UNIT II INTERIOR OF THE EARTH
... The Rock Cycle: All the three types of rocks are formed in different ways. The rock cycle is the process that makes and recycles rocks. We know that most of the rocks on earth began as igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are formed from cooling and solidification of the magma. When igneous rocks are expose ...
... The Rock Cycle: All the three types of rocks are formed in different ways. The rock cycle is the process that makes and recycles rocks. We know that most of the rocks on earth began as igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are formed from cooling and solidification of the magma. When igneous rocks are expose ...
oceanic ridges
... Another subduction zone—this one with oceanic material on both sides. O-O Modern example of volcanic islands: Japan ...
... Another subduction zone—this one with oceanic material on both sides. O-O Modern example of volcanic islands: Japan ...
Precambrian Time: Vast and Puzzling
... fossils, which makes correlating rock layers difficult. Many Precambrian rocks are metamorphosed and deformed, extremely eroded, or hidden by overlying strata. ...
... fossils, which makes correlating rock layers difficult. Many Precambrian rocks are metamorphosed and deformed, extremely eroded, or hidden by overlying strata. ...
Final S2 ES Option one
... Summarize the limitations of using the rates of erosion and deposition to determine the absolute age of rock formations. Explain how the process of radioactive decay can be used to determine the absolute age of rocks. Describe four ways in which entire organisms can be preserved as fossils. List fiv ...
... Summarize the limitations of using the rates of erosion and deposition to determine the absolute age of rock formations. Explain how the process of radioactive decay can be used to determine the absolute age of rocks. Describe four ways in which entire organisms can be preserved as fossils. List fiv ...
Minerals, Rocks, Plate Tectonics Review
... d. Weathering and erosion 16. Some magma hardens, and then it is exposed to intense heat and pressure. What does this process create? a. Sediment b. Igneous rock c. Sedimentary rock d. Metamorphic rock 17. A volcanic eruption occurs. Magma rises up the volcano’s vents and soon reaches the surface. W ...
... d. Weathering and erosion 16. Some magma hardens, and then it is exposed to intense heat and pressure. What does this process create? a. Sediment b. Igneous rock c. Sedimentary rock d. Metamorphic rock 17. A volcanic eruption occurs. Magma rises up the volcano’s vents and soon reaches the surface. W ...
Direct geological evidence for oceanic detachment faulting: The Mid
... 2001, personal commun.). Drill cores and dredge hauls yielded peridotite, gabbro, and diabase together with their altered and deformed equivalents (Fig. 1C). Basalts are found only as small clasts (,5 cm) within sedimentary breccias on the surface of the massif. Fault rocks are abundant on the top o ...
... 2001, personal commun.). Drill cores and dredge hauls yielded peridotite, gabbro, and diabase together with their altered and deformed equivalents (Fig. 1C). Basalts are found only as small clasts (,5 cm) within sedimentary breccias on the surface of the massif. Fault rocks are abundant on the top o ...
GEOL 1010 - Research at UVU
... that form over subduction zones. b) Most or all of the true, large batholiths in the world formed over subduction zones. The batholiths are made of many individual plutons that were emplaced over the life of the subduction zone (tens of millions of years), and they are intermediate to felsic in comp ...
... that form over subduction zones. b) Most or all of the true, large batholiths in the world formed over subduction zones. The batholiths are made of many individual plutons that were emplaced over the life of the subduction zone (tens of millions of years), and they are intermediate to felsic in comp ...
Science: Directed Reading Study Guide
... _________________ _______________________. The cracks (rifts) are filled with _______________________ from the mantle to form new crust. 7. __________________________ occur along the faults and _______________________ form where magma reaches the surface. 8. Most divergent boundaries are formed on t ...
... _________________ _______________________. The cracks (rifts) are filled with _______________________ from the mantle to form new crust. 7. __________________________ occur along the faults and _______________________ form where magma reaches the surface. 8. Most divergent boundaries are formed on t ...
Science CH 6 Lesson 4
... • During subduction, pieces of rock are scraped off the bottom plate, called accretion. • They accumulate and eventually form mountain chains called accreted terranes. • California’s coastal mountains where formed by accreted terranes. • California’s gold was collected in its rocks this way. ...
... • During subduction, pieces of rock are scraped off the bottom plate, called accretion. • They accumulate and eventually form mountain chains called accreted terranes. • California’s coastal mountains where formed by accreted terranes. • California’s gold was collected in its rocks this way. ...
Rock Types and Stratigraphy
... ammonia, nitrogen, hydrogen thiocyanate, carbonyl sulphide, silicon tetrafluoride, ferric chloride, aluminium chloride, ammonium chloride and argon have also been noted in volcanic gases. It has often been found that hydrogen chloride is, next to steam, the major gas produced during an eruption but ...
... ammonia, nitrogen, hydrogen thiocyanate, carbonyl sulphide, silicon tetrafluoride, ferric chloride, aluminium chloride, ammonium chloride and argon have also been noted in volcanic gases. It has often been found that hydrogen chloride is, next to steam, the major gas produced during an eruption but ...
Untitled - Studentportalen
... was based on direct observations. He thought that the rigid continents moved in the soft ocean floors; the nature of the latter was unknown. He never reached a reasonable conclusion about the velocity of the movements of the continents. Neither of the mechanism behind the drift of the continents. He ...
... was based on direct observations. He thought that the rigid continents moved in the soft ocean floors; the nature of the latter was unknown. He never reached a reasonable conclusion about the velocity of the movements of the continents. Neither of the mechanism behind the drift of the continents. He ...
Name:
... scientists found that rocks are YOUNGER closest to the mid-ocean ridge and progressively older as you move further away from the ridge. This suggests that magma is continuously rising up from the mid-ocean ridge and hardening to push the two plates apart from one another. Second, alternating magneti ...
... scientists found that rocks are YOUNGER closest to the mid-ocean ridge and progressively older as you move further away from the ridge. This suggests that magma is continuously rising up from the mid-ocean ridge and hardening to push the two plates apart from one another. Second, alternating magneti ...
This is another Regents Review Packet to help you.
... arrive at a station that is 3,000 km away? (hint: ADD the P-wave travel time to the origin time) 8. List as many characteristics that you can about these earth layers: a. CRUST b. MANTLE c. OUTER CORE d. INNER CORE 9. If you plotted the locations of hundreds of earthquakes, what pattern would you no ...
... arrive at a station that is 3,000 km away? (hint: ADD the P-wave travel time to the origin time) 8. List as many characteristics that you can about these earth layers: a. CRUST b. MANTLE c. OUTER CORE d. INNER CORE 9. If you plotted the locations of hundreds of earthquakes, what pattern would you no ...
AE-December-2016-04-BS-14
... 5. The most widespread metamorphic rocks exposed at the Earth's surface are formed by: a. Regional metamorphism b. Hydrothermal metamorphism c. Contact metamorphism d. Burial metamorphism e. Meteorite impact metamorphism 6. When does permanent rock deformation occur? a. once its elastic limit is sur ...
... 5. The most widespread metamorphic rocks exposed at the Earth's surface are formed by: a. Regional metamorphism b. Hydrothermal metamorphism c. Contact metamorphism d. Burial metamorphism e. Meteorite impact metamorphism 6. When does permanent rock deformation occur? a. once its elastic limit is sur ...
The lithosphere, geodynamics and Archean mineral systems
... Minerals Targeting International PL, Suite 26, 17 Prowse St, West Perth, WA 6005, Australia ...
... Minerals Targeting International PL, Suite 26, 17 Prowse St, West Perth, WA 6005, Australia ...
A Model of Three Faults
... 1. Color the paper fault model handout according to the color key provided. 2. Glue the fault model onto a piece of construction paper. 3. Cut out the fault model and fold each side down to form a box with the drawn features on top. 4. Glue the corners together. The box is a three dimensional model ...
... 1. Color the paper fault model handout according to the color key provided. 2. Glue the fault model onto a piece of construction paper. 3. Cut out the fault model and fold each side down to form a box with the drawn features on top. 4. Glue the corners together. The box is a three dimensional model ...
