CellsTest
... Animals and plants share the same kinds of cells. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from existing cells. ...
... Animals and plants share the same kinds of cells. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from existing cells. ...
6th Grade Science
... nucleus. Cytoplasm contains a large amount of _______________ and many chemicals and structures that carry out the life ______________________ in the cell. These structures that the cytoplasm contains are called _____________________. Unlike a gelatin dessert, however, cytoplasm constantly _________ ...
... nucleus. Cytoplasm contains a large amount of _______________ and many chemicals and structures that carry out the life ______________________ in the cell. These structures that the cytoplasm contains are called _____________________. Unlike a gelatin dessert, however, cytoplasm constantly _________ ...
Mitosis ppt
... When cells begin to divide, the first thing that happens is that the chromatin in the nucleus begins to wind up, separating the strands from each other. ...
... When cells begin to divide, the first thing that happens is that the chromatin in the nucleus begins to wind up, separating the strands from each other. ...
Test Review Notes
... Cell theory 3 major components of cell theory All living organisms are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life Cells arise from pre-existing cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory Hans and Zacharias Janssen-1590 inventors of 1st compound microscope Robert Hooke-1665 used the ...
... Cell theory 3 major components of cell theory All living organisms are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life Cells arise from pre-existing cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory Hans and Zacharias Janssen-1590 inventors of 1st compound microscope Robert Hooke-1665 used the ...
Specialised Cells
... • Plants and animals are multicellular (consist of many cells). • They contain many different types of cells. • Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. • This is known as CELL SPECIALISM • Not all cells look the same. • Some cells have a special shape and features to ...
... • Plants and animals are multicellular (consist of many cells). • They contain many different types of cells. • Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. • This is known as CELL SPECIALISM • Not all cells look the same. • Some cells have a special shape and features to ...
Cell Structure
... a. Plant cells have everything found in animal cells as well as: i. Cell Wall: A hard outer covering over the cell membrane. It gives rigid support to the cell. It is selectively permeable. ii. Chloroplasts: Disk-shaped organelles that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. They are responsible phot ...
... a. Plant cells have everything found in animal cells as well as: i. Cell Wall: A hard outer covering over the cell membrane. It gives rigid support to the cell. It is selectively permeable. ii. Chloroplasts: Disk-shaped organelles that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. They are responsible phot ...
benchmark #1 study guide
... 24. What is mitosis? In what type of cells does this process occur? What happens to the chromosome number of a cell during mitosis? 25. What are the phases of normal cell division (mitosis)? 26. What do the terms diploid and haploid mean? 27. What is meiosis? In what type of cells does this process ...
... 24. What is mitosis? In what type of cells does this process occur? What happens to the chromosome number of a cell during mitosis? 25. What are the phases of normal cell division (mitosis)? 26. What do the terms diploid and haploid mean? 27. What is meiosis? In what type of cells does this process ...
Class Test
... 5. Each word in the left-hand column below is related to one of the words in the right-hand column. Write them down in the correct pairs. _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 6. From the list on the right, p ...
... 5. Each word in the left-hand column below is related to one of the words in the right-hand column. Write them down in the correct pairs. _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 6. From the list on the right, p ...
“Guided Reading and Study” Student Notes Chapter 2.4, “Looking
... b. Replace each incorrect response with the CORRECT response, as seen below. c. Study each question and response by really thinking about the ‘meaning’ of what each statement is ‘messaging’. d. Next, in your own mind, paraphrase what you have just studied! Then, practice studying aloud with some ...
... b. Replace each incorrect response with the CORRECT response, as seen below. c. Study each question and response by really thinking about the ‘meaning’ of what each statement is ‘messaging’. d. Next, in your own mind, paraphrase what you have just studied! Then, practice studying aloud with some ...
Cell organelles you need to know for unit test
... Cell organelles= parts of the cell 1. Cytoplasm-mostly made up of water, this jelly like organelle found inside the cell that holds all the other cells in place. 2. Cell wall- Found only in plants it is a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape, it also provides support which helps plants grow ...
... Cell organelles= parts of the cell 1. Cytoplasm-mostly made up of water, this jelly like organelle found inside the cell that holds all the other cells in place. 2. Cell wall- Found only in plants it is a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape, it also provides support which helps plants grow ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • Rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants – Protects the cell – Supports the cell ...
... • Rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants – Protects the cell – Supports the cell ...
Bio102 Problems
... A. mitochondria have their own DNA. B. mitochondria have a cell wall, like prokaryotic cells. C. mitochondria are approximately the same size as a prokaryotic cell. D. mitochondria have two membranes. ...
... A. mitochondria have their own DNA. B. mitochondria have a cell wall, like prokaryotic cells. C. mitochondria are approximately the same size as a prokaryotic cell. D. mitochondria have two membranes. ...
Cells - Life Learning Cloud
... All plant cells have the structures in an animal cell and: Cell wall made of cellulose which strengthens the cell and gives it support. Many, but not all, plant cells also have: Chloroplasts, found in all the green parts of the plant. They are green because they contain chlorophyll. They absorb ligh ...
... All plant cells have the structures in an animal cell and: Cell wall made of cellulose which strengthens the cell and gives it support. Many, but not all, plant cells also have: Chloroplasts, found in all the green parts of the plant. They are green because they contain chlorophyll. They absorb ligh ...
Mitochondrion
... Diffusion-movement of gases from higher concentrations to lower concentrations Passive Transport-materials do not need energy to move from higher concentration to lower to a lower concentration Active Transport-materials need energy to move from a higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis- ...
... Diffusion-movement of gases from higher concentrations to lower concentrations Passive Transport-materials do not need energy to move from higher concentration to lower to a lower concentration Active Transport-materials need energy to move from a higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis- ...
Cell Division
... Take a piece of clay and divide it in half. Now you have two pieces of clay, each half the size of the original piece. Divide each of the two new pieces in half, producing 4 pieces, each a quarter the size of the original piece. Observe and Think What ...
... Take a piece of clay and divide it in half. Now you have two pieces of clay, each half the size of the original piece. Divide each of the two new pieces in half, producing 4 pieces, each a quarter the size of the original piece. Observe and Think What ...
HOMEWORK: REVIEW CELL LIFE CYCLE AND MITOSIS
... 3) The picture to the right shows onion root tip cells. Label 1 cell in EACH of the following phases: a. b. c. d. e. ...
... 3) The picture to the right shows onion root tip cells. Label 1 cell in EACH of the following phases: a. b. c. d. e. ...
Cell Organelles Book - Birmingham City Schools
... • Proteins are made by ______________ on ER surface • They are then threaded into the interior of the Rough ER to be modified and ...
... • Proteins are made by ______________ on ER surface • They are then threaded into the interior of the Rough ER to be modified and ...
A counter-example to Paul`s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as
... A counter-example to Paul’s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as Marquis points out. When a human cancer cell appears in my body, it is a human individual according to the criterion in premise 1: “a life is begun which is neither that of the father nor the mother; it is rather new human life with it ...
... A counter-example to Paul’s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as Marquis points out. When a human cancer cell appears in my body, it is a human individual according to the criterion in premise 1: “a life is begun which is neither that of the father nor the mother; it is rather new human life with it ...
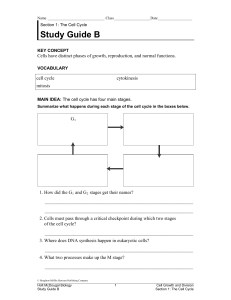
Study Guide B
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death (or PCD) is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death, but necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Recently a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternate form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations.