Diseases project
... ensure that if they do happen to get infected they try to take care of themselves first. By putting other family members and friends in danger, that one person who got infected first is at risk for creating a bigger population of sick people. Those are all more fortunate, should put a team of peop ...
... ensure that if they do happen to get infected they try to take care of themselves first. By putting other family members and friends in danger, that one person who got infected first is at risk for creating a bigger population of sick people. Those are all more fortunate, should put a team of peop ...
Intro to Virology
... a. Plaque assays - plating dilutions of virus particles on a lawn of host cells; clear zones result from viral damage to the cells; results are expressed as plaque-forming units (PFU) b. Infectious dose assays - determining the smallest amount of virus needed to cause a measurable effect, usually on ...
... a. Plaque assays - plating dilutions of virus particles on a lawn of host cells; clear zones result from viral damage to the cells; results are expressed as plaque-forming units (PFU) b. Infectious dose assays - determining the smallest amount of virus needed to cause a measurable effect, usually on ...
Lecture 1: Virus properties
... DNA integrates into host DNA (provirus), may remain dormant Expressed by host RNA pol II, to make HIV mRNAs, regulated by splicing Virus particles bud from cell surface Transmission: sexual, intravenous drug use, vertical transmission, contaminated blood products Entry: virus binds cells expressing ...
... DNA integrates into host DNA (provirus), may remain dormant Expressed by host RNA pol II, to make HIV mRNAs, regulated by splicing Virus particles bud from cell surface Transmission: sexual, intravenous drug use, vertical transmission, contaminated blood products Entry: virus binds cells expressing ...
Infectious disease • Cholera, malaria, tuberculosis (TB) and HIV
... can prevent the virus passing from one person to another during intercourse. If a person is diagnosed with HIV, all their sexual contacts should be traced and informed that they may have the virus. The chances of HIV passing from an HIV – positive mother to her fetus is greatly reduced if the mother ...
... can prevent the virus passing from one person to another during intercourse. If a person is diagnosed with HIV, all their sexual contacts should be traced and informed that they may have the virus. The chances of HIV passing from an HIV – positive mother to her fetus is greatly reduced if the mother ...
Topic 10 Viruses
... – Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules, found in bacteria and yeast, that replicate independently from the main chromosome(s) and can be transferred between cells – Transposons are DNA segments that can move from one location to another within a cell’s genome – Viruses, plasmids, and transposon ...
... – Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules, found in bacteria and yeast, that replicate independently from the main chromosome(s) and can be transferred between cells – Transposons are DNA segments that can move from one location to another within a cell’s genome – Viruses, plasmids, and transposon ...
Call for Applications: APA Medical Student Senior
... participation of medical students (particularly from racial and ethnic minorities) in HIV-related care and research and provide them with a means of obtaining essential HIV-related mental health training through an integrated approach to patient care. Description of the Project This September Electi ...
... participation of medical students (particularly from racial and ethnic minorities) in HIV-related care and research and provide them with a means of obtaining essential HIV-related mental health training through an integrated approach to patient care. Description of the Project This September Electi ...
Office of Institutional Advancement
... the family to move to locations around the world, commented how unfortunate it was that people there didn’t have access to good medical care. “The family legend is that I declared right then that I would become a doctor to help people like that,” recalls Squires. As director of Jefferson’s Division ...
... the family to move to locations around the world, commented how unfortunate it was that people there didn’t have access to good medical care. “The family legend is that I declared right then that I would become a doctor to help people like that,” recalls Squires. As director of Jefferson’s Division ...
Immune System Notes
... This is just an example of one type of virus, there are many different shapes and forms but all have genetic material and a protein coat. How does a virus attack cells and reproduce? Step 1 -Virus sets down on a body cell and injects its genetic material (DNA or RNA) into the cell ...
... This is just an example of one type of virus, there are many different shapes and forms but all have genetic material and a protein coat. How does a virus attack cells and reproduce? Step 1 -Virus sets down on a body cell and injects its genetic material (DNA or RNA) into the cell ...
World Aids Day
... Currently there are approximately 33.4 million living with HIV and 2.7 million peolpe newly infected with HIV in the world every year. Everyday 5,500 people around the world die from HIV, according to WHO statistics. Whats is HIV/Aids? HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and w ...
... Currently there are approximately 33.4 million living with HIV and 2.7 million peolpe newly infected with HIV in the world every year. Everyday 5,500 people around the world die from HIV, according to WHO statistics. Whats is HIV/Aids? HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and w ...
Tobacco mosaic virus is viruses that cause disease in
... plant remains sick for 4 months. Virus jug adapt to survive from season to season on weeds included Solanaceae, such as amethyst and ceplukan. After the virus enters the host, it begins to multiply by inducing the host cells to form more viruses. Generally there are two ways that viruses infect cell ...
... plant remains sick for 4 months. Virus jug adapt to survive from season to season on weeds included Solanaceae, such as amethyst and ceplukan. After the virus enters the host, it begins to multiply by inducing the host cells to form more viruses. Generally there are two ways that viruses infect cell ...
Immunology
... -intact skin and low pH of the skin -acidity of stomach -tears from the eye -sneezing and coughing -complement components -neutrophils -NK (certain types of Lymphocytes) -inflammation -etc… ...
... -intact skin and low pH of the skin -acidity of stomach -tears from the eye -sneezing and coughing -complement components -neutrophils -NK (certain types of Lymphocytes) -inflammation -etc… ...
Hepatitis A virus
... Patients should get plenty of rest and eat a nutritious diet. They should also ensure they do not spread HAV by washing their hands after using the toilet and before ...
