BIODIVERSITY-ECOSYSTEM FUNCTION RESEARCH
... BDEF studies of the last decade almost universally invoke the global decline in biodiversity as the primary impetus for research (Naeem et al. 1999). Conservation management and measurement of ecosystem functions (e.g., carbon credits) also occur on relatively large scales, from watersheds to nation ...
... BDEF studies of the last decade almost universally invoke the global decline in biodiversity as the primary impetus for research (Naeem et al. 1999). Conservation management and measurement of ecosystem functions (e.g., carbon credits) also occur on relatively large scales, from watersheds to nation ...
Land-use intensification reduces functional redundancy and
... redundancy provides resilience (sometimes called ÔinsuranceÕ) against the loss of functions and services provided by that group if different species show compensatory responses following environmental change (Naeem 1998). This view, however, is only valid if species richness corresponds directly to ...
... redundancy provides resilience (sometimes called ÔinsuranceÕ) against the loss of functions and services provided by that group if different species show compensatory responses following environmental change (Naeem 1998). This view, however, is only valid if species richness corresponds directly to ...
Contemporary Regulation Of Marine Living Resources And
... chapter 1 fisheries management food and agriculture - if marine living resources were infinite and that states should ensure that the level of fishing is commensurate with the state of fisheries resources, limiting abuse marine protected areas a limited solution - designation of marine protected are ...
... chapter 1 fisheries management food and agriculture - if marine living resources were infinite and that states should ensure that the level of fishing is commensurate with the state of fisheries resources, limiting abuse marine protected areas a limited solution - designation of marine protected are ...
Introduction to Landscape Ecology
... Perturbation at one scale may be equilibrium at a larger scale. Notion of natural range of variation and application as a guide for management ...
... Perturbation at one scale may be equilibrium at a larger scale. Notion of natural range of variation and application as a guide for management ...
BASIN: Basin-scale Analysis, Synthesis, and INtegration
... value of co-ordinating the scientific activities of the EU and North American countries to assess, predict, and mitigate the impact of climate and anthropogenic forcing on marine ecosystems and services of the North Atlantic. A crucial step towards such a co-ordinated approach is the development of ...
... value of co-ordinating the scientific activities of the EU and North American countries to assess, predict, and mitigate the impact of climate and anthropogenic forcing on marine ecosystems and services of the North Atlantic. A crucial step towards such a co-ordinated approach is the development of ...
Powerpoint
... • The Arctic Ocean is rich in nutrients from the surrounding landmasses and supports large populations of plankton, which feed a diversity of fish in the open water and under the ice. • These fish are food for ocean birds, whales, and seals. Fish and seals then provide food for polar bears and peopl ...
... • The Arctic Ocean is rich in nutrients from the surrounding landmasses and supports large populations of plankton, which feed a diversity of fish in the open water and under the ice. • These fish are food for ocean birds, whales, and seals. Fish and seals then provide food for polar bears and peopl ...
assessment of finfish cage aquaculture in the
... • proportion of feed wasted (values tested 0, 5, 10%; discussions suggested values may range between 2 and 15%). Research is ongoing to address the above noted uncertainties. 5. There was agreement that the resuspension module should not be applied, until we better understand the conditions under wh ...
... • proportion of feed wasted (values tested 0, 5, 10%; discussions suggested values may range between 2 and 15%). Research is ongoing to address the above noted uncertainties. 5. There was agreement that the resuspension module should not be applied, until we better understand the conditions under wh ...
Extinction or Survival? Behavioral Flexibility in Response
... For example, animals can respond to changing conditions phenologically/physiologically (e.g., by changing the timing of life cycles [3]). Alternately, when change is very rapid and occurs during the lifetime of an individual, some individuals could respond through phenotypic plasticity [4]. For exam ...
... For example, animals can respond to changing conditions phenologically/physiologically (e.g., by changing the timing of life cycles [3]). Alternately, when change is very rapid and occurs during the lifetime of an individual, some individuals could respond through phenotypic plasticity [4]. For exam ...
