unit 4 overview
... purpose. Some cells carry oxygen while others fight disease. Some single- celled organisms such as protists sole function is to survive. In this unit you will learn about various cell types, their many different structures, and how they carry out many of life’s functions. TEXTBOOK – Chapter 7 and Se ...
... purpose. Some cells carry oxygen while others fight disease. Some single- celled organisms such as protists sole function is to survive. In this unit you will learn about various cell types, their many different structures, and how they carry out many of life’s functions. TEXTBOOK – Chapter 7 and Se ...
Cellular Architecture
... Detoxification centers Possess enzyme catalase important in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide ...
... Detoxification centers Possess enzyme catalase important in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide ...
What is coBacterial Growth and Reproduction
... The bacterial flagella is unique and fifers from the eukaryotic flagella which is consistent in its structure having the classic “9 + 2” arrangement of microtubules. The bacterial flagella therefore is an analogous structure and not homologous with the eukaryotic flagella. The bacterial flagella rot ...
... The bacterial flagella is unique and fifers from the eukaryotic flagella which is consistent in its structure having the classic “9 + 2” arrangement of microtubules. The bacterial flagella therefore is an analogous structure and not homologous with the eukaryotic flagella. The bacterial flagella rot ...
Eukaryotic Cell
... It is enclosed within the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope is made of two membranes, unique to eukaryotes “Houses” DNA-extremely long polymers that encode the genetic information Giant DNA molecules become visible in the form of chromosomes as the cell compacts the molecules to prepare for cel ...
... It is enclosed within the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope is made of two membranes, unique to eukaryotes “Houses” DNA-extremely long polymers that encode the genetic information Giant DNA molecules become visible in the form of chromosomes as the cell compacts the molecules to prepare for cel ...
Animal Cell - Eagan High School
... Helps the cell maintain its shape. Assists with movement of materials Serve as “tracks” along which organelles move Form cilia & flagella too Assist in movement of DNA (chromosomes) in mitosis ...
... Helps the cell maintain its shape. Assists with movement of materials Serve as “tracks” along which organelles move Form cilia & flagella too Assist in movement of DNA (chromosomes) in mitosis ...
Cell Organelle Chart
... Stores food, enzyme, and other material Support Power house of cell – produces energy for growth, development, and movement Helps in cell division (mitosis) ...
... Stores food, enzyme, and other material Support Power house of cell – produces energy for growth, development, and movement Helps in cell division (mitosis) ...
Diversity of Cell Structure and Function
... 2. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have some of the same components, but also some different components. Use the diagrams of the eukaryotic animal cell and the prokaryotic bacterial cell to show each component from the following list that is found in each type of cell: cell wall, endoplasmic retic ...
... 2. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have some of the same components, but also some different components. Use the diagrams of the eukaryotic animal cell and the prokaryotic bacterial cell to show each component from the following list that is found in each type of cell: cell wall, endoplasmic retic ...
Biology 102 Exam I Study Guide How many kingdoms are there
... This category of bacteria are responsible for a substantial amount of the oxygen that is produced in the atmosphere? This category of bacteria is very important to humans and agriculture and is found in root nodules of legumes (pea family)? This structure of bacteria is external to the cell wall and ...
... This category of bacteria are responsible for a substantial amount of the oxygen that is produced in the atmosphere? This category of bacteria is very important to humans and agriculture and is found in root nodules of legumes (pea family)? This structure of bacteria is external to the cell wall and ...
Anatomy of Bacteria
... • “the symbiotic relationship of two organisms of different species in which one gains some benefit such as protection or nourishment and the other is not harmed or benefited” – e.g. bacteria on skin surface; microorganisms within the digestive tract ...
... • “the symbiotic relationship of two organisms of different species in which one gains some benefit such as protection or nourishment and the other is not harmed or benefited” – e.g. bacteria on skin surface; microorganisms within the digestive tract ...
