Geology 111 - A3 - Global geology at the turn of the century
... continents, including Antarctica, also snails, earthworms and freshwater fish. Permanentists, who held that the oceans and continents have always been fixed, had some trouble explaining these anomalies. They dreamed up features such as land bridges across the oceans, so that these plants and animals ...
... continents, including Antarctica, also snails, earthworms and freshwater fish. Permanentists, who held that the oceans and continents have always been fixed, had some trouble explaining these anomalies. They dreamed up features such as land bridges across the oceans, so that these plants and animals ...
Plate tectonics.notebook
... plates slide past one another horizontally strike slip fault causes earthquakes What is behind all this? Convection current cycle of heating, rising, cooling and sinking page 204 ...
... plates slide past one another horizontally strike slip fault causes earthquakes What is behind all this? Convection current cycle of heating, rising, cooling and sinking page 204 ...
Final Exam Review Guide
... Describe what occurs at each type of plate boundary. Include the types of geologic activities and features that exist at these locations. Identify 3 types of evidence found at each type of plate boundary that can be used to support the theory of plate tectonics. ...
... Describe what occurs at each type of plate boundary. Include the types of geologic activities and features that exist at these locations. Identify 3 types of evidence found at each type of plate boundary that can be used to support the theory of plate tectonics. ...
gEOLOGy AND earth structure
... Earth. Two principal divisions of Earths surface are the continents and ocean basins. The continental shelf and continental slope mark the continent-ocean basin transition. Major continental features include mountains and shields. Important zones on the ocean floor are trenches and the extensive oce ...
... Earth. Two principal divisions of Earths surface are the continents and ocean basins. The continental shelf and continental slope mark the continent-ocean basin transition. Major continental features include mountains and shields. Important zones on the ocean floor are trenches and the extensive oce ...
Geochemical Characterization of Intermediate to Silicic Rocks in the
... enriched in subduction-related ophiolites as a result of shallow to deep enrichment associated with subduction zone processes. The field occurrence and the geochemical character of leucocratic rocks in ophiolites show considerable variations, providing additional constraints on the petrogenesis of o ...
... enriched in subduction-related ophiolites as a result of shallow to deep enrichment associated with subduction zone processes. The field occurrence and the geochemical character of leucocratic rocks in ophiolites show considerable variations, providing additional constraints on the petrogenesis of o ...
Splitting continents - Workspace
... no new oceans or mountain chains will be created. Because of plate tectonics, in the past the continents have undergone cycles of collision and amalgamation followed by splitting and separation. These major reorganisations of the landmasses have dictated many climatic and evolutionary developments. ...
... no new oceans or mountain chains will be created. Because of plate tectonics, in the past the continents have undergone cycles of collision and amalgamation followed by splitting and separation. These major reorganisations of the landmasses have dictated many climatic and evolutionary developments. ...
Metamorphic processes in the subducting slab and overlying mantle
... (e.g., Abers et al., 2003; Hacker et al., 2003). Of critical importance is the measurement or calculation of shear moduli—and their variation with pressure and temperature—in crustal minerals. Studies of metamorphic rocks that reached various depths in ancient subduction zones are critical to unders ...
... (e.g., Abers et al., 2003; Hacker et al., 2003). Of critical importance is the measurement or calculation of shear moduli—and their variation with pressure and temperature—in crustal minerals. Studies of metamorphic rocks that reached various depths in ancient subduction zones are critical to unders ...
Rocks Sunshine State STANDARDS SC.D.1.3.1: The student knows
... geologist studying layers of sedimentary rocks can tell something about what conditions were like in the past. For instance, fossils of fish or shells in a layer of rock show that the area was covered by a lake or an ocean long ago. Fossils are not the only way to tell something about what past cond ...
... geologist studying layers of sedimentary rocks can tell something about what conditions were like in the past. For instance, fossils of fish or shells in a layer of rock show that the area was covered by a lake or an ocean long ago. Fossils are not the only way to tell something about what past cond ...