Seagrasses in the age of sea turtle conservation and
... represent a return to a natural state and may be grazed well below seagrass biomasses that might have existed under less trophically-downgraded conditions. It is unquestionable that further turtle conservation efforts are required in many areas of the world to restore turtle populations to levels th ...
... represent a return to a natural state and may be grazed well below seagrass biomasses that might have existed under less trophically-downgraded conditions. It is unquestionable that further turtle conservation efforts are required in many areas of the world to restore turtle populations to levels th ...
Extinction or Survival? Behavioral Flexibility in Response
... For example, animals can respond to changing conditions phenologically/physiologically (e.g., by changing the timing of life cycles [3]). Alternately, when change is very rapid and occurs during the lifetime of an individual, some individuals could respond through phenotypic plasticity [4]. For exam ...
... For example, animals can respond to changing conditions phenologically/physiologically (e.g., by changing the timing of life cycles [3]). Alternately, when change is very rapid and occurs during the lifetime of an individual, some individuals could respond through phenotypic plasticity [4]. For exam ...
File
... • Secondary succession can occur in ecosystems that have been disturbed or disrupted by humans, animals, or by natural process such as storms, floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions. ...
... • Secondary succession can occur in ecosystems that have been disturbed or disrupted by humans, animals, or by natural process such as storms, floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions. ...
Ground Work: Basic Concepts of Ecological Restoration
... amendments or planting cultivated species (nurse crops), are sometimes used. However, these temporary interventions are only undertaken where they assist the site’s return to an appropriate, self-regulating suite of native species. Conservation is a general term for the protection of existing specie ...
... amendments or planting cultivated species (nurse crops), are sometimes used. However, these temporary interventions are only undertaken where they assist the site’s return to an appropriate, self-regulating suite of native species. Conservation is a general term for the protection of existing specie ...
David Brown - Montana State University
... Salmonid habitat relationships; effects of Oregon fire on aquatic ecosystems; ecology of high State mountain lakes University ...
... Salmonid habitat relationships; effects of Oregon fire on aquatic ecosystems; ecology of high State mountain lakes University ...
Using Traditional Ecological Knowledge to Improve Holistic
... the user’s traditional ecological knowledge (TEK). Our counterintuitive results show that specific management strategies should be considered for each particular fishing seascape within the HLS while taking into account the differences among ecological structures and fishery dynamics. The insights f ...
... the user’s traditional ecological knowledge (TEK). Our counterintuitive results show that specific management strategies should be considered for each particular fishing seascape within the HLS while taking into account the differences among ecological structures and fishery dynamics. The insights f ...
A review of the indicators for ecosystem structure and functioning
... each of these deliverables was to provide a review of the available indicators at the levels of respectively, the population, the community, and the ecosystem. As there is a lot of overlap between these levels, both in terms of the available indicators as well as the data on which these indicators c ...
... each of these deliverables was to provide a review of the available indicators at the levels of respectively, the population, the community, and the ecosystem. As there is a lot of overlap between these levels, both in terms of the available indicators as well as the data on which these indicators c ...
JNCC Report No. 585: Conceptual Ecological Modelling of Shallow
... Sub-model 1. Suspension and Deposit Feeding Infauna Sub-model 2. Small Mobile Fauna or Tube/Burrow Dwelling Crustaceans Sub-model 3. Mobile Epifauna, Predators and Scavengers Sub-model 4. Attached Epifauna and Macroalgae Confidence model 1. Suspension and Deposit Feeding Infauna Confidence model 2. ...
... Sub-model 1. Suspension and Deposit Feeding Infauna Sub-model 2. Small Mobile Fauna or Tube/Burrow Dwelling Crustaceans Sub-model 3. Mobile Epifauna, Predators and Scavengers Sub-model 4. Attached Epifauna and Macroalgae Confidence model 1. Suspension and Deposit Feeding Infauna Confidence model 2. ...
pdf
... Ecosystem effects of recent changes in fishing strategies in the South Brazil Bight (SBB) area, including increasing squid catches by shrimp bottom trawlers and fishing for young sardines as bait, for the skipjack tuna pole-and-line fishery were investigated by modelling the SBB coastal ecosystem fo ...
