Relative Age of Rocks and
... When the top layer of sedimentary rock is eroded and then new sediment is deposited where the layer used to be, there is a gap in what geologists can learn. The rock can be folded by converging plates or molten magma can shift the layers so they are angled or wavy. ...
... When the top layer of sedimentary rock is eroded and then new sediment is deposited where the layer used to be, there is a gap in what geologists can learn. The rock can be folded by converging plates or molten magma can shift the layers so they are angled or wavy. ...
Week 2 Essential Reading
... fallen. H~rod()ru.' k 41\4-420 lie) thought that the lower part of Egypt was a former marine hay. reput edly saying 'Egypt is the gift of the river', referring to the year-by-year accumulation of river-borne silt in the Nile delta region. Aris'rorle Ol:l4-322 lie) conjec tured that land and sea ch ...
... fallen. H~rod()ru.' k 41\4-420 lie) thought that the lower part of Egypt was a former marine hay. reput edly saying 'Egypt is the gift of the river', referring to the year-by-year accumulation of river-borne silt in the Nile delta region. Aris'rorle Ol:l4-322 lie) conjec tured that land and sea ch ...
llyn dulyn
... can be traced throughout the immediate area. The 3rd member, which has no representative in the Capel Curig area, comprises up to 75 m of thinly banded welded tuff with distinctive layers of collapsed pumice and evidence of upward grading. Originally interpreted as a single unit by Howells et al. (1 ...
... can be traced throughout the immediate area. The 3rd member, which has no representative in the Capel Curig area, comprises up to 75 m of thinly banded welded tuff with distinctive layers of collapsed pumice and evidence of upward grading. Originally interpreted as a single unit by Howells et al. (1 ...
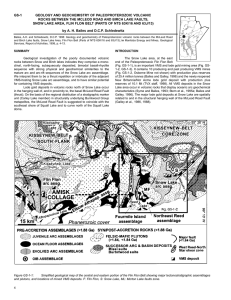
Geology and geochemistry of Paleoproterozoic volcanic rocks
... Folds other than F3 are rarely observed in the McLeod RoadBirch Lake allochthon, northwest of the town of Snow Lake. These folds have a north-northeast, shallow-plunging fold axis, and an east-northeast moderately steep dipping axial plane. These folds were interpreted by Galley et al. (1998) to hav ...
... Folds other than F3 are rarely observed in the McLeod RoadBirch Lake allochthon, northwest of the town of Snow Lake. These folds have a north-northeast, shallow-plunging fold axis, and an east-northeast moderately steep dipping axial plane. These folds were interpreted by Galley et al. (1998) to hav ...
Oceanic Crust
... • "Now I hear the sea sounds about me; • the night high tide is rising, swirling with a confused rush of waters against the rocks below …. • Once this rocky coast beneath me was a plain of sand; • then the sea rose and found a new shore line. • And again in some shadowy future the surf will have gro ...
... • "Now I hear the sea sounds about me; • the night high tide is rising, swirling with a confused rush of waters against the rocks below …. • Once this rocky coast beneath me was a plain of sand; • then the sea rose and found a new shore line. • And again in some shadowy future the surf will have gro ...
TECTONIC AND GEOLOGIC EVOLUTION OF THAILAND
... All of them except the Khorat Basin in the northeast are more or less linear and trend roughly north-south. Their northern ends abut against the west-north-west to north-west trending fold belt aligned along the Red River and lying more or less on the border of Laos and Yunnan and in North Vietnam. ...
... All of them except the Khorat Basin in the northeast are more or less linear and trend roughly north-south. Their northern ends abut against the west-north-west to north-west trending fold belt aligned along the Red River and lying more or less on the border of Laos and Yunnan and in North Vietnam. ...
File - Ian Whaley Dillman EES
... thicker continental crust. This forms what is called a subduction zone. As the oceanic crust sinks, a deep oceanic _ trench__, or valley, is formed at the edge of the continent. The crust continues to be forced deeper into the earth, where high heat and pressure cause trapped water and other gasses ...
