Cratons of the Indian Shield
... with their basement gneisses) occurred when their regional foliation (axial plane S2) had a steep disposition with respect to the rising isotherms during regional metamorphism. This is in contrast if the structurally duplicated (or tectonically thickened) crust at depth had gentle inclination of the ...
... with their basement gneisses) occurred when their regional foliation (axial plane S2) had a steep disposition with respect to the rising isotherms during regional metamorphism. This is in contrast if the structurally duplicated (or tectonically thickened) crust at depth had gentle inclination of the ...
The Almeria-Nijar Basin
... minerals may crystallise in an ideal manner, creating rocks with large-sized crystals such as granites. ...
... minerals may crystallise in an ideal manner, creating rocks with large-sized crystals such as granites. ...
Superposed Fault Systems of the Southernmost
... Two major thrust systems are located along the eastern Blue Ridge – western Blue Ridge boundary in the Alabama and Georgia Appalachians. The pre-metamorphic Hillabee thrust is near the trailing edge of the Talladega belt thrust sheet and is associated with emplacement of a backarc volcanic suite ato ...
... Two major thrust systems are located along the eastern Blue Ridge – western Blue Ridge boundary in the Alabama and Georgia Appalachians. The pre-metamorphic Hillabee thrust is near the trailing edge of the Talladega belt thrust sheet and is associated with emplacement of a backarc volcanic suite ato ...
Cratons and Fold Belts of India - ReadingSample - Beck-Shop
... with their basement gneisses) occurred when their regional foliation (axial plane S2) had a steep disposition with respect to the rising isotherms during regional metamorphism. This is in contrast if the structurally duplicated (or tectonically thickened) crust at depth had gentle inclination of the ...
... with their basement gneisses) occurred when their regional foliation (axial plane S2) had a steep disposition with respect to the rising isotherms during regional metamorphism. This is in contrast if the structurally duplicated (or tectonically thickened) crust at depth had gentle inclination of the ...
The Agulhas – Karoo Geoscience Transect: from a sheared margin
... can be extinct island arcs, extinct spreading ridges, seamounts, or disrupted fragments of continental crust, are passive features that are embedded within the oceanic lithosphere. When large enough, they resist subduction, do not return to the mantle but accrete to existing continents. A prime exam ...
... can be extinct island arcs, extinct spreading ridges, seamounts, or disrupted fragments of continental crust, are passive features that are embedded within the oceanic lithosphere. When large enough, they resist subduction, do not return to the mantle but accrete to existing continents. A prime exam ...
Review of Upper Paleozoic and Lower Mesozoic stratigraphy and
... are allochthonous with respect to North America, but some developed not far from their present position. It has been suggested that the Coahuila and Sierra Madre terranes (Oaxaquia block), part of Gondwana during Early Paleozoic, collided with North America by Late Paleozoic time. However, their Mis ...
... are allochthonous with respect to North America, but some developed not far from their present position. It has been suggested that the Coahuila and Sierra Madre terranes (Oaxaquia block), part of Gondwana during Early Paleozoic, collided with North America by Late Paleozoic time. However, their Mis ...
Please Click Here for the Article PDF
... as a retro-arc ("behind arc") fold-andthrust belt with thrust faults generally dipping west in contrast to the eastward subduction of the oceanic plates. Field observations and sandbox analog experiments have shown that a region undergoing plate-scale compressional stress often produces a doubly-ver ...
... as a retro-arc ("behind arc") fold-andthrust belt with thrust faults generally dipping west in contrast to the eastward subduction of the oceanic plates. Field observations and sandbox analog experiments have shown that a region undergoing plate-scale compressional stress often produces a doubly-ver ...
OMAN: an obduction
... passive margin was flexed down to form the “Aruma” foreland basin. Upward flexure and erosion, then subsidence and slumping into the syntectonic foredeep ended in the Campanian (70 Ma) with the formation of a subduction obduction type mountain range. ...
... passive margin was flexed down to form the “Aruma” foreland basin. Upward flexure and erosion, then subsidence and slumping into the syntectonic foredeep ended in the Campanian (70 Ma) with the formation of a subduction obduction type mountain range. ...
Lecture 31: Stable Isotope Applications II
... We noted earlier that the equilibrium constant of isotope exchange reactions, K, was proportional to the inverse square temperature and that isotopic fractionation at high temperature will be limited. In magmatic systems, another factor limiting the fractionation of stable isotopes is the limited va ...
