Cell Theory and Cell Structure
... • Who are the scientists who contributed to the cell theory and what did they contribute? • What are the parts of the cell theory? • What are the two largest groupings of cells and what ...
... • Who are the scientists who contributed to the cell theory and what did they contribute? • What are the parts of the cell theory? • What are the two largest groupings of cells and what ...
Cell Theory and Cell Structure
... Organisms may be: • Unicellular – composed of one cell • Multicellular - composed of many cells ...
... Organisms may be: • Unicellular – composed of one cell • Multicellular - composed of many cells ...
Slide ()
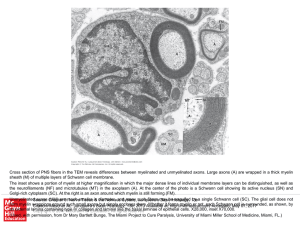
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Growth and multiplication in bacteria
... Characterized by a period during which there is no increase in the number of cells. Cells enlarge ,as enzymes and metabolic intermediates are built up Duration of Lag phase varies with the Spp., size of the inoculum, nature of the culture medium and environmental factors . ...
... Characterized by a period during which there is no increase in the number of cells. Cells enlarge ,as enzymes and metabolic intermediates are built up Duration of Lag phase varies with the Spp., size of the inoculum, nature of the culture medium and environmental factors . ...
Cell Organelle Review Game
... 2. Only one team member from each team can run to the board. It is preferred that the same student does the running each time. 3. The students must have the appropriate cell organelle in the appropriate cell or cells to gain points. For example, if a student puts the illustration of a cell wall in b ...
... 2. Only one team member from each team can run to the board. It is preferred that the same student does the running each time. 3. The students must have the appropriate cell organelle in the appropriate cell or cells to gain points. For example, if a student puts the illustration of a cell wall in b ...
7th Grade Science Cells Study Guide You will have a Cell Test on
... 1. What is a cell? 2. Describe the contributions of Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Shliedan/Swann to cell theory? [page 60-61 Cornell notes] 3. What are the benefits of being a multicellular organism? 4. Comparing cells (Prokaryotes to Eukaryotes) – structure, organelles and function. [Make a T chart or Venn d ...
... 1. What is a cell? 2. Describe the contributions of Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Shliedan/Swann to cell theory? [page 60-61 Cornell notes] 3. What are the benefits of being a multicellular organism? 4. Comparing cells (Prokaryotes to Eukaryotes) – structure, organelles and function. [Make a T chart or Venn d ...
Eukaryotic cell
... 1. compression-resisting function, dynamic behavior, binding GTP for polymerization, intracellular transport (associated with dyneins and kinesins, they transport organelles like mitochondria or vesicles, the axoneme of cilia and flagella, the mitotic spindle ...
... 1. compression-resisting function, dynamic behavior, binding GTP for polymerization, intracellular transport (associated with dyneins and kinesins, they transport organelles like mitochondria or vesicles, the axoneme of cilia and flagella, the mitotic spindle ...
Define Cell Parts
... mitochondrion provides energy for the cell vacuole contains the waste golgi apparatus packs protein nucleus controls the cell rhibosomes synthesizes (transforms) protein cytoplasm holds the cell’s organelles in place cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside microvilli involved ...
... mitochondrion provides energy for the cell vacuole contains the waste golgi apparatus packs protein nucleus controls the cell rhibosomes synthesizes (transforms) protein cytoplasm holds the cell’s organelles in place cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside microvilli involved ...
Notes-Organelles - Svetz-wiki
... molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi apparatus from ER proteins are packaged and exported near membrane Jobs of the Golgi Apparat ...
... molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi apparatus from ER proteins are packaged and exported near membrane Jobs of the Golgi Apparat ...
Passive Vs. Active Transport
... • Active Transport: When an input of energy is required to move materials through a cell membrane. – How do plant roots get their nutrients? • Transport protein pulls the nutrient through the cell membrane. ...
... • Active Transport: When an input of energy is required to move materials through a cell membrane. – How do plant roots get their nutrients? • Transport protein pulls the nutrient through the cell membrane. ...
Ch. 7 Review
... multicellular organism is a. cell specialization. b. a tissue. c. an organ system. d. an organ. ...
... multicellular organism is a. cell specialization. b. a tissue. c. an organ system. d. an organ. ...
1st semester exam review
... What is the regulation of lifemaintaining conditions inside an organism despite the changes in its environment? ...
... What is the regulation of lifemaintaining conditions inside an organism despite the changes in its environment? ...
lessonuploads/Chapter 1 Section 2 vocab chart HO
... made primarily of RNA; most numerous organelle; Float freely in cytoplasm or attach to membranes or ...
... made primarily of RNA; most numerous organelle; Float freely in cytoplasm or attach to membranes or ...
Cell part
... made primarily of RNA; most numerous organelle; Float freely in cytoplasm or attach to membranes or ...
... made primarily of RNA; most numerous organelle; Float freely in cytoplasm or attach to membranes or ...
Cell and The Microscope
... move it up and down to focus the slide. 5) Adjust the light by using the condenser and the diaphragm. 6) Now use the fine focus knob to better focus your slide. ...
... move it up and down to focus the slide. 5) Adjust the light by using the condenser and the diaphragm. 6) Now use the fine focus knob to better focus your slide. ...
unit 4 – syllabus - Effingham County Schools
... and glucose; produces carbon dioxide and water 3. ____________________division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells in which each new cell receives a copy of the original chromosomes 4. ____________________the green pigment in chloroplasts where photosynthesis occurs 5. _____________________the physic ...
... and glucose; produces carbon dioxide and water 3. ____________________division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells in which each new cell receives a copy of the original chromosomes 4. ____________________the green pigment in chloroplasts where photosynthesis occurs 5. _____________________the physic ...
File
... c. the same concentration of solutes as the cell. d. too many solutes. ____ 32. Transport proteins play a role in both a. passive and active transport. b. exocytosis and endocytosis. c. diffusion and vesicle transport. d. phagocytosis and passive transport. ____ 33. Which process requires no energy ...
... c. the same concentration of solutes as the cell. d. too many solutes. ____ 32. Transport proteins play a role in both a. passive and active transport. b. exocytosis and endocytosis. c. diffusion and vesicle transport. d. phagocytosis and passive transport. ____ 33. Which process requires no energy ...
Joanne Tracy “Innovation at the Cutting Edge of Academic Publishing”
... biological sciences. In this capacity, she is responsible for the overall strategic direction of the business, product development and acquisition, as well as the innovation processes. Cell Press is a recognized leader in innovation of the presentation of scientific literature, introducing new eleme ...
... biological sciences. In this capacity, she is responsible for the overall strategic direction of the business, product development and acquisition, as well as the innovation processes. Cell Press is a recognized leader in innovation of the presentation of scientific literature, introducing new eleme ...
Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm The control center of the cell and
... ER, but without the ribosomes. Produces lipids, involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. ...
... ER, but without the ribosomes. Produces lipids, involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. ...
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death (or PCD) is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death, but necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Recently a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternate form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations.