Tethyan and Indian subduction viewed from the Himalayan high
... (3) Ultrahigh-pressure rocks on both sides of the western syntaxis (Kaghan and Tso Morari massifs) formed during the early stage of subduction/exhumation of the Indian northern margin at the time of the Paleocene–Eocene boundary. (4) Granulitized eclogites in the Lesser Himalaya Sequence in southern ...
... (3) Ultrahigh-pressure rocks on both sides of the western syntaxis (Kaghan and Tso Morari massifs) formed during the early stage of subduction/exhumation of the Indian northern margin at the time of the Paleocene–Eocene boundary. (4) Granulitized eclogites in the Lesser Himalaya Sequence in southern ...
Chapter 21: Fossils and the Rock Record
... younger than the schist, because the granite cuts across the schist. In earthquake-prone areas, such as California, and in ancient, mountainous regions, such as the Adirondacks of New York, there are many faults. As you learned in Chapter 20, a fault is a fracture in Earth along which movement takes ...
... younger than the schist, because the granite cuts across the schist. In earthquake-prone areas, such as California, and in ancient, mountainous regions, such as the Adirondacks of New York, there are many faults. As you learned in Chapter 20, a fault is a fracture in Earth along which movement takes ...
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
... List the forces that power Earth's rock cycle 2. Igneous Rocks Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks Demonstrate how the rate of cooling affects an igneous rock's texture Classify igneous rocks according to texture and composition 3. Sedimentary Rocks Describe the majo ...
... List the forces that power Earth's rock cycle 2. Igneous Rocks Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks Demonstrate how the rate of cooling affects an igneous rock's texture Classify igneous rocks according to texture and composition 3. Sedimentary Rocks Describe the majo ...
Geodynpub_files/Boutelier, 2004
... strength of its layers reduces. The weakening continental crust reaches maximal depth of about 120 km and cannot subduct deeper because its frontal part starts to flow up. The subducted crust undergoes complex deformation, including indicated upward ductile flow of the most deeply subducted portions ...
... strength of its layers reduces. The weakening continental crust reaches maximal depth of about 120 km and cannot subduct deeper because its frontal part starts to flow up. The subducted crust undergoes complex deformation, including indicated upward ductile flow of the most deeply subducted portions ...
Paleozoic stratigraphy, tectonics and metallogeny
... Groundhog, Cloutier and Gray Creek formations) that crop out across the Pelly Mountains (Fig. 2; TempelmanKluit, 2012). The Cloutier formation, named for exposures near Cloutier Creek, contains greater than 500 m of mafic lava and volcaniclastic rocks that represent the volcanic centre of the belt. ...
... Groundhog, Cloutier and Gray Creek formations) that crop out across the Pelly Mountains (Fig. 2; TempelmanKluit, 2012). The Cloutier formation, named for exposures near Cloutier Creek, contains greater than 500 m of mafic lava and volcaniclastic rocks that represent the volcanic centre of the belt. ...
Continental subduction and exhumation of high
... strength of its layers reduces. The weakening continental crust reaches maximal depth of about 120 km and cannot subduct deeper because its frontal part starts to flow up. The subducted crust undergoes complex deformation, including indicated upward ductile flow of the most deeply subducted portions ...
... strength of its layers reduces. The weakening continental crust reaches maximal depth of about 120 km and cannot subduct deeper because its frontal part starts to flow up. The subducted crust undergoes complex deformation, including indicated upward ductile flow of the most deeply subducted portions ...
Preliminary Investigation of the Thermotectonic History of the Central
... Saskatchewan, by the Saskatchewan Geological Survey (2003), included low-grade metasedimentary rocks of the Crew Lake Belt (formerly part of the La Ronge Domain) as part of the Rottenstone Domain (Figure 1). On Reindeer Lake, several lithotectonic assemblages have been distinguished within the Rotte ...
... Saskatchewan, by the Saskatchewan Geological Survey (2003), included low-grade metasedimentary rocks of the Crew Lake Belt (formerly part of the La Ronge Domain) as part of the Rottenstone Domain (Figure 1). On Reindeer Lake, several lithotectonic assemblages have been distinguished within the Rotte ...
Information Circular No. 358
... The geotectonic units of the Danba and Pan-Xi areas form part of the Songpan-Garze orogenic belt and the Panzhihua-Xichang intracontinental rift belt (GMGR, 1998). The Songpan-Garze belt in western Sichuan occurs between the Jinshajiang ophiolitic melange and the Longmenshan-Xiaojinhe fault zones, a ...
... The geotectonic units of the Danba and Pan-Xi areas form part of the Songpan-Garze orogenic belt and the Panzhihua-Xichang intracontinental rift belt (GMGR, 1998). The Songpan-Garze belt in western Sichuan occurs between the Jinshajiang ophiolitic melange and the Longmenshan-Xiaojinhe fault zones, a ...
Detrital Zircons from Missi Metasedimentary Rocks, Flin Flon Basin
... the Reindeer Zone did not occur until about 1810 Ma (Machado, 1990), and so the Flin Flon area was probably separated from Superior Province Archean rocks by an ocean basin at the time of Missi sedimentation. Bickford et al. (1990) suggest that collision between the Reindeer Zone, and the Rae-Hearne ...
... the Reindeer Zone did not occur until about 1810 Ma (Machado, 1990), and so the Flin Flon area was probably separated from Superior Province Archean rocks by an ocean basin at the time of Missi sedimentation. Bickford et al. (1990) suggest that collision between the Reindeer Zone, and the Rae-Hearne ...
12.710 – Problem Set 4 solutions 1. What is “the geothermal
... 10. What is the fundamental difference between granite and rhyolite? Gabbro and basalt? Granite and rhyolite have the same chemical composition, but granites cool more slowly beneath the Earth’s surface (intrusive or plutonic rocks), while rhyolites cool quickly after eruption on the surface (extru ...
... 10. What is the fundamental difference between granite and rhyolite? Gabbro and basalt? Granite and rhyolite have the same chemical composition, but granites cool more slowly beneath the Earth’s surface (intrusive or plutonic rocks), while rhyolites cool quickly after eruption on the surface (extru ...
YOUNG RHYODACITE DIKES FOUND IN THE QUEENS TUNNEL
... extend over 10 feet (parallel to hammer handle) into surrounding amphibole gneiss. Relative Age Relationships of Dikes to Faults As indicated above (See Table 1), emplacement of the dikes took place along preexisting faults, fault zones, fold axial surfaces, shear zones, and joints in the host rocks ...
... extend over 10 feet (parallel to hammer handle) into surrounding amphibole gneiss. Relative Age Relationships of Dikes to Faults As indicated above (See Table 1), emplacement of the dikes took place along preexisting faults, fault zones, fold axial surfaces, shear zones, and joints in the host rocks ...
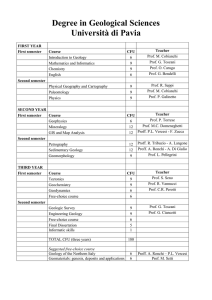
Bachelor Degree in Geological Sciences
... endogenous and exogenous systems: the plate tectonics. Earth deformations: faults, folds and other structures. Plate tectonics and orogeny. Earthquakes and volcanoes. The exogenous system: cratons, mountain ranges and ocean basins; biosphere, cryosphere, idrosphere, atmosphere; the sedimentary rocks ...
... endogenous and exogenous systems: the plate tectonics. Earth deformations: faults, folds and other structures. Plate tectonics and orogeny. Earthquakes and volcanoes. The exogenous system: cratons, mountain ranges and ocean basins; biosphere, cryosphere, idrosphere, atmosphere; the sedimentary rocks ...
Document
... The most important characteristics of porphyry systems [5, 6, 7] are as follows: (1) Occurrence of ore-bearing minor porphyry intrusions (<2 km in diameter) composed of calc-alkaline and potassic, moderately alkaline rocks. The ore is also hosted in volcanic, sedimentary, and other country rocks. C ...
... The most important characteristics of porphyry systems [5, 6, 7] are as follows: (1) Occurrence of ore-bearing minor porphyry intrusions (<2 km in diameter) composed of calc-alkaline and potassic, moderately alkaline rocks. The ore is also hosted in volcanic, sedimentary, and other country rocks. C ...
J
... depths, the flow may continue to be focused and may discharge through a chimney, or it may follow more tortuous pathways and be discharged as a more diffuse flow (like water flowing through a sponge). Continued high-temperature reactions between the rock and the upward-flowing, metalrich, magnesium- ...
... depths, the flow may continue to be focused and may discharge through a chimney, or it may follow more tortuous pathways and be discharged as a more diffuse flow (like water flowing through a sponge). Continued high-temperature reactions between the rock and the upward-flowing, metalrich, magnesium- ...
Chapter 14 - Mesozoic Geology
... • Subduction of the Farallon plate – beneath the North American plate continued during this time, – resulting in numerous overlapping, – low-angle thrust faults – in which blocks of older strata – were thrust eastward – on top of younger strata ...
... • Subduction of the Farallon plate – beneath the North American plate continued during this time, – resulting in numerous overlapping, – low-angle thrust faults – in which blocks of older strata – were thrust eastward – on top of younger strata ...
geophysical and geological detection of the intramoesian
... The Intramoesian Fault has been considered a trans-crustal fault separating two main compartments of the Moesian Platform: the Dobrogean sector, eastward, and the WallachianPrebalkan sector, westward. Recently, the Intramoesian Fault was considered as a regional tectonic contact separating an “older ...
... The Intramoesian Fault has been considered a trans-crustal fault separating two main compartments of the Moesian Platform: the Dobrogean sector, eastward, and the WallachianPrebalkan sector, westward. Recently, the Intramoesian Fault was considered as a regional tectonic contact separating an “older ...