... We noted earlier that the equilibrium constant of isotope exchange reactions, K, was proportional to the inverse square temperature and that isotopic fractionation at high temperature will be limited. In magmatic systems, another factor limiting the fractionation of stable isotopes is the limited va ...
hydrothe~mal alteration of basaltic andesite and other rocks in drill
... tionships between the compositions of waters and the observed alteration patterns. The generalized geology of the thermal area is shown in figure 1. The basement rocks consist of a granodiorite pluton of late Mesozoic age intruded into metamorphosed sedimentary and volcanic rocks of probable early M ...
... tionships between the compositions of waters and the observed alteration patterns. The generalized geology of the thermal area is shown in figure 1. The basement rocks consist of a granodiorite pluton of late Mesozoic age intruded into metamorphosed sedimentary and volcanic rocks of probable early M ...
Faults and Folds on the Colorado Plateau
... monoclines were due to the Laramide uplift which occurred as the North American continental crust collided with oceanic plate to the west 75 to 50 Ma ago. 1 - The monoclines are upper-crustal expressions of near-vertical components of movements on reactivated, Precambrian, high-angle fault zones. 2 ...
... monoclines were due to the Laramide uplift which occurred as the North American continental crust collided with oceanic plate to the west 75 to 50 Ma ago. 1 - The monoclines are upper-crustal expressions of near-vertical components of movements on reactivated, Precambrian, high-angle fault zones. 2 ...
pre-quaternary faults in iran
... comes from a study of small scale aerial photograph mosaics and his evidence is topographical rather than geological. In his own words evidence for horizontal movement along this 1200 kmfault line was found in three places only: "the best locality shows tailing streams and three small streams that a ...
... comes from a study of small scale aerial photograph mosaics and his evidence is topographical rather than geological. In his own words evidence for horizontal movement along this 1200 kmfault line was found in three places only: "the best locality shows tailing streams and three small streams that a ...
Metamorphic and Magmatic Consequences of Subduction of Young
... Field, petrologic and whole-rock chemical data indicate that tonalitic-trondhjemitic rocks from the La Corea mélange represent melts formed during partial melting of subducted amphibolites. Primary mineral assemblage consists of plagioclase + quartz + phengite ± epidote ± paragonite ± pargasite. SHR ...
... Field, petrologic and whole-rock chemical data indicate that tonalitic-trondhjemitic rocks from the La Corea mélange represent melts formed during partial melting of subducted amphibolites. Primary mineral assemblage consists of plagioclase + quartz + phengite ± epidote ± paragonite ± pargasite. SHR ...
the Scanned PDF
... zircons, transitional types between typical "igneous" and "contamination" zircons being common. This assemblageis clearly shown in the histogram (Fig. 1) which is similar to that for zircon from the normal granite, except for the larger number of elongated crystals-6/o ol the crystals have an elonga ...
... zircons, transitional types between typical "igneous" and "contamination" zircons being common. This assemblageis clearly shown in the histogram (Fig. 1) which is similar to that for zircon from the normal granite, except for the larger number of elongated crystals-6/o ol the crystals have an elonga ...
CTY Course Syllabus Dynamic Earth Day 1 Lesson/Lecture Topic
... Stanford, predicting earthquakes, subduction zone earthquakes, volcanic hazards, different types of volcanoes & their plate boundary setting, how SiO2 content effects lava viscosity and eruptions and volcano appearance, how human lives, life on earth in general and climate are affected by volcanic e ...
... Stanford, predicting earthquakes, subduction zone earthquakes, volcanic hazards, different types of volcanoes & their plate boundary setting, how SiO2 content effects lava viscosity and eruptions and volcano appearance, how human lives, life on earth in general and climate are affected by volcanic e ...
Isotopes and geochronology
... • Cooling of basic intrusions • Crystallization of basic volcanic rocks (rapid cooling) – they are difficult to date by the Rb/Sr and U/Pb methods (especially if very old, partly altered and do not contain zircon) ...
... • Cooling of basic intrusions • Crystallization of basic volcanic rocks (rapid cooling) – they are difficult to date by the Rb/Sr and U/Pb methods (especially if very old, partly altered and do not contain zircon) ...
Collision tectonics of the Mediterranean region
... TABLE 1. MAIN COLLISION ZONES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION AND THEIR TECTONIC AND GEODYNAMIC FEATURES ...
... TABLE 1. MAIN COLLISION ZONES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION AND THEIR TECTONIC AND GEODYNAMIC FEATURES ...
Earth`s crust deformations in geosynclines
... suppose the speed to be at least a few cm per year, it is unlikely th at sucb a current could continue for the whole period of an active geosyncline which persists probably over some fifty million years or more; in th at time it would make more than one complete revolution while the study of convect ...
... suppose the speed to be at least a few cm per year, it is unlikely th at sucb a current could continue for the whole period of an active geosyncline which persists probably over some fifty million years or more; in th at time it would make more than one complete revolution while the study of convect ...
Clues to Earth`s Past
... Since the discovery of radiometric dating, geologists have tried to find Earth’s oldest rocks. The oldest rock formation dated by geologists using radiometric means is in Canada. It is estimated to be between 4.03 billion and 4.28 billion years old. However, individual crystals of the mineral zircon ...
... Since the discovery of radiometric dating, geologists have tried to find Earth’s oldest rocks. The oldest rock formation dated by geologists using radiometric means is in Canada. It is estimated to be between 4.03 billion and 4.28 billion years old. However, individual crystals of the mineral zircon ...
PlatemarginsL3and4 9.74MB 2017-03-29 12:41:32
... • Where plates move apart in oceanic areas they produce mid-ocean ridges. • Where they move apart in continental crust they produce rift valleys. • The space between the diverging plates is filled with basaltic lava upwelling from below. • Constructive margins are some of the youngest parts of the E ...
... • Where plates move apart in oceanic areas they produce mid-ocean ridges. • Where they move apart in continental crust they produce rift valleys. • The space between the diverging plates is filled with basaltic lava upwelling from below. • Constructive margins are some of the youngest parts of the E ...
Rocks from space - Oxford University Museum of Natural History
... Moldavites are a specific type of tektite, found across Europe from an impact in southern Germany 14 million years ago. ...
... Moldavites are a specific type of tektite, found across Europe from an impact in southern Germany 14 million years ago. ...
Volcanic Earthquake Swarms
... Buurman has gathered datasets from volcanoes all over the world, including Iceland, the US Pacific northwest, the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East and Mexico. The next step in the research programme, however, will be taken by returning, once again, to the seismic data recorded along the A ...
... Buurman has gathered datasets from volcanoes all over the world, including Iceland, the US Pacific northwest, the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East and Mexico. The next step in the research programme, however, will be taken by returning, once again, to the seismic data recorded along the A ...
Geologic Time Scale and Earth Her/History Detailed notes
... mammals, including Dimetrodon) Increase in the diversity of insects; insects are huge. First land snails. Sharks are abundant. Great forests of ferns, gymnosperms, horsetails. Sphenopsids (like today’s socalled Horse Tails or Equisetum) become more prevalent. Continents are uplifted providing more t ...
... mammals, including Dimetrodon) Increase in the diversity of insects; insects are huge. First land snails. Sharks are abundant. Great forests of ferns, gymnosperms, horsetails. Sphenopsids (like today’s socalled Horse Tails or Equisetum) become more prevalent. Continents are uplifted providing more t ...
Word
... giant insects and the increase of tree ferns. Amphibians reach greatest number and diversity. First reptiles appear in the late Carboniferous. This is perhaps the greatest ‘innovation’ of this period- an Amniote egg. This is the design allowed tetrapods to lay eggs away from water- a first in the fo ...
... giant insects and the increase of tree ferns. Amphibians reach greatest number and diversity. First reptiles appear in the late Carboniferous. This is perhaps the greatest ‘innovation’ of this period- an Amniote egg. This is the design allowed tetrapods to lay eggs away from water- a first in the fo ...
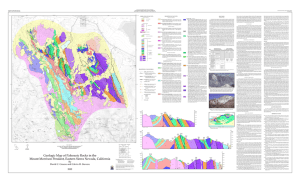
Geologic Map of Paleozoic Rocks in the Mount Morrison Pendant
... through Devonian metasedimentary rocks are juxtaposed against less deformed Mississippian through Permian metasedimentary rocks across the Laurel-Convict fault. The lower Paleozoic (Cambrian through Devonian) rocks are generally north striking and overturned, dipping steeply to the east. The section ...
... through Devonian metasedimentary rocks are juxtaposed against less deformed Mississippian through Permian metasedimentary rocks across the Laurel-Convict fault. The lower Paleozoic (Cambrian through Devonian) rocks are generally north striking and overturned, dipping steeply to the east. The section ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.