... Patients should get plenty of rest and eat a nutritious diet. They should also ensure they do not spread HAV by washing their hands after using the toilet and before ...
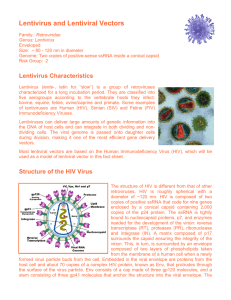
Lentivirus and Lentiviral Vectors
... The life cycle of HIV begins with viral entry, a multi-step interaction between the HIV envelope and the host target cell surface receptors. In the initial step of entry, the HIV gp120 protein binds to the host target cell CD4 receptor, thereby anchoring HIV to the host cell. This interaction genera ...
... The life cycle of HIV begins with viral entry, a multi-step interaction between the HIV envelope and the host target cell surface receptors. In the initial step of entry, the HIV gp120 protein binds to the host target cell CD4 receptor, thereby anchoring HIV to the host cell. This interaction genera ...
guidance guidelines - UNSW Research Gateway
... One of the benefits of using these retroviral vector systems is that they integrate into the chromosome of the target cell and therefore, after a period of time, the resulting transfected cell line or the animal will no longer contain virus but will continue to express the gene of interest. The safe ...
... One of the benefits of using these retroviral vector systems is that they integrate into the chromosome of the target cell and therefore, after a period of time, the resulting transfected cell line or the animal will no longer contain virus but will continue to express the gene of interest. The safe ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... o Virus’ requirements for _____________________________ – can the virus latch on? o Availability of ______________________ for multiplying – can host multiply virus? Viral host range gives potential in ___________________________ o Use of bacteriophage to treat ______________________ infections o ...
... o Virus’ requirements for _____________________________ – can the virus latch on? o Availability of ______________________ for multiplying – can host multiply virus? Viral host range gives potential in ___________________________ o Use of bacteriophage to treat ______________________ infections o ...
Unknown Viruses Dr. Robert Gallo, Director, Institute of Human
... tested for the infection. A fellow doctor, Niel Constantine, from the Institute of Human Virology, drew his blood and tested for IgG and IgM antibodies as well as for West Nile Virus RNA. The tests did not prove conclusive, and Dr. Gallo was diagnosed with an “unknown virus.” Such a diagnosis draws ...
... tested for the infection. A fellow doctor, Niel Constantine, from the Institute of Human Virology, drew his blood and tested for IgG and IgM antibodies as well as for West Nile Virus RNA. The tests did not prove conclusive, and Dr. Gallo was diagnosed with an “unknown virus.” Such a diagnosis draws ...
Biohazard Sorting Application Form This form must be filled out
... cannot be started until this application has been reviewed and approved. Additional information may be requested before approval can be considered. Please allow at least one week for the review and approval process to be completed. Date: Project Title: ...
... cannot be started until this application has been reviewed and approved. Additional information may be requested before approval can be considered. Please allow at least one week for the review and approval process to be completed. Date: Project Title: ...
Viruses, Prions, and Viroids Notes
... A. Viruses are a unique group of biological entities 1. They are not capable of surviving without a host cell (lack metabolic machinery) 2. They do, however, contain all the information necessary to direct metabolic processes 3. They are often classified as infectious particles rather than microorga ...
... A. Viruses are a unique group of biological entities 1. They are not capable of surviving without a host cell (lack metabolic machinery) 2. They do, however, contain all the information necessary to direct metabolic processes 3. They are often classified as infectious particles rather than microorga ...
Virus - WordPress.com
... A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms Viruses are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Viruses are parasites. They can't multiply on their own, s ...
... A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms Viruses are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Viruses are parasites. They can't multiply on their own, s ...
11mb ppt
... glycosaminoglycans, can serve as viral receptors. Different viruses employ different cellular receptors. A given virus isolate may employ several alternate cellular molecules as receptors. In some instances, viral entry requires two or more different coreceptors on the cell surface. Usually, both co ...
... glycosaminoglycans, can serve as viral receptors. Different viruses employ different cellular receptors. A given virus isolate may employ several alternate cellular molecules as receptors. In some instances, viral entry requires two or more different coreceptors on the cell surface. Usually, both co ...
Notes on Infectious Disease backup
... Infectious Disease Definition: Diseases transmitted(spread) by pathogens(germs) ...
... Infectious Disease Definition: Diseases transmitted(spread) by pathogens(germs) ...
Antiviral Agents – Dr.Roshna
... If virus replicates in presence of drug, mutations that allow faster replication (drug resistance) will be selected Selection of drug resistance mutations will allow higher levels of viremia and progression of immunologic disease unless drugs changed and replication again controlled Drug resistance ...
... If virus replicates in presence of drug, mutations that allow faster replication (drug resistance) will be selected Selection of drug resistance mutations will allow higher levels of viremia and progression of immunologic disease unless drugs changed and replication again controlled Drug resistance ...
HIV

The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that causes HIV infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). AIDS is a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. Infection with HIV occurs by the transfer of blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as helper T cells (specifically CD4+ T cells), macrophages, and dendritic cells. HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4+ T cells through a number of mechanisms, including apoptosis of uninfected bystander cells, direct viral killing of infected cells, and killing of infected CD4+ T cells by CD8 cytotoxic lymphocytes that recognize infected cells. When CD4+ T cell numbers decline below a critical level, cell-mediated immunity is lost, and the body becomes progressively more susceptible to opportunistic infections.