Document
... Xenoliths, restites, and other enclaves? Migmatites (“mixed rocks”) are gradational ...
... Xenoliths, restites, and other enclaves? Migmatites (“mixed rocks”) are gradational ...
here - Zandrivier farm
... The deformed and folded rocks that you can see whilst driving through Seweweekspoort are some of the best examples of intensely folded rocks of the Belt. The main compressional force came from the south resulting in the roughly east-west trend of the mountain chain. This can be seen in the image be ...
... The deformed and folded rocks that you can see whilst driving through Seweweekspoort are some of the best examples of intensely folded rocks of the Belt. The main compressional force came from the south resulting in the roughly east-west trend of the mountain chain. This can be seen in the image be ...
slyllabus
... Students have already learned crystallography, mineralogy, optical mineralogy and petrography before taking this course. So, they will continue to learn the principles behind rock forming processes and petrogenesis of igneous rocks in this course, both as means of identifying and describing the rock ...
... Students have already learned crystallography, mineralogy, optical mineralogy and petrography before taking this course. So, they will continue to learn the principles behind rock forming processes and petrogenesis of igneous rocks in this course, both as means of identifying and describing the rock ...
SES4UOrogenic Case Study
... faults and some strike-slip faults) as well as folding. The immense region involved in the continental collision, the vast temporal length of the orogeny and the thickness of the pile of sediments and igneous rocks known to have been involved are evidence that at the peak of the mountain-building pr ...
... faults and some strike-slip faults) as well as folding. The immense region involved in the continental collision, the vast temporal length of the orogeny and the thickness of the pile of sediments and igneous rocks known to have been involved are evidence that at the peak of the mountain-building pr ...
SES4UOrogenic Case Study
... faults and some strike-slip faults) as well as folding. The immense region involved in the continental collision, the vast temporal length of the orogeny and the thickness of the pile of sediments and igneous rocks known to have been involved are evidence that at the peak of the mountain-building pr ...
... faults and some strike-slip faults) as well as folding. The immense region involved in the continental collision, the vast temporal length of the orogeny and the thickness of the pile of sediments and igneous rocks known to have been involved are evidence that at the peak of the mountain-building pr ...
Mineral Resources
... Sedimentary Rocks – form by deposition and consolidation of sediments (e.g., sand, mud, etc.) or by evaporation of water and crystallization of dissolved materials. Metamorphic Rocks – form by the action of heat and pressure on some other rock. ...
... Sedimentary Rocks – form by deposition and consolidation of sediments (e.g., sand, mud, etc.) or by evaporation of water and crystallization of dissolved materials. Metamorphic Rocks – form by the action of heat and pressure on some other rock. ...
Rocks - earthjay science
... Many metamorphic rocks (particularly foliated rocks) form due to the pressure, heat and processes associated with convergent plate boundaries. Higher degrees of metamorphism are associated with deeper burial and more extreme conditions. Use what you have learned about metamorphic rocks to describe t ...
... Many metamorphic rocks (particularly foliated rocks) form due to the pressure, heat and processes associated with convergent plate boundaries. Higher degrees of metamorphism are associated with deeper burial and more extreme conditions. Use what you have learned about metamorphic rocks to describe t ...
G2S15Lesson2 SedMet
... Many metamorphic rocks (particularly foliated rocks) form due to the pressure, heat and processes associated with convergent plate boundaries. Higher degrees of metamorphism are associated with deeper burial and more extreme conditions. Use what you have learned about metamorphic rocks to describe t ...
... Many metamorphic rocks (particularly foliated rocks) form due to the pressure, heat and processes associated with convergent plate boundaries. Higher degrees of metamorphism are associated with deeper burial and more extreme conditions. Use what you have learned about metamorphic rocks to describe t ...
Strike-Slip Faults
... forces due to shearing. The two fault blocks move past each other horizontally. ...
... forces due to shearing. The two fault blocks move past each other horizontally. ...
notes symp
... Introduction In southern Death Valley normal and strike-slip faulting associated with extensional basin formation began less than 15 Ma ago and continues today. Geologic features such as: granitic plutons, dikes, sills, and volcanic fields are concurrent with extension (Calzia et al., 2000). This pr ...
... Introduction In southern Death Valley normal and strike-slip faulting associated with extensional basin formation began less than 15 Ma ago and continues today. Geologic features such as: granitic plutons, dikes, sills, and volcanic fields are concurrent with extension (Calzia et al., 2000). This pr ...
Jenkins_GSAtalk_v17may16
... Conclusions • Relict igneous texture to mylonitic fabrics. • REE abundances similar to Proterozoic and Archean dikes. – Not floor rocks. – Not Stillwater cumulates. – No known roof rocks have been identified. ...
... Conclusions • Relict igneous texture to mylonitic fabrics. • REE abundances similar to Proterozoic and Archean dikes. – Not floor rocks. – Not Stillwater cumulates. – No known roof rocks have been identified. ...
Geology The difference between rocks and minerals
... Sandstone, for instance, is a result of depositions of sand from beaches and rivers. You can find them mostly in deltas, since this is where the rivers flow into the ocean. Metamorphic rocks are actually products of rocks that have undergone changes. A metamorphic rock may have originally been an ig ...
... Sandstone, for instance, is a result of depositions of sand from beaches and rivers. You can find them mostly in deltas, since this is where the rivers flow into the ocean. Metamorphic rocks are actually products of rocks that have undergone changes. A metamorphic rock may have originally been an ig ...
