The Cell Theory
... of a cell. • An example of an organelle is the nucleus which controls cell functions. ...
... of a cell. • An example of an organelle is the nucleus which controls cell functions. ...
Label a Plant Cell (Up to 16yrs old / GCSE)
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 1 ...
... 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 1 ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Living Things
... 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuole in its cells, which again a plant has and the animal cells would only have small vacuole. 10. Reproduction, because an indiv ...
... 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuole in its cells, which again a plant has and the animal cells would only have small vacuole. 10. Reproduction, because an indiv ...
A. Specific Aims Developing B cells undergo regulated cell division
... A-MuLV-transformed pro-B cells treated with STI-571 and study spontaneous mechanisms leading to the resistance of leukemic pro-B cells to STI-571 treatment. A.2 To determine the role(s) of c-Abl in normal B cell development. The cytoplasmic src-family protein tyrosine kinase c-Abl is expressed in al ...
... A-MuLV-transformed pro-B cells treated with STI-571 and study spontaneous mechanisms leading to the resistance of leukemic pro-B cells to STI-571 treatment. A.2 To determine the role(s) of c-Abl in normal B cell development. The cytoplasmic src-family protein tyrosine kinase c-Abl is expressed in al ...
Marine Biology Cell Assessment 1) Cyanide is a poison that
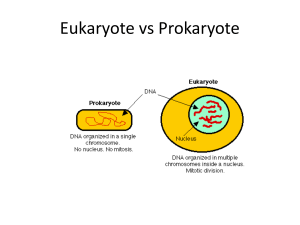
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
government - Humble ISD
... Vocabulary: Resolution, magnification, ocular lens, stage, objective lens ...
... Vocabulary: Resolution, magnification, ocular lens, stage, objective lens ...
Cell Project
... Due:____1/29/2016_______ Make a 3 dimensional model of either a plant or animal cell Cell model must contain the following organelles: o Nucleus o cytoplasm o mitochondria o vacuole o cell membrane o chloroplast (plant only) o Chlorophyll (plant only) o cell wall (plant only) Materials for the ...
... Due:____1/29/2016_______ Make a 3 dimensional model of either a plant or animal cell Cell model must contain the following organelles: o Nucleus o cytoplasm o mitochondria o vacuole o cell membrane o chloroplast (plant only) o Chlorophyll (plant only) o cell wall (plant only) Materials for the ...
Practice Cell Organelle Quiz
... ______ Finishes and Packages molecules to be released to the outside of the cell ______ Whip-like projection on outside of cell ...
... ______ Finishes and Packages molecules to be released to the outside of the cell ______ Whip-like projection on outside of cell ...
Cell Processes Study Guide
... Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fermentation is cellular respiration in the absence (NO) of oxygen – produces lactic acid as a waste product that will cause muscle cramps. Cells need nutrients to: grow and develop, divide, and to perform functions Home ...
... Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fermentation is cellular respiration in the absence (NO) of oxygen – produces lactic acid as a waste product that will cause muscle cramps. Cells need nutrients to: grow and develop, divide, and to perform functions Home ...
Joe Corbo Briefly describe the function and component parts of a
... Describe the location within the ventricular epithelium of a neural progenitor at the various stages of the cell cycle. What is this movement process called? ...
... Describe the location within the ventricular epithelium of a neural progenitor at the various stages of the cell cycle. What is this movement process called? ...
Plant Cell
... The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
... The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
Cell power point
... DNA is the blueprints for the cell. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. This is what genes are made of. ...
... DNA is the blueprints for the cell. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. This is what genes are made of. ...
Chapter 13, Lesson 1
... mitochondria. 5. Ribosomes, makes protein; proteins are part of the membrane and are needed for some chemical reactions. “Protein Factories” 6. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) folded membranes in which materials can be processed and moved around. “Highway” 7. Golgi Bodies, stacked, flattened membrane, so ...
... mitochondria. 5. Ribosomes, makes protein; proteins are part of the membrane and are needed for some chemical reactions. “Protein Factories” 6. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) folded membranes in which materials can be processed and moved around. “Highway” 7. Golgi Bodies, stacked, flattened membrane, so ...
Cell Organelles
... Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids ...
... Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids ...
Cells Review and Cellingo Game
... Manuela will give you a clue for the word, not the word itself If you have the word that goes with the clue on your card, cross it off Remember to say BINGO if you win! (Or say “Cell-ingo!”) ...
... Manuela will give you a clue for the word, not the word itself If you have the word that goes with the clue on your card, cross it off Remember to say BINGO if you win! (Or say “Cell-ingo!”) ...
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death (or PCD) is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death, but necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Recently a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternate form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations.