Study Guide: Academic Standard 8-3 Earth`s Structure and Processes
... Convergent Boundary: Where two plates come together and collide: activity depends upon the types of crust that meet. More dense oceanic plate slides under less dense continental plate or another oceanic plate (subduction zone), some crust is destroyed. Two continental plates converge, both plates bu ...
... Convergent Boundary: Where two plates come together and collide: activity depends upon the types of crust that meet. More dense oceanic plate slides under less dense continental plate or another oceanic plate (subduction zone), some crust is destroyed. Two continental plates converge, both plates bu ...
GEOLOGY Regional Geology The Brucejack Property is located in
... Alteration on the Brucejack Property is characterized by variable, but generally intensely quartz-sericitepyrite altered rocks that define a distinctive and continuous north-south arcuate (west-concave) band of gossanous rocks that is up to several hundreds of metres wide, and approximately five kil ...
... Alteration on the Brucejack Property is characterized by variable, but generally intensely quartz-sericitepyrite altered rocks that define a distinctive and continuous north-south arcuate (west-concave) band of gossanous rocks that is up to several hundreds of metres wide, and approximately five kil ...
Name
... Directions: Please answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What kind of crust makes up tectonic plates? 2. What did Wegener call the one large landmass when all the continents were together? 3. Where does new oceanic lithosphere form (hint: it happens in the ocean)? 4. What t ...
... Directions: Please answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What kind of crust makes up tectonic plates? 2. What did Wegener call the one large landmass when all the continents were together? 3. Where does new oceanic lithosphere form (hint: it happens in the ocean)? 4. What t ...
Name: :____________Per:___ Plate Tectonics Test 1. Who was the
... 3. Heated material expands and rises, then cools. As it cools, it becomes denser and falls. This circular movement of material is called _ a. conduction b. radiation c. convection currents d. thermodynamics 4. The theory that states that the continents were once connected but drifted apart over time ...
... 3. Heated material expands and rises, then cools. As it cools, it becomes denser and falls. This circular movement of material is called _ a. conduction b. radiation c. convection currents d. thermodynamics 4. The theory that states that the continents were once connected but drifted apart over time ...
Nature of the Earth and Universe Spring 2011 Exam 2 Name: April
... E. the point of highest velocity can’t be predicted 3. As velocity drops abruptly when a stream or river enters quieter waters of an ocean or lake a depositional feature called a _____ is formed. A. floodplain B. slump C. delta D. yazoo E. alluvial fan 4. The drainage pattern that forms when there a ...
... E. the point of highest velocity can’t be predicted 3. As velocity drops abruptly when a stream or river enters quieter waters of an ocean or lake a depositional feature called a _____ is formed. A. floodplain B. slump C. delta D. yazoo E. alluvial fan 4. The drainage pattern that forms when there a ...
RockReviewIgneousProcess
... particles derived from weathered rocks Chemical Sediments include minerals carried in solution such as calcite and halite Organic Sediments are composed of living materials (plant/animal material and fossils/shells) ...
... particles derived from weathered rocks Chemical Sediments include minerals carried in solution such as calcite and halite Organic Sediments are composed of living materials (plant/animal material and fossils/shells) ...
Lab: Metamorphism: minerals, rocks and plate tectonics!
... sometime during their history. During this period of burial, they are subjected to higher temperatures and pressures found beneath the surface (Figure 6-1). The weight of the overlying sediment and rock provides most of the pressure, but tectonic forces within the Earth, such as those at convergent ...
... sometime during their history. During this period of burial, they are subjected to higher temperatures and pressures found beneath the surface (Figure 6-1). The weight of the overlying sediment and rock provides most of the pressure, but tectonic forces within the Earth, such as those at convergent ...
Chapter 3 Plate Tectonics
... • The earth once had a single landmass that broke up into large pieces, which have since drifted apart. • The name of this giant landmass is Pangaea which means all earth. • Wegner’s –Theory of continental drift • One supporting piece of evidence is the fossil Glossopteris( extinct now longer livin ...
... • The earth once had a single landmass that broke up into large pieces, which have since drifted apart. • The name of this giant landmass is Pangaea which means all earth. • Wegner’s –Theory of continental drift • One supporting piece of evidence is the fossil Glossopteris( extinct now longer livin ...
Name: Igneous Rocks Homework Extrusive Igneous Rocks: #23
... #23. What is the luster of this igneous rock sample ? _________________ Do you see any mineral grains in this rock ? What is the name of this igneous rock ? ...
... #23. What is the luster of this igneous rock sample ? _________________ Do you see any mineral grains in this rock ? What is the name of this igneous rock ? ...
Chapter 6: Plate Tectonics
... o Convergent Plate Boundaries – compressional in nature, include oceanoceanic and oceanic-continent subduction (characterized by andesitic volcanism) as well as continent-continent collision o Transform Plate Boundaries – mark the locations where plates move past one another horizontally 6.5 Orogene ...
... o Convergent Plate Boundaries – compressional in nature, include oceanoceanic and oceanic-continent subduction (characterized by andesitic volcanism) as well as continent-continent collision o Transform Plate Boundaries – mark the locations where plates move past one another horizontally 6.5 Orogene ...
Describing Matter & Energy
... movement of Earth’s plates produces volcanoes, mountain ranges, earthquakes, and features of the ocean floor. ...
... movement of Earth’s plates produces volcanoes, mountain ranges, earthquakes, and features of the ocean floor. ...
Basement Sucks - School of Earth and Environment
... Basement rocks are potentially large sinks for water because they are dehydrated and consume water in incipient retrograde reactions. Such reactions mean that fluid pressure can be below hydrostatic values throughout the stable crust. However basement rocks are also generally highly impermeable so t ...