... thicker continental crust. This forms what is called a subduction zone. As the oceanic crust sinks, a deep oceanic _ trench__, or valley, is formed at the edge of the continent. The crust continues to be forced deeper into the earth, where high heat and pressure cause trapped water and other gasses ...
How the Earth Works
... body) are iron-nickel alloys. -The core is earth's source of internal heat because it contains radioactive materials which release heat as they break down into more stable substances. ...
... body) are iron-nickel alloys. -The core is earth's source of internal heat because it contains radioactive materials which release heat as they break down into more stable substances. ...
Transitional environments
... • Sorting and rounding are two textural features – Sorting refers to the variation in size of particles – “well sorted” – particles are similarly sized – “poorly sorted” – particles vary in size within a rock ...
... • Sorting and rounding are two textural features – Sorting refers to the variation in size of particles – “well sorted” – particles are similarly sized – “poorly sorted” – particles vary in size within a rock ...
Georesistivity Signature of Crystalline Rocks in the Romblon Island
... Hsu et al. 2004). As it was being translated southward, ...
... Hsu et al. 2004). As it was being translated southward, ...
Structural setting of the neo archean terrains in the - HAL
... metamorphic data obtained in the area. The ECB unit is structured during the Late Archean – Lower Proterozoic (at 2.4-2.5 Ga), with (i) granulite metamorphism at 9 - 6 kbar and 850 ± 50 °C of lower-mid crust and amphibolite metamorphism (P ≤ 5 kbar, T ≤ 750°C) of the upper crustal levels. (ii) The l ...
... metamorphic data obtained in the area. The ECB unit is structured during the Late Archean – Lower Proterozoic (at 2.4-2.5 Ga), with (i) granulite metamorphism at 9 - 6 kbar and 850 ± 50 °C of lower-mid crust and amphibolite metamorphism (P ≤ 5 kbar, T ≤ 750°C) of the upper crustal levels. (ii) The l ...
The Chemistry of Rocks in the Wissahickon Valley
... determine the manner in which minerals crystalize which determines the type of igneous rock that forms. Where the magma cools; (inside the earth: intrusive) or (outside the earth: extrusive) and the rate of cooling also influence the physical and chemical properties of the rock. Igneous rocks are al ...
... determine the manner in which minerals crystalize which determines the type of igneous rock that forms. Where the magma cools; (inside the earth: intrusive) or (outside the earth: extrusive) and the rate of cooling also influence the physical and chemical properties of the rock. Igneous rocks are al ...
plate tectonics - Math/Science Nucleus
... that give clues to the inside of the Earth. The evidence is very different, but yet when you plot the data a picture emerges. The zones in which earthquakes and volcanoes occur provide us with the notion that the Earth is broken like cracked eggs in defined “plates.” In this lab you will put your re ...
... that give clues to the inside of the Earth. The evidence is very different, but yet when you plot the data a picture emerges. The zones in which earthquakes and volcanoes occur provide us with the notion that the Earth is broken like cracked eggs in defined “plates.” In this lab you will put your re ...
Directed Reading A - sgeneva
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain ________________ at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes causes the ________________ in metamorphic rocks to alig ...
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain ________________ at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes causes the ________________ in metamorphic rocks to alig ...
Origin of high Mg# andesite and the continental crust
... of 795 analyses of Archean igneous and metaigneous rocks, and 234 analyses of Cenozoic, island arc-related plutonic rocks. The following hypotheses are offered to explain these distributions of HMA: 1. H M A were formed more commonly in the Archean than at present [e.g. 10]. 2. H M A are initially m ...
... of 795 analyses of Archean igneous and metaigneous rocks, and 234 analyses of Cenozoic, island arc-related plutonic rocks. The following hypotheses are offered to explain these distributions of HMA: 1. H M A were formed more commonly in the Archean than at present [e.g. 10]. 2. H M A are initially m ...
