Study Guide Review
... Explain the process of osmosis. Use examples from our lab (egg osmosis lab) to support your answer. ...
... Explain the process of osmosis. Use examples from our lab (egg osmosis lab) to support your answer. ...
Mitosis
... How long is one cell cycle? Depends on the cell- skin cells = ~24 hours, nerve cells = never after maturity, cancer cells = very short Remember: every cell only has a certain # of divisions it can undergo, then it dies = apoptosis (programmed cell death) ...
... How long is one cell cycle? Depends on the cell- skin cells = ~24 hours, nerve cells = never after maturity, cancer cells = very short Remember: every cell only has a certain # of divisions it can undergo, then it dies = apoptosis (programmed cell death) ...
3.5.3 - OpenStudy
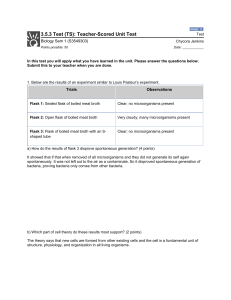
... It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving bacteria only comes from other bacteria. ...
... It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving bacteria only comes from other bacteria. ...
Pre-AP Biology Cell Transport Worksheet
... 4. What would happen to a plant cell in each of the following solutions? a. Hypertonic: The cell would ____________________________ because the water molecules would _____________________. b. Hypotonic: The cell would _______________________________ because the water molecules would _______________ ...
... 4. What would happen to a plant cell in each of the following solutions? a. Hypertonic: The cell would ____________________________ because the water molecules would _____________________. b. Hypotonic: The cell would _______________________________ because the water molecules would _______________ ...
01A cell transformation
... Predisposition to cancer is often the consequence of a mutation that occurs in germ cells (ovum or spermatozoid). All the cells of the embryo carrry this mutant. As a consequence a fewer number of alterations suffices to acquire the unlucky transforming mutation. Moreover, in the case of breast canc ...
... Predisposition to cancer is often the consequence of a mutation that occurs in germ cells (ovum or spermatozoid). All the cells of the embryo carrry this mutant. As a consequence a fewer number of alterations suffices to acquire the unlucky transforming mutation. Moreover, in the case of breast canc ...
Cell Observations Lab
... Conclusion Questions You may need to research some of these using your notebook or textbooks. I. ...
... Conclusion Questions You may need to research some of these using your notebook or textbooks. I. ...
WHAT DO WE NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE CELL : Topics covered
... How do we get glucose? - it depends on the organism i. Plants Sun + CO2 + H2O (photosynthesis)--> glucose + O2. a. The energy from the sun is stored in the bonds between the carbons in glucose. b. The mitochondria (in all eukaryotes) will break down glucose (or glycogen or fat) when needed to obtain ...
... How do we get glucose? - it depends on the organism i. Plants Sun + CO2 + H2O (photosynthesis)--> glucose + O2. a. The energy from the sun is stored in the bonds between the carbons in glucose. b. The mitochondria (in all eukaryotes) will break down glucose (or glycogen or fat) when needed to obtain ...
Chapter 4 Topic: Cell structure Main concepts: •Cells were first
... • Lysosomes are small bags of digestive enzymes. They pick up and digest waste products within the cell. They can also cause cell death if ruptured. One-celled organisms used lysosomes to digest food that is inside of food vacuoles. • Plant cells have a large central vacuole for water regulation, su ...
... • Lysosomes are small bags of digestive enzymes. They pick up and digest waste products within the cell. They can also cause cell death if ruptured. One-celled organisms used lysosomes to digest food that is inside of food vacuoles. • Plant cells have a large central vacuole for water regulation, su ...
Lesson Overview
... Growth factors : external regulators that stimulate the growth and division of cells. Important during embryonic development and wound healing. ...
... Growth factors : external regulators that stimulate the growth and division of cells. Important during embryonic development and wound healing. ...
Division Plane Orientation in Plant Cells
... to the plant body organization. In order to determine how much cell geometry alone predicts division plane orientation, we used a mathematical modeling approach. Probabilistic division plane predictions of cells were made based on century-old observations of symmetric plant division: the daughter ce ...
... to the plant body organization. In order to determine how much cell geometry alone predicts division plane orientation, we used a mathematical modeling approach. Probabilistic division plane predictions of cells were made based on century-old observations of symmetric plant division: the daughter ce ...