Relative and Absolute Dating
... a. during the formation of the green shale b. before the grey limestone c. during the formation of the grey limestone d. during the formation of the black shale ...
... a. during the formation of the green shale b. before the grey limestone c. during the formation of the grey limestone d. during the formation of the black shale ...
Planet Earth - Topic 2 (ANSWERS)
... 1. Scientists have grouped rocks into three major families they are igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Each can be identified by its appearance. *Type I - Igneous rock forms when hot magma or lava cools and solidifies. 3. Magma is melted rock found below the Earth’s crust, where temperature ...
... 1. Scientists have grouped rocks into three major families they are igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Each can be identified by its appearance. *Type I - Igneous rock forms when hot magma or lava cools and solidifies. 3. Magma is melted rock found below the Earth’s crust, where temperature ...
Evaluating Evidence of Plate Tectonics
... • Explaining your evidence (back up each one of your pieces of evidence with reasoning for why it supports your claim) ...
... • Explaining your evidence (back up each one of your pieces of evidence with reasoning for why it supports your claim) ...
left click to view and right click to download.
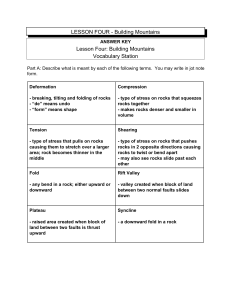
... Pressure applied quickly will cause a rock to fault; applied slowly, a rock will fold. 2. List four ways that mountains can be created. Folding, faulting, dome building, volcanic activity, colliding continents 3. What is the difference between an underwater trench and an underwater ridge? Underwater ...
... Pressure applied quickly will cause a rock to fault; applied slowly, a rock will fold. 2. List four ways that mountains can be created. Folding, faulting, dome building, volcanic activity, colliding continents 3. What is the difference between an underwater trench and an underwater ridge? Underwater ...
Geology of Howth
... Their shells and bones which were made up of the mineral calcium carbonate built up to form sedimentary rocks known as limestones. There are different types of limestones in the Howth and Sutton areas because the sea in which they were deposited changed through time. Most of the limestones are rich ...
... Their shells and bones which were made up of the mineral calcium carbonate built up to form sedimentary rocks known as limestones. There are different types of limestones in the Howth and Sutton areas because the sea in which they were deposited changed through time. Most of the limestones are rich ...
Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics
... continents to move? Plate Tectonics •Theory to explain how forces deep within Earth can cause seafloors to spread and continents to move. ...
... continents to move? Plate Tectonics •Theory to explain how forces deep within Earth can cause seafloors to spread and continents to move. ...
Pre-Quiz 1: Chapter 15 and 24 10 points ____ 1. What is another
... _____ 3. What is the Earth’s core made out of? a. crust b. metal c. rock d. heat _____ 4. What happens at a divergent boundary? a. Plates moves apart b. Plates crash together c. Plates slide past each other _____ 5. Name at least one form of heat transfer. Radiation, convection, or conduction Post-q ...
... _____ 3. What is the Earth’s core made out of? a. crust b. metal c. rock d. heat _____ 4. What happens at a divergent boundary? a. Plates moves apart b. Plates crash together c. Plates slide past each other _____ 5. Name at least one form of heat transfer. Radiation, convection, or conduction Post-q ...
The Rock Cycle - Simpson County Schools
... Sometimes if one plate doesn’t slide underneath another, the the plates will collide and push each other upward. mountains When this happens, they melt and recrystallize due to the heat and pressure put on them. ...
... Sometimes if one plate doesn’t slide underneath another, the the plates will collide and push each other upward. mountains When this happens, they melt and recrystallize due to the heat and pressure put on them. ...
Caledonian Structures of the Southern Uplands
... The deformation events that are the subject of this volume are generally construed to be the result of the closing of the Iapetus between the mid-Ordovician Period and the early Devonian, associated with marginally directed subduction zones. The models for this closure are largely based on Dewey (19 ...
... The deformation events that are the subject of this volume are generally construed to be the result of the closing of the Iapetus between the mid-Ordovician Period and the early Devonian, associated with marginally directed subduction zones. The models for this closure are largely based on Dewey (19 ...
Chapter 8: Major Elements
... Linear chain of andesitic volcanoes (granites below) Creation of mountain ranges (also linear chains) Andean type - continental arc Himalayan type - collisional (a terminal type) ...
... Linear chain of andesitic volcanoes (granites below) Creation of mountain ranges (also linear chains) Andean type - continental arc Himalayan type - collisional (a terminal type) ...
Sedimentary Rocks and Depositional Environments
... Broken down to form sediments – Sediments – fragments of rock, individual mineral grains (quartz), parts of plants or animals, clay minerals, and other minerals ...
... Broken down to form sediments – Sediments – fragments of rock, individual mineral grains (quartz), parts of plants or animals, clay minerals, and other minerals ...
3A8 Week 01 Lecture 03-Rocks and minerals 02
... • The original rock is termed a protolith • The composition of the protolith and the conditions of metamorphism and deformation will largely determine the end structure and composition of the metamorphic rock ...
... • The original rock is termed a protolith • The composition of the protolith and the conditions of metamorphism and deformation will largely determine the end structure and composition of the metamorphic rock ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.