... Basement rocks are potentially large sinks for water because they are dehydrated and consume water in incipient retrograde reactions. Such reactions mean that fluid pressure can be below hydrostatic values throughout the stable crust. However basement rocks are also generally highly impermeable so t ...
What They Say in Hong Kong Geography Books and Exam
... young fold mountains. In time, the growth of the mountains slow down…These mountains are old fold mountains. What we actually know: No. Most mountains formed when continents collided with each other. Old fold mountains are those that formed long ago, and the collision has long ended; young fold mou ...
... young fold mountains. In time, the growth of the mountains slow down…These mountains are old fold mountains. What we actually know: No. Most mountains formed when continents collided with each other. Old fold mountains are those that formed long ago, and the collision has long ended; young fold mou ...
MMEW Field Trip-99 - University of Minnesota Duluth
... marks, graded bedding, and cross bedding are evident in several locations. Deformation and metamorphism resulting from the 1.85 billion-year-old Penokean Orogeny (mountain building event) has recrystallized the rocks (e.g., made slate from shale), tilted and folded the sedimentary bedding, and produ ...
... marks, graded bedding, and cross bedding are evident in several locations. Deformation and metamorphism resulting from the 1.85 billion-year-old Penokean Orogeny (mountain building event) has recrystallized the rocks (e.g., made slate from shale), tilted and folded the sedimentary bedding, and produ ...
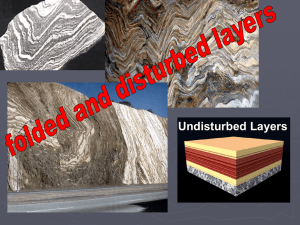
deforming the earth`s crust text
... fault looking across the fault when it moved, the ground on the other side would appear to move to your left or right. The San Andreas Fault in California is a spectacular example of a strike-slip fault. ...
... fault looking across the fault when it moved, the ground on the other side would appear to move to your left or right. The San Andreas Fault in California is a spectacular example of a strike-slip fault. ...
The metamorphic evolution of the Mozambique Belt in Central
... path, dominated by decompression during final stages of exhumation. The IBC segment of the Eastern Granulites forms a ‘beta’-shaped retrograde path accompanied by strike-slip tectonics at granulite facies metamorphic conditions. We interpret this highly dynamic initial cooling stage at a particular ...
... path, dominated by decompression during final stages of exhumation. The IBC segment of the Eastern Granulites forms a ‘beta’-shaped retrograde path accompanied by strike-slip tectonics at granulite facies metamorphic conditions. We interpret this highly dynamic initial cooling stage at a particular ...
map-view - Bakersfield College
... Measuring the “strike” of strata • represents the intersection of the tilted layer and the imaginary horizontal plane • A MAP symbol – showing the “directional trend” of strata Measuring the directional ...
... Measuring the “strike” of strata • represents the intersection of the tilted layer and the imaginary horizontal plane • A MAP symbol – showing the “directional trend” of strata Measuring the directional ...
Energy In The Rock Cycle
... • Chemical reactions within the earth’s crust change rocks from one form to another. ...
... • Chemical reactions within the earth’s crust change rocks from one form to another. ...
The changing Earth. - Concord High School
... Describe: Differentiate and distinguish by providing characteristics, features and properties Explain: Cause and effect = LINK purpose or function of EACH feature or characteristic listed above (Use linking words such as: As a result.., This leads to .., This provides .., As a consequence.., Therefo ...
... Describe: Differentiate and distinguish by providing characteristics, features and properties Explain: Cause and effect = LINK purpose or function of EACH feature or characteristic listed above (Use linking words such as: As a result.., This leads to .., This provides .., As a consequence.., Therefo ...
Galana River area in SE Kenya, four tectonostratigraphic units can
... granulite facies metamor-phism (~644-629 Ma) is found in domains showing S-SW directed low angle thrusting (Taita Hills) and NNW-SSE strike slip deformation (western Galana River). In an eastward direction, a late Pan-African granulite facies metamorphism (~550 Ma) occurs in a domain where structure ...
... granulite facies metamor-phism (~644-629 Ma) is found in domains showing S-SW directed low angle thrusting (Taita Hills) and NNW-SSE strike slip deformation (western Galana River). In an eastward direction, a late Pan-African granulite facies metamorphism (~550 Ma) occurs in a domain where structure ...
Slide 1
... Metamorphic rocks get their name from meta (change) and morph (form). Any rock can become a metamorphic rock, usually this involves burial leading to a rise in temperature and pressure. The minerals of the original rock changes. Arizona’s metamorphic rocks are quartzite, gneiss and schist. ...
... Metamorphic rocks get their name from meta (change) and morph (form). Any rock can become a metamorphic rock, usually this involves burial leading to a rise in temperature and pressure. The minerals of the original rock changes. Arizona’s metamorphic rocks are quartzite, gneiss and schist. ...
Unit #5 - Blue Valley Schools
... (fragments from other rocks) must be older than the rock that contains them ...
... (fragments from other rocks) must be older than the rock that contains them ...
Practice Test – Geology 106, Chapter 17 from The Changing Earth
... of Modern Geology”), states that geologic processes are, have always been , and will always remain constant (“uniform”). Coal deposits in Antarctica provide an example of this law’s application: we know that coal requires fresh water, temperate climates, and massive amounts of plant material to form ...
... of Modern Geology”), states that geologic processes are, have always been , and will always remain constant (“uniform”). Coal deposits in Antarctica provide an example of this law’s application: we know that coal requires fresh water, temperate climates, and massive amounts of plant material to form ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.