- Heritage Manitoba
... The Shield is a large area of igneous and high‐grade metamorphic rock which forms the ancient geological core of North America. It is more than 3.96 billion years old, dating to the Archeon Eon of the Precambrian Era, and makes up some of the earth’s oldest rock. At one time, most of the Shield’s ...
... The Shield is a large area of igneous and high‐grade metamorphic rock which forms the ancient geological core of North America. It is more than 3.96 billion years old, dating to the Archeon Eon of the Precambrian Era, and makes up some of the earth’s oldest rock. At one time, most of the Shield’s ...
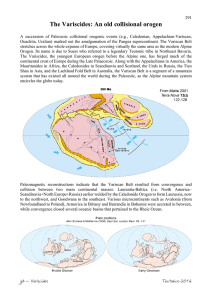
The Variscides
... (eclogites, granulites, and blueschists), ophiolitic fragments, mélanges, and upper mantle rocks. All sections display large recumbent folds and ductile low-angle thrust sheets which carry high grade rocks over great distances (c. 200 km). Polyphase, syntectonic metamorphism lasted from early high-p ...
... (eclogites, granulites, and blueschists), ophiolitic fragments, mélanges, and upper mantle rocks. All sections display large recumbent folds and ductile low-angle thrust sheets which carry high grade rocks over great distances (c. 200 km). Polyphase, syntectonic metamorphism lasted from early high-p ...
Final Exam Practice Quiz 1. What is the chief source of energy for
... 12. Volcanic rocks such as pumice that have small cavities left by escaping gas bubbles are described as 'coarse-grained' in texture. a) True b) False 13. Salt and gypsum are chemically-formed sedimentary rocks. a) True b) False Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which one of the following islands was formed a ...
... 12. Volcanic rocks such as pumice that have small cavities left by escaping gas bubbles are described as 'coarse-grained' in texture. a) True b) False 13. Salt and gypsum are chemically-formed sedimentary rocks. a) True b) False Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which one of the following islands was formed a ...
5. Explain the 3 different types of faults.
... Most take place near the edges of tectonic plates Earthquakes can occur at: ◦ Convergent Boundaries (Reverse Fault) ◦ Divergent Boundaries (Normal Fault) ◦ Transform Boundaries (Strike-Slip Fault) ...
... Most take place near the edges of tectonic plates Earthquakes can occur at: ◦ Convergent Boundaries (Reverse Fault) ◦ Divergent Boundaries (Normal Fault) ◦ Transform Boundaries (Strike-Slip Fault) ...
Geology Lab Write-up for Next Week`s Lab
... Coquina is composed almost entirely of shell or fossil fragments. Limestone may or may not contain fossils. Both will react to HCl. Limestone containing fossils is referred to as ...
... Coquina is composed almost entirely of shell or fossil fragments. Limestone may or may not contain fossils. Both will react to HCl. Limestone containing fossils is referred to as ...
Earth`s Interior
... (1) Density is very high when averaged with crust and mantle (2) Evidence for iron (a) Meteorites may represent basic material that created the solar system and 10% are composed of Fe and Ni (may represent the cores of fragmented planetismals and asteroids (b) Seismic and density data along with ass ...
... (1) Density is very high when averaged with crust and mantle (2) Evidence for iron (a) Meteorites may represent basic material that created the solar system and 10% are composed of Fe and Ni (may represent the cores of fragmented planetismals and asteroids (b) Seismic and density data along with ass ...
Chapter 7
... • Continental collisions form mountain belts with: – Folded sedimentary rocks – Faulting – Metamorphism – Igneous intrusions • Slabs of continental crust may override one another • Suture zone = zone of convergence between two continental plates ...
... • Continental collisions form mountain belts with: – Folded sedimentary rocks – Faulting – Metamorphism – Igneous intrusions • Slabs of continental crust may override one another • Suture zone = zone of convergence between two continental plates ...
Atomic Spectra
... Coquina is composed almost entirely of shell or fossil fragments. Limestone may or may not contain fossils. Both will react to HCl. Limestone containing fossils is referred to as ...
... Coquina is composed almost entirely of shell or fossil fragments. Limestone may or may not contain fossils. Both will react to HCl. Limestone containing fossils is referred to as ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.