Obj. 2.1.1 Layers of the Earth A
... d. transitional stress 2. Tensional stresses commonly cause which of the following? a. strike-slip faults c. thrust faults b. reverse faults d. normal faults 3. Compressional stresses can result in the formation of ____. a. rift valleys c. thrust faults b. horsts and grabens d. normal faults 4. Faul ...
... d. transitional stress 2. Tensional stresses commonly cause which of the following? a. strike-slip faults c. thrust faults b. reverse faults d. normal faults 3. Compressional stresses can result in the formation of ____. a. rift valleys c. thrust faults b. horsts and grabens d. normal faults 4. Faul ...
pdf for preview - sciencepowerpoint.com
... 10 - Name for Basaltic lava (Flows Easily) 13 - An instrument used to measure the shaking caused by an earthquake 16 - Shaking of the Earth’s crust from a sudden release of energy. 17 - The Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates. These plates float on the mantle like ...
... 10 - Name for Basaltic lava (Flows Easily) 13 - An instrument used to measure the shaking caused by an earthquake 16 - Shaking of the Earth’s crust from a sudden release of energy. 17 - The Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates. These plates float on the mantle like ...
The location of volcanoes
... • The Earth’s crust is divided up into plates • These plates ‘float’ or move very slowly (a few mm per year) on the molten material of the mantle. This movement is caused by convection currents in the mantle. ...
... • The Earth’s crust is divided up into plates • These plates ‘float’ or move very slowly (a few mm per year) on the molten material of the mantle. This movement is caused by convection currents in the mantle. ...
Lesson 1: What are earthquakes and where do they occur
... The New Madrid Fault • If there is no plate boundary in the middle of the United States, why did these earthquakes take place? • Geologists are beginning to understand the answer. The New Madrid Fault Zone is part of an ancient plate boundary. In this area, the North American Plate tried to form a ...
... The New Madrid Fault • If there is no plate boundary in the middle of the United States, why did these earthquakes take place? • Geologists are beginning to understand the answer. The New Madrid Fault Zone is part of an ancient plate boundary. In this area, the North American Plate tried to form a ...
03 Chapter 3_Igneous Rock - Lightweight OCW University of
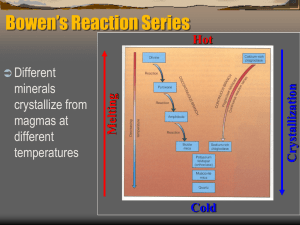
... Evolution of magmas Partial melting and magma formation • Formation of granitic magmas – Most likely form as the end product of crystallization of andesitic magma – Granitic magmas are higher in silica and therefore more viscous than other magmas – Because of their viscosity, they lose their mobili ...
... Evolution of magmas Partial melting and magma formation • Formation of granitic magmas – Most likely form as the end product of crystallization of andesitic magma – Granitic magmas are higher in silica and therefore more viscous than other magmas – Because of their viscosity, they lose their mobili ...
Test Review
... than the layers above it and younger than the layers below it. C. Metamorphic rock is older than nearby sedimentary rock because sedimentary rock is deposited before metamorphic rock forms. D. The exact age of a sedimentary rock layer can be found using the layers above and below it, even if the lay ...
... than the layers above it and younger than the layers below it. C. Metamorphic rock is older than nearby sedimentary rock because sedimentary rock is deposited before metamorphic rock forms. D. The exact age of a sedimentary rock layer can be found using the layers above and below it, even if the lay ...
on April 6, 2015 gsabulletin.gsapubs.org Downloaded from
... of the Pocuro fault and extends eastward for about 25 km. Upper Cretaceous volcanic strata are gently warped into broad, open, north-trending folds, with local sharp flexures and faulted mainly by normal faults. The eastern part of the subprovince is cut by a narrow belt of Tertiary plutonic rocks, ...