1 - Assets - Cambridge - Cambridge University Press
... As mentioned, the rocks that make up Earth’s sedimentary shell are mainly shales, sandstones, and carbonate rocks. Past estimates, by different workers, of the relative proportion of these rock types in the total sedimentary pile have varied significantly. Estimates by Ronov (1983), on the basis of ...
... As mentioned, the rocks that make up Earth’s sedimentary shell are mainly shales, sandstones, and carbonate rocks. Past estimates, by different workers, of the relative proportion of these rock types in the total sedimentary pile have varied significantly. Estimates by Ronov (1983), on the basis of ...
Directed Reading A - Holicong9thGradeScience
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain ________________ at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes causes the ________________ in metamorphic rocks to alig ...
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain ________________ at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes causes the ________________ in metamorphic rocks to alig ...
Geosphere - Written - Geological Society of India
... contains a thin clay layer with significant geochemical anomalies such as high iridium concentrations. It is dated to an numerical age of 65.5 Ma. Which chronostratigraphic boundary corresponds to this layer? ...
... contains a thin clay layer with significant geochemical anomalies such as high iridium concentrations. It is dated to an numerical age of 65.5 Ma. Which chronostratigraphic boundary corresponds to this layer? ...
chapter9_Proterozoic..
... and nickel are known from Australia, Zimbabwe (Africa) and Canada. These are similar to the black smokers on the seafloor. About 25% of the world’s chromium reserves are also in Archean rocks, along with platinum deposits. Archean pegmatites in the African Shield and the ...
... and nickel are known from Australia, Zimbabwe (Africa) and Canada. These are similar to the black smokers on the seafloor. About 25% of the world’s chromium reserves are also in Archean rocks, along with platinum deposits. Archean pegmatites in the African Shield and the ...
Volcanoes - Wsimg.com
... lava and poisonous gases from a crater at its summit. • This describes just one of many types of volcano, and the features of volcanoes are much more complicated ...
... lava and poisonous gases from a crater at its summit. • This describes just one of many types of volcano, and the features of volcanoes are much more complicated ...
Kelsey Beechler ERTH 201 Lab East African Rift Valley Rift valleys
... on the planet and what potential negative causes may occur due to this activity. Also, it gives great insight into geologic movements, processes, and information about the type of rock being affected. Lastly, it can give insight to if this occurred previously, in a historical context, and what impac ...
... on the planet and what potential negative causes may occur due to this activity. Also, it gives great insight into geologic movements, processes, and information about the type of rock being affected. Lastly, it can give insight to if this occurred previously, in a historical context, and what impac ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... • Seafloor rocks, and mantle rocks beneath them, cool and become more dense with distance from mid-oceanic ridge • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches and the very low heat flow ...
... • Seafloor rocks, and mantle rocks beneath them, cool and become more dense with distance from mid-oceanic ridge • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches and the very low heat flow ...
seafloorpapermodel_questions1_7
... About 40 years ago, scientists discovered that there are both age and magnetic patterns in the seafloor. This discovery allowed another piece of the puzzle about plate tectonics to fall into place. What scientists found was that new seafloor has continually been forming over millions of years at the ...
... About 40 years ago, scientists discovered that there are both age and magnetic patterns in the seafloor. This discovery allowed another piece of the puzzle about plate tectonics to fall into place. What scientists found was that new seafloor has continually been forming over millions of years at the ...
structural or climatic control in granite landforms? the
... Granite landforms have been interpreted in terms of climatic geomorphology, or morphogenetic regions, but the field evidence overwhelmingly points to structural control. Some features are developed after the exposure of the granitic bodies, for joggling of the brittle crust continues and external ag ...
... Granite landforms have been interpreted in terms of climatic geomorphology, or morphogenetic regions, but the field evidence overwhelmingly points to structural control. Some features are developed after the exposure of the granitic bodies, for joggling of the brittle crust continues and external ag ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.