Nov 2008 - University of Nottingham
... Sir William Dunn School of Pathology Oxford University In the talk I will describe our studies of Sulfolobus, a hyperthermophilic crenarchaeal genus. In common with other archaea, they have transcription and replication machineries that resemble an ancestral form of the eukaryotic apparatus. The rel ...
... Sir William Dunn School of Pathology Oxford University In the talk I will describe our studies of Sulfolobus, a hyperthermophilic crenarchaeal genus. In common with other archaea, they have transcription and replication machineries that resemble an ancestral form of the eukaryotic apparatus. The rel ...
Cell Organelle Organelle Function City Part Cell Membrane
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
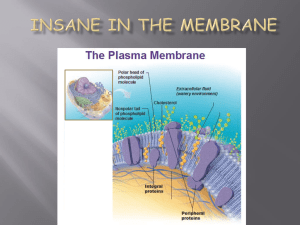
CellMembranes - Mexico Central School District
... Extends into and completely through the Phospholipid Bilayer, from the outer surface to the inner surface. ...
... Extends into and completely through the Phospholipid Bilayer, from the outer surface to the inner surface. ...
TAKS Obj 2 -BIOLOGY
... Plant Cells have, and Animal Cells don’t • Chloroplasts – organelle responsible for photosynthesis • Cell Walls – a structure outside of the membrane to provide support • Very large vacuoles to store extra water ...
... Plant Cells have, and Animal Cells don’t • Chloroplasts – organelle responsible for photosynthesis • Cell Walls – a structure outside of the membrane to provide support • Very large vacuoles to store extra water ...
Cells Powerpoint
... •Membrane bound nucleus •Organelles of different functions •Larger in size (some visible with no microscope) •All other living things ...
... •Membrane bound nucleus •Organelles of different functions •Larger in size (some visible with no microscope) •All other living things ...
Cell wall
... of metabolism are excreted from the cell, and will accumulate in the capsule. This binds them up, and prevents the waste from interfering with cell metabolism. ...
... of metabolism are excreted from the cell, and will accumulate in the capsule. This binds them up, and prevents the waste from interfering with cell metabolism. ...
AP BIOLOGY-EXAM REVIEW The Cell
... membrane? How are molecules transported that do not easily cross the membrane? ...
... membrane? How are molecules transported that do not easily cross the membrane? ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be able to put them in to order from least to most complex and explain each one. CELL PARTS: Be able ...
... How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be able to put them in to order from least to most complex and explain each one. CELL PARTS: Be able ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. • The structure and function of organelles found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. • How chloroplasts and mitochondria evolved through endosymbiosis (Endosymbiotic Theory) ...
... • The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. • The structure and function of organelles found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. • How chloroplasts and mitochondria evolved through endosymbiosis (Endosymbiotic Theory) ...
Chapter 6
... Microfilaments • Protein = actin • Smallest fibers • Support cell on smaller scale • Cell movement • Eg. ameboid movement, cytoplasmic streaming, muscle cell contraction ...
... Microfilaments • Protein = actin • Smallest fibers • Support cell on smaller scale • Cell movement • Eg. ameboid movement, cytoplasmic streaming, muscle cell contraction ...
Bacteria are protected by a rigid cell wall composed of
... and archaea. A peptidoglycan cell wall composed of disaccharides and amino acids gives bacteria structural support. The bacterial cell wall is often a target for antibiotic treatment. ...
... and archaea. A peptidoglycan cell wall composed of disaccharides and amino acids gives bacteria structural support. The bacterial cell wall is often a target for antibiotic treatment. ...
12/10/09
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
The Cell - CCRI Faculty Web
... All cells surrounded by a plasma membrane Phospholipid bilayer material inside a cell is the cytoplasm Everything between the plasma membrane and the region of DNA Gives cells their shape Assist in movement of cell and organelles ...
... All cells surrounded by a plasma membrane Phospholipid bilayer material inside a cell is the cytoplasm Everything between the plasma membrane and the region of DNA Gives cells their shape Assist in movement of cell and organelles ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.