench 14. Wh ...
Chemistry: Atoms First, McMurry and Fay, 1st Edition
... glacial deposits of South Africa, Australia, South America, and Antarctica. It grew in a cold, wet climates. Plants with elongate, ...
... glacial deposits of South Africa, Australia, South America, and Antarctica. It grew in a cold, wet climates. Plants with elongate, ...
pdf 1.5Mb
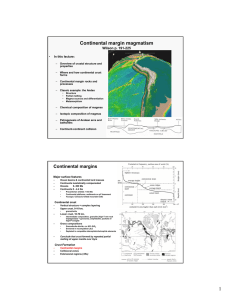
... volcanics. From Atherton et al. (1979) In M. P. Atherton and J. Tarney (eds.), Origin of Granite Batholiths: Geochemical Evidence. Shiva. Kent. Winter (2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic ...
... volcanics. From Atherton et al. (1979) In M. P. Atherton and J. Tarney (eds.), Origin of Granite Batholiths: Geochemical Evidence. Shiva. Kent. Winter (2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic ...
File
... Radioactive processes in the core give heat to the mantle. Convection currents then cause the plates to move slowly. Oceanic plates are more dense than continental so in destructive collisions there is subduction and partial re-melting of the oceanic plates. Plates are cooler at ocean margins and so ...
... Radioactive processes in the core give heat to the mantle. Convection currents then cause the plates to move slowly. Oceanic plates are more dense than continental so in destructive collisions there is subduction and partial re-melting of the oceanic plates. Plates are cooler at ocean margins and so ...