... Ecosystem effects of recent changes in fishing strategies in the South Brazil Bight (SBB) area, including increasing squid catches by shrimp bottom trawlers and fishing for young sardines as bait, for the skipjack tuna pole-and-line fishery were investigated by modelling the SBB coastal ecosystem fo ...
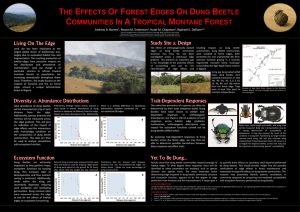
Global change and Mediterranean forests
... common land-use conversion during the last centuries. In particular, Mediterranean forests have widely disappeared because of exploitation and substitution by agricultural landscapes and, more recently, by urban development around cities and in coastal areas (Blondel et al. 2010). These changes in l ...
... common land-use conversion during the last centuries. In particular, Mediterranean forests have widely disappeared because of exploitation and substitution by agricultural landscapes and, more recently, by urban development around cities and in coastal areas (Blondel et al. 2010). These changes in l ...
File - Elko High School Ecology
... • The Arctic Ocean is rich in nutrients from the surrounding landmasses and supports large populations of plankton, which feed a diversity of fish in the open water and under the ice. • These fish are food for ocean birds, whales, and seals. Fish and seals then provide food for polar bears and peopl ...
... • The Arctic Ocean is rich in nutrients from the surrounding landmasses and supports large populations of plankton, which feed a diversity of fish in the open water and under the ice. • These fish are food for ocean birds, whales, and seals. Fish and seals then provide food for polar bears and peopl ...
ECOLOGICAL MECHANISMS LINKING PROTECTED AREAS TO
... areas, resulting in changes in ecological function and biodiversity within protected areas. Recent satellite-based change analyses are revealing that human populations and intense land use have grown rapidly in recent decades around many protected areas (Hansen et al. 2004). In the tropics, road con ...
... areas, resulting in changes in ecological function and biodiversity within protected areas. Recent satellite-based change analyses are revealing that human populations and intense land use have grown rapidly in recent decades around many protected areas (Hansen et al. 2004). In the tropics, road con ...
PDF, 2241 KB - URPP GCB
... Recent dynamics of Arctic Tundra vegetation communities and their implications for earth system processes. ................................................................................................................................. 28 Essential Ecosystem services variables and sustainable devel ...
... Recent dynamics of Arctic Tundra vegetation communities and their implications for earth system processes. ................................................................................................................................. 28 Essential Ecosystem services variables and sustainable devel ...
Intro to Ecosystems
... *This is because it causes the species to compete with one another for resources, and only one will prevail. *Therefore, one species will typically have to relocate, or adapt to another niche- which is not an easy thing to do- or risk extinction. http://www.grln.net/Giraffe3.jpg ...
... *This is because it causes the species to compete with one another for resources, and only one will prevail. *Therefore, one species will typically have to relocate, or adapt to another niche- which is not an easy thing to do- or risk extinction. http://www.grln.net/Giraffe3.jpg ...
Ecological resilience

In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or disturbance by resisting damage and recovering quickly. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. Human activities that adversely affect ecosystem resilience such as reduction of biodiversity, exploitation of natural resources, pollution, land-use, and anthropogenic climate change are increasingly causing regime shifts in ecosystems, often to less desirable and degraded conditions. Interdisciplinary discourse on resilience now includes consideration of the interactions of humans and ecosystems via socio-ecological systems, and the need for shift from the maximum sustainable yield paradigm to environmental resource management which aims to build ecological resilience through ""resilience analysis, adaptive resource management, and adaptive governance"".