Igneous Rocks - VarsityField
... If you were to drill a hole through the crust of a midmid-ocean ridge, what intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect to encounter at or near the surface? What intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect at the base of the crust? Water is abundant in the sedimentary rocks and o ...
... If you were to drill a hole through the crust of a midmid-ocean ridge, what intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect to encounter at or near the surface? What intrusive or extrusive igneous rocks might you expect at the base of the crust? Water is abundant in the sedimentary rocks and o ...
THE TECTONIC RELATIONSHIPS OF THE HILLABEE CHLORITE
... In southern Cleburne County, Alabama, the Coosa block is thrust over the Talladega block along the Hollins Line thrust fault. The Talladega block is composed of low grade metamorphic rocks, and contains evidence for four structural events. The units in the Talladega block indicate a continental orig ...
... In southern Cleburne County, Alabama, the Coosa block is thrust over the Talladega block along the Hollins Line thrust fault. The Talladega block is composed of low grade metamorphic rocks, and contains evidence for four structural events. The units in the Talladega block indicate a continental orig ...
Global Tectonics - dynamicearth.de
... More recent calculations have disputed this conventional view, at least for the Late Archean. Van Thienen et al. (2005) suggested that the increased heat flux from the Archean mantle could have been dissipated by thinning the lithosphere and thereby increasing the heat flow through the lithosphere. ...
... More recent calculations have disputed this conventional view, at least for the Late Archean. Van Thienen et al. (2005) suggested that the increased heat flux from the Archean mantle could have been dissipated by thinning the lithosphere and thereby increasing the heat flow through the lithosphere. ...
Primary - Maggie`s Earth Adventures
... much of the crust is granite. This is the continental crust. It is about 20 to 30 miles deep. On the ocean floor, the crust may only be about 4 miles deep. The oceanic crust is mainly made up of basalt. Below the crust is the mantle. This layer is about 84% of Planet Earth. The mantle is made of mag ...
... much of the crust is granite. This is the continental crust. It is about 20 to 30 miles deep. On the ocean floor, the crust may only be about 4 miles deep. The oceanic crust is mainly made up of basalt. Below the crust is the mantle. This layer is about 84% of Planet Earth. The mantle is made of mag ...
introduction - KFUPM Faculty List
... there rocks also affected by metamorphism to greenschist and ...
... there rocks also affected by metamorphism to greenschist and ...
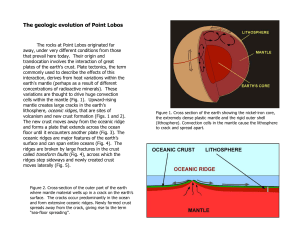
The geologic evolution of Point Lobos
... Figure 15. During the early Eocene, gravel, sand and mud accumulated in the submarine canyon that existed somewhere on an ancient continental margin in what today is Southern California. ...
... Figure 15. During the early Eocene, gravel, sand and mud accumulated in the submarine canyon that existed somewhere on an ancient continental margin in what today is Southern California. ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... Now, we get onto the common rock forming processes. What are the processes by which different types of rocks come into being? The first think that comes into mind is crystallization of partially molten matter. Now, what is partially molten matter? Say, underneath the surface of the earth, you get un ...
... Now, we get onto the common rock forming processes. What are the processes by which different types of rocks come into being? The first think that comes into mind is crystallization of partially molten matter. Now, what is partially molten matter? Say, underneath the surface of the earth, you get un ...
Rocks-Minerals - WordPress.com
... Electrons can be thought of as being transferred from one atom to another in an ionic bond. Common table salt (NaCl) is a mineral composed of chlorine and sodium linked together by ionic bonds. The mineral name for NaCl is halite. An element like chlorine can also form bonds without forming ions. Fo ...
... Electrons can be thought of as being transferred from one atom to another in an ionic bond. Common table salt (NaCl) is a mineral composed of chlorine and sodium linked together by ionic bonds. The mineral name for NaCl is halite. An element like chlorine can also form bonds without forming ions. Fo ...
Landforms and landscapes
... been found in rocks younger than those in Western Australia. The oldest rock, also around 4000 million years old, has been identified in a relatively stable area in Canada. So why are some of these rocks, thought to be present at the time when the Earth came into being, so much older than many other ...
... been found in rocks younger than those in Western Australia. The oldest rock, also around 4000 million years old, has been identified in a relatively stable area in Canada. So why are some of these rocks, thought to be present at the time when the Earth came into being, so much older than many other ...
Chapter 4 - Teacher Friendly Guides
... time, topography changes as a result of weathering and erosion, as well as the type and structure of the underlying bedrock. It is also a story of plate tectonics, volcanoes, folding, faulting, uplift, and mountain building. The Southwest’s topographic zones are under the influence of the destructiv ...
... time, topography changes as a result of weathering and erosion, as well as the type and structure of the underlying bedrock. It is also a story of plate tectonics, volcanoes, folding, faulting, uplift, and mountain building. The Southwest’s topographic zones are under the influence of the destructiv ...
PLATE BOUNDARIES AND CALIFORNIA
... Many of California’s landforms were produced by plate tectonic activity, which continues today. What you’ll learn: • Describe California’s current plate tectonic setting and how plate movements have produced landforms. • Predict future changes in California’s tectonic setting and topography. ...
... Many of California’s landforms were produced by plate tectonic activity, which continues today. What you’ll learn: • Describe California’s current plate tectonic setting and how plate movements have produced landforms. • Predict future changes in California’s tectonic setting and topography. ...
How does Earth`s continental crust form? Scientists have
... arc crust like steam on a kitchen ceiling. Scientists have found compelling evidence to suggest that this could have produced the vast majority of lower continental crust through Earth history. ...