... of the Pocuro fault and extends eastward for about 25 km. Upper Cretaceous volcanic strata are gently warped into broad, open, north-trending folds, with local sharp flexures and faulted mainly by normal faults. The eastern part of the subprovince is cut by a narrow belt of Tertiary plutonic rocks, ...
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity
... Dakota is composed of granite. The Columbia River Plateau of Washington and Oregon is composed of basalt. Using a Venn Diagram, compare and contrast the two locations highlighting the composition of the rocks, the texture of the rock, and the location (depth) where the rocks formed. ...
... Dakota is composed of granite. The Columbia River Plateau of Washington and Oregon is composed of basalt. Using a Venn Diagram, compare and contrast the two locations highlighting the composition of the rocks, the texture of the rock, and the location (depth) where the rocks formed. ...
Igneous Rocks PPT
... Notice that igneous rocks are first classified by whether they formed at earth’s surface (Extrusive) or deep underground (Intrusive) ...
... Notice that igneous rocks are first classified by whether they formed at earth’s surface (Extrusive) or deep underground (Intrusive) ...
Chapter 19 - Heritage Collegiate
... evidence was found showing the ocean crust deformed where a continent moved through it. By 1968, enough data had been gathered to explain how the continents drifted apart after the break up of Pangaea. The explanation for the movement of the continents is called the theory of plate tectonics. It ess ...
... evidence was found showing the ocean crust deformed where a continent moved through it. By 1968, enough data had been gathered to explain how the continents drifted apart after the break up of Pangaea. The explanation for the movement of the continents is called the theory of plate tectonics. It ess ...
Word - Manchester Geological Association
... across the Highlands of Scotland and the northern part of Ireland, settled on the term ‘Dalradian’, after the ancient kingdom of Dal Riada, which was occupied by a tribe of Scottish and Irish Celts and covered the same area. The Dalradian succession is a thick sequence of sedimentary rocks with mino ...
... across the Highlands of Scotland and the northern part of Ireland, settled on the term ‘Dalradian’, after the ancient kingdom of Dal Riada, which was occupied by a tribe of Scottish and Irish Celts and covered the same area. The Dalradian succession is a thick sequence of sedimentary rocks with mino ...
A Tectonic explanation of the May 12, 2008, Sichuan Earthquake
... large, curved strike-slip faults that guide the crustal flow around the corner. This “flow” is actually accomplished in jerks when earthquakes rupture these faults. Many of China’s largest, most destructive earthquakes occur here. ...
... large, curved strike-slip faults that guide the crustal flow around the corner. This “flow” is actually accomplished in jerks when earthquakes rupture these faults. Many of China’s largest, most destructive earthquakes occur here. ...
Sc 7 Unit 5 Rocks and Minerals
... This ExploreLearning Gizmo allows the user to classify virtual rock samples based on their appearance according to the common characteristics of igneous, ...
... This ExploreLearning Gizmo allows the user to classify virtual rock samples based on their appearance according to the common characteristics of igneous, ...
Canggaan (Deformation) - Universiti Sains Malaysia
... Types of folds (formed as a result of plastic deformation) During mountain building or compressional stress, rocks may deform plastically to produce folds. The up-folds and the down-folds are adjacent to one another, and grade into one another. In geology each is given a separate descriptive name. ...
... Types of folds (formed as a result of plastic deformation) During mountain building or compressional stress, rocks may deform plastically to produce folds. The up-folds and the down-folds are adjacent to one another, and grade into one another. In geology each is given a separate descriptive name. ...
Bundle 1 - Humble ISD
... Fact: Weathering is the physical or chemical break down of rocks and erosion is the process of transporting sediment. The processes can happen at nearly the same time but they are completely different processes. Erosion is always bad. Fact: Delta areas, like the Mississippi and the Nile, were create ...
... Fact: Weathering is the physical or chemical break down of rocks and erosion is the process of transporting sediment. The processes can happen at nearly the same time but they are completely different processes. Erosion is always bad. Fact: Delta areas, like the Mississippi and the Nile, were create ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.