Plate Tectonics and Earth`s Structure
... Look at the outlines of North and South America. Now do the same for Africa. Do you see a pattern? The bulge of Africa seems to fit into the area between the two Americas, right at the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. Is there a reason for this match? In 1912 the German scientist Alfred Wegener ...
... Look at the outlines of North and South America. Now do the same for Africa. Do you see a pattern? The bulge of Africa seems to fit into the area between the two Americas, right at the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. Is there a reason for this match? In 1912 the German scientist Alfred Wegener ...
Geology of the Springbrook Plateau
... Springbrook National Park is located on the northern flank of the extinct Tweed Volcano, a broad shield volcano which erupted between 23 and 24 million years ago. At that time this part of the Australian crustal plate, which is moving 7cm northwards each year, was over a ‘hot spot’. Hot spots form d ...
... Springbrook National Park is located on the northern flank of the extinct Tweed Volcano, a broad shield volcano which erupted between 23 and 24 million years ago. At that time this part of the Australian crustal plate, which is moving 7cm northwards each year, was over a ‘hot spot’. Hot spots form d ...
Magmatism and tectonics in a tilted crustal section through a
... shortening leads to, or is the structural response to precursory magmatic thickening in the arc. As higher precision U-Pb ages become more readily available for more plutons in the Cordilleran arc, it seems likely that batholith emplacement was an episodic phenomenon superimposed on a longer-term ba ...
... shortening leads to, or is the structural response to precursory magmatic thickening in the arc. As higher precision U-Pb ages become more readily available for more plutons in the Cordilleran arc, it seems likely that batholith emplacement was an episodic phenomenon superimposed on a longer-term ba ...
plate boundary
... The rock of the crust is pulled apart In normal faults, tension causes the hanging wall (the higher piece of land) to slip down toward the footwall (the lower piece of land). The Rio Grande rift valley in New Mexico ...
... The rock of the crust is pulled apart In normal faults, tension causes the hanging wall (the higher piece of land) to slip down toward the footwall (the lower piece of land). The Rio Grande rift valley in New Mexico ...
53 Al – Aluminium
... feldspar, such as anorthosite and nepheline syenite (Wedepohl 1978) and late tectonic peraluminous granite in the Variscan basement (Faure et al. 2004). McLennan and Murray (1999) quote average values for river particulates and loess as 9.4 and 6.9% Al respectively. Although most naturally-occurring ...
... feldspar, such as anorthosite and nepheline syenite (Wedepohl 1978) and late tectonic peraluminous granite in the Variscan basement (Faure et al. 2004). McLennan and Murray (1999) quote average values for river particulates and loess as 9.4 and 6.9% Al respectively. Although most naturally-occurring ...
3:n:1:di - EVA - Universidad de la República
... Magmatic belts as well as earthquake activity are closely related to plate boundaries. The average yearly production of magmatic (volcanic and plutonic) rocks formed at destructive plate margins is slightly less than l0 km3 (Schmincke, 2004). The melting that produces magmatism is caused by complex ...
... Magmatic belts as well as earthquake activity are closely related to plate boundaries. The average yearly production of magmatic (volcanic and plutonic) rocks formed at destructive plate margins is slightly less than l0 km3 (Schmincke, 2004). The melting that produces magmatism is caused by complex ...
Plate Boundaries
... The rock of the crust is pulled apart In normal faults, tension causes the hanging wall (the higher piece of land) to slip down toward the footwall (the lower piece of land). The Rio Grande rift valley in New Mexico ...
... The rock of the crust is pulled apart In normal faults, tension causes the hanging wall (the higher piece of land) to slip down toward the footwall (the lower piece of land). The Rio Grande rift valley in New Mexico ...
Ore Bin / Oregon Geology magazine / journal
... to wander along a shoreline that some 15 m. y. (million years) ago, in Miocene time, was also a coastal area. Unlike the present coast, however, it was then the site of active volcanoes that erupted lava, fragmental debris, and ash both on the Iand surface and on the adj acent ocean floor. The Mioce ...
... to wander along a shoreline that some 15 m. y. (million years) ago, in Miocene time, was also a coastal area. Unlike the present coast, however, it was then the site of active volcanoes that erupted lava, fragmental debris, and ash both on the Iand surface and on the adj acent ocean floor. The Mioce ...
Please read chapters 10 and 5 CHAPTER 5–Sedimentary Rocks 1
... 2) The iron minerals hematite and limonite result from the chemical weathering of iron-rich minerals by the process of A) oxidation. B) dissolution. C) electrolysis. D) exsolution. E) exfoliation. Answer: A 3) Which of the following common rocks would be most susceptible to chemical weathering? A) s ...
... 2) The iron minerals hematite and limonite result from the chemical weathering of iron-rich minerals by the process of A) oxidation. B) dissolution. C) electrolysis. D) exsolution. E) exfoliation. Answer: A 3) Which of the following common rocks would be most susceptible to chemical weathering? A) s ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.