... arc crust like steam on a kitchen ceiling. Scientists have found compelling evidence to suggest that this could have produced the vast majority of lower continental crust through Earth history. ...
Chapter 11 Section 1
... • Scientists use several features of folds to identify and describe the folds. • The sloping sides of a fold are called limbs. • The limbs meet at the bend in the rock layers, which is called the hinge. • If both halves of a fold are symmetrical, then the fold has an axial plane. The axial plane is ...
... • Scientists use several features of folds to identify and describe the folds. • The sloping sides of a fold are called limbs. • The limbs meet at the bend in the rock layers, which is called the hinge. • If both halves of a fold are symmetrical, then the fold has an axial plane. The axial plane is ...
PLATE BOUNDARIES AND CALIFORNIA
... Many of California’s landforms were produced by plate tectonic activity, which continues today. What you’ll learn: • Describe California’s current plate tectonic setting and how plate movements have produced landforms. • Predict future changes in California’s tectonic setting and topography. ...
... Many of California’s landforms were produced by plate tectonic activity, which continues today. What you’ll learn: • Describe California’s current plate tectonic setting and how plate movements have produced landforms. • Predict future changes in California’s tectonic setting and topography. ...
Chapter 5
... Many of California’s landforms were produced by plate tectonic activity, which continues today. What you’ll learn: • Describe California’s current plate tectonic setting and how plate movements have produced landforms. • Predict future changes in California’s tectonic setting and topography. ...
... Many of California’s landforms were produced by plate tectonic activity, which continues today. What you’ll learn: • Describe California’s current plate tectonic setting and how plate movements have produced landforms. • Predict future changes in California’s tectonic setting and topography. ...
GEO_143_mid_term_I_k..
... The Geology of Pacific Northwest Rocks and Minerals Mid Term I (100 points) (19) 2 pts.________ rocks form by crystallization and consolidation of molten magma. A) Igneous B) Primary C) Sedimentary D) Indigenous (20) 2 pts.________ rocks always originate at the surface of the solid Earth. A) Second ...
... The Geology of Pacific Northwest Rocks and Minerals Mid Term I (100 points) (19) 2 pts.________ rocks form by crystallization and consolidation of molten magma. A) Igneous B) Primary C) Sedimentary D) Indigenous (20) 2 pts.________ rocks always originate at the surface of the solid Earth. A) Second ...
Plate Tectonics
... Continents that were once connected also have identical landform shapes and features and identical rock formations ...
... Continents that were once connected also have identical landform shapes and features and identical rock formations ...
Chapter 21: Metamorphism
... • Uplift and erosion • Metamorphism often continues after major deformation ceases § Metamorphic pattern is simpler than the structural one • Pattern of increasing metamorphic grade from both directions toward the core area From Understanding Earth, Press and Siever. Freeman. ...
... • Uplift and erosion • Metamorphism often continues after major deformation ceases § Metamorphic pattern is simpler than the structural one • Pattern of increasing metamorphic grade from both directions toward the core area From Understanding Earth, Press and Siever. Freeman. ...
CRUSTAL GROWTH IN SOUTHERN ARIZONA: U
... the craton. Our data suggest that sedimentation within the Pinal block was proximal to the continental margin and occurred later than 1.68 Ga and ended before the intrusion of granitoids at 1.65 Ga. We show that the North American crust grew rapidly and progressively by addition of juvenile but evol ...
... the craton. Our data suggest that sedimentation within the Pinal block was proximal to the continental margin and occurred later than 1.68 Ga and ended before the intrusion of granitoids at 1.65 Ga. We show that the North American crust grew rapidly and progressively by addition of juvenile but evol ...
12.479 Trace-Element Geochemistry
... Trace element geochemistry contributed significantly to constraining the processes that create the basaltic oceanic crust. Specifically, the glass that forms when MORB magma erupts into seawater is unequivocally a quenched melt. However, this glass, and MORB whole-rocks in general, are characterized ...
... Trace element geochemistry contributed significantly to constraining the processes that create the basaltic oceanic crust. Specifically, the glass that forms when MORB magma erupts into seawater is unequivocally a quenched melt. However, this glass, and MORB whole-rocks in general, are characterized ...
Intrusive felsic-mafic net-veined complexes in north
... volumes of mafic magma have been involved, as in the Mount ErIe Complex near Duchess, only very small amounts of intermediate hybrid rocks are present. The likelihood of voluminous andesitic and dacitic volcanic rocks resulting from assimilation of crystalline rocks or even glassy rocks, as suggeste ...
... volumes of mafic magma have been involved, as in the Mount ErIe Complex near Duchess, only very small amounts of intermediate hybrid rocks are present. The likelihood of voluminous andesitic and dacitic volcanic rocks resulting from assimilation of crystalline rocks or even glassy rocks, as suggeste ...
terra nova national park
... believe that many of the original rocks were probably impure, clay-rich sediments and that others were volcanic rocks. The severely deformed rocks of the Love Cove Group are exposed in several long rock-cuts along the Trans-Canada Highway between the road to Charlottetown and the large quarry near P ...
... believe that many of the original rocks were probably impure, clay-rich sediments and that others were volcanic rocks. The severely deformed rocks of the Love Cove Group are exposed in several long rock-cuts along the Trans-Canada Highway between the road to Charlottetown and the large quarry near P ...
Convergent-Boundary Mountains
... – Seafloor structures, such as seamounts, must also be in isostatic equilibrium with the mantle. – Elevation of Earth’s crust depends upon the thickness of the crust as well as its density. – Mountain roots can be many times as deep as a mountain is high. ...
... – Seafloor structures, such as seamounts, must also be in isostatic equilibrium with the mantle. – Elevation of Earth’s crust depends upon the thickness of the crust as well as its density. – Mountain roots can be many times as deep as a mountain is high. ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.