The Body in Motion
... cell extract spun in a centrifuge Centrifugal force separates extract Pellet – heavier cell organelles Supernatant – liquid poured off ...
... cell extract spun in a centrifuge Centrifugal force separates extract Pellet – heavier cell organelles Supernatant – liquid poured off ...
Cell Membrane
... Cytoplasm contains a large amount of water and many chemicals and structures that carry out the life processes in the cell. These structures that the cytoplasm contains are called organelles. Unlike a gelatin dessert, however, cytoplasm constantly moves or streams. ...
... Cytoplasm contains a large amount of water and many chemicals and structures that carry out the life processes in the cell. These structures that the cytoplasm contains are called organelles. Unlike a gelatin dessert, however, cytoplasm constantly moves or streams. ...
Cell analogy project
... You will be working in pairs. Use any materials you would like for your 3-D cell. Grades will be based on neatness, creativity, appropriate analogies, and your labels. You must include these structures in your cell: Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smo ...
... You will be working in pairs. Use any materials you would like for your 3-D cell. Grades will be based on neatness, creativity, appropriate analogies, and your labels. You must include these structures in your cell: Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smo ...
UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic environment. In your sketches, use an arrow to show which way water will move (into the cell, out of the cell, or both in/out equally). ...
... hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic environment. In your sketches, use an arrow to show which way water will move (into the cell, out of the cell, or both in/out equally). ...
Design Challenge - cell model
... You will be responsible for designing and building a three-dimensional model of a cell that features of all the organelles a cell needs in order to function properly. This will require you to research organelles on top of the ones presented in class. You may choose to design a plant or animal cell; ...
... You will be responsible for designing and building a three-dimensional model of a cell that features of all the organelles a cell needs in order to function properly. This will require you to research organelles on top of the ones presented in class. You may choose to design a plant or animal cell; ...
Cell Review Worksheet Cell Theory
... b. Which organelle creates the energy required by cells? ____________________________________________ c. Which organelles create proteins? ____________________________________________________________ d. Which organelles processes and transports proteins? ____________________________________________ ...
... b. Which organelle creates the energy required by cells? ____________________________________________ c. Which organelles create proteins? ____________________________________________________________ d. Which organelles processes and transports proteins? ____________________________________________ ...
Cell City / Inspiration Lab
... bodies and all living cells must remove wastes as well. Supermarkets and restaurants provide food. Our bodies need food and so do all cells. Cells, or bodies, or cities can’t thrive unless they can perform all the functions needed to sustain life. ...
... bodies and all living cells must remove wastes as well. Supermarkets and restaurants provide food. Our bodies need food and so do all cells. Cells, or bodies, or cities can’t thrive unless they can perform all the functions needed to sustain life. ...
Cells and Organelles
... Mitochondria provide the energy a cell needs to move, divide and produce. Here I’ll give you a better explanation. You could call them the power plant of the cell. It helps the Cell get energy, it’s what allows the cell to do all types of activities. The size of a Mitochondria is similar to a bacter ...
... Mitochondria provide the energy a cell needs to move, divide and produce. Here I’ll give you a better explanation. You could call them the power plant of the cell. It helps the Cell get energy, it’s what allows the cell to do all types of activities. The size of a Mitochondria is similar to a bacter ...
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... 1. All organisms are made of cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. THIS IS IMPORTANT BECAUSE IT SHOWS THAT ALL LIVING THINGS SHARE A SIMILAR STRUCTURE ...
... 1. All organisms are made of cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. THIS IS IMPORTANT BECAUSE IT SHOWS THAT ALL LIVING THINGS SHARE A SIMILAR STRUCTURE ...
Cell Organelle Quiz
... 2. Smaller parts of the cell that have special functions to maintain all life processes of the cell. 3. One process for moving substances across the cell membrane, depending on the concentration of the substances on both sides of the membrane. 4. The amount of dissolved particles, called solutes, in ...
... 2. Smaller parts of the cell that have special functions to maintain all life processes of the cell. 3. One process for moving substances across the cell membrane, depending on the concentration of the substances on both sides of the membrane. 4. The amount of dissolved particles, called solutes, in ...
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death (or PCD) is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death, but necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Recently a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternate form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations.