Exam 4 Review Questions
... 61. Generally speaking, members of which class(es) of flatworms are not parasites? a) Turbellaria b) Trematoda c) Cestoda d) Monongena e) both a & b 63. Which of the following statements about tapeworm feeding is correct? a) they have complete digestive tracts b) they ingest food with their mouths c ...
... 61. Generally speaking, members of which class(es) of flatworms are not parasites? a) Turbellaria b) Trematoda c) Cestoda d) Monongena e) both a & b 63. Which of the following statements about tapeworm feeding is correct? a) they have complete digestive tracts b) they ingest food with their mouths c ...
articulators
... • Vowels have to form the vocal tract into a tube with one ([],[a, ]) or two (most other vowels) main cavities. For this the tongue dorsum (which comprises the mass of the tongue) is moved up and down, backwards & forwards, • Consonants have to form an obstruction to the airflow. For this any cons ...
... • Vowels have to form the vocal tract into a tube with one ([],[a, ]) or two (most other vowels) main cavities. For this the tongue dorsum (which comprises the mass of the tongue) is moved up and down, backwards & forwards, • Consonants have to form an obstruction to the airflow. For this any cons ...
flatworms, roundworms and segmented worms
... parasitic (dependent on a host organism for survival) and free-living forms of this group. Flatworms, either parasitic or free-living forms, have both sexes on the same individual, a condition referred to as hermaphroditic. Another term that describes this condition is monoecious. Some parasitic spe ...
... parasitic (dependent on a host organism for survival) and free-living forms of this group. Flatworms, either parasitic or free-living forms, have both sexes on the same individual, a condition referred to as hermaphroditic. Another term that describes this condition is monoecious. Some parasitic spe ...
THE PHARYNX Internal Aspect
... In the posterior part of the roof and the upper part of the posterior wall of the nasal part of the pharynx is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the pharyngeal tonsil. This may be prominent in children but becomes indistinct or disappears by adulthood. In children there is a similar accumulati ...
... In the posterior part of the roof and the upper part of the posterior wall of the nasal part of the pharynx is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the pharyngeal tonsil. This may be prominent in children but becomes indistinct or disappears by adulthood. In children there is a similar accumulati ...
TSM33 - Neck and Pharynx
... o Middle constrictor – from the hyoid bone o Inferior constrictor – from the thyroid cartilage These muscles are effectively suspended from the base of the skull at the pharyngeal tubercle o They are all continuous posteriorly and meet along the pharyngeal raphe o They are all innervated by branches ...
... o Middle constrictor – from the hyoid bone o Inferior constrictor – from the thyroid cartilage These muscles are effectively suspended from the base of the skull at the pharyngeal tubercle o They are all continuous posteriorly and meet along the pharyngeal raphe o They are all innervated by branches ...
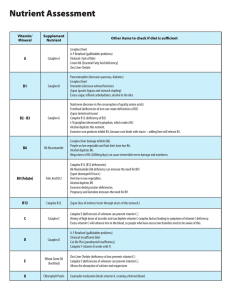
hat is Ideal Protein - Herndon-reston
... Cataplex B (potassium together with B1 deficiencies effect the heart function) Renafood (kidney disease can cause the potassium to become excessive in the body- kidney dialysis patients need to make sure they do not consume excessive potassium). Diuretics deplete potassium. Diarrhea, long term laxat ...
... Cataplex B (potassium together with B1 deficiencies effect the heart function) Renafood (kidney disease can cause the potassium to become excessive in the body- kidney dialysis patients need to make sure they do not consume excessive potassium). Diuretics deplete potassium. Diarrhea, long term laxat ...
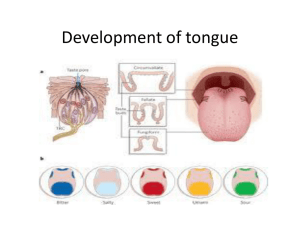
Development of tongue
... Foramen cecum is found just behind the tuberculum impare.is related to the development of the thyroid gland .posterior to it ,the hypo brachial eminence is found ,which has two part a. Cranial part which give rise to posterior of the tongue b. caudal part .give rise to the epiglottis ...
... Foramen cecum is found just behind the tuberculum impare.is related to the development of the thyroid gland .posterior to it ,the hypo brachial eminence is found ,which has two part a. Cranial part which give rise to posterior of the tongue b. caudal part .give rise to the epiglottis ...
- Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute
... beak is inserted within the ‘lower’ (ventral) beak to tear tissue of the prey with a scissors-like cutting action. The gut has spontaneous peristaltic activity. The chopped food passes from the buccal cavity through the oesophagus to the stomach, where most of the digestion takes place. The digestiv ...
... beak is inserted within the ‘lower’ (ventral) beak to tear tissue of the prey with a scissors-like cutting action. The gut has spontaneous peristaltic activity. The chopped food passes from the buccal cavity through the oesophagus to the stomach, where most of the digestion takes place. The digestiv ...
Skeletal System
... The funnel shaped pharynx (throat) connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx and esophagus inferiorly It serves as a common pathway for food and air The pharynx extends for about 5 inches from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebrae Its three regions are nasopharyn ...
... The funnel shaped pharynx (throat) connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx and esophagus inferiorly It serves as a common pathway for food and air The pharynx extends for about 5 inches from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebrae Its three regions are nasopharyn ...
Chapter 6 Stool tests
... • macrophage:normal: 0, (+): colitis , bacterial dysentery • tumor cell: colon carcinoma, rectum carcinoma ...
... • macrophage:normal: 0, (+): colitis , bacterial dysentery • tumor cell: colon carcinoma, rectum carcinoma ...
Medical Nutrition Therapy of Gastrointestinal Disorder
... – Conflicting studies: protective or harmful effects of -3 & -6 FAs. – -3: antiinflammatory properties, protective against mucosal injury by drugs and H. pylori. – Ideal dose or form of lipids in the diet has not been established. • Malnutrition: – Micronutrient deficiencies or protein-calorie ma ...
... – Conflicting studies: protective or harmful effects of -3 & -6 FAs. – -3: antiinflammatory properties, protective against mucosal injury by drugs and H. pylori. – Ideal dose or form of lipids in the diet has not been established. • Malnutrition: – Micronutrient deficiencies or protein-calorie ma ...
pharyngitis: to treat or not to treat
... The Nose esophagus The of Mouth In front upper 6 The vertebra larynx Cervical ...
... The Nose esophagus The of Mouth In front upper 6 The vertebra larynx Cervical ...
- Surgery (Journal)
... colon relatively longer. The normal haustra and appendices epiploicae are not present, giving it a very smooth outline. The haustra appear over the first 6 months. ...
... colon relatively longer. The normal haustra and appendices epiploicae are not present, giving it a very smooth outline. The haustra appear over the first 6 months. ...
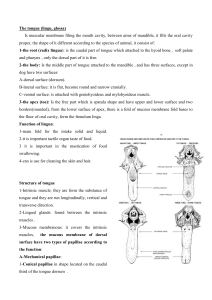
The tongue (lingu, glossa)
... 5- The tunica mucosa of the tongue of ox is often pigmented and may be spotted. 6- In ox the apical half of the dorsum , rostral to the torus , is covered by filiform papillae directed caudally , these are cornified and sharp , especially on the apex, and impart the roughness which makes the bovine ...
... 5- The tunica mucosa of the tongue of ox is often pigmented and may be spotted. 6- In ox the apical half of the dorsum , rostral to the torus , is covered by filiform papillae directed caudally , these are cornified and sharp , especially on the apex, and impart the roughness which makes the bovine ...
The Thoracic Cavity
... bodies (at level of T12) – runs superiorly – empties into Sup. Vena Cava – drains right posterior intercostal veins – Connects to hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos that drain left side ...
... bodies (at level of T12) – runs superiorly – empties into Sup. Vena Cava – drains right posterior intercostal veins – Connects to hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos that drain left side ...
Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC MEDICAL
... MBSImP Overall Impression: Lip closure for intraoral bolus containment resulted in no labial escape. Tongue control during bolus hold allowed bolus escape to the lateral buccal cavity/floor of mouth. Bolus preparation and mastication demonstrated disorganized chewing/mashing with solid pieces of the ...
... MBSImP Overall Impression: Lip closure for intraoral bolus containment resulted in no labial escape. Tongue control during bolus hold allowed bolus escape to the lateral buccal cavity/floor of mouth. Bolus preparation and mastication demonstrated disorganized chewing/mashing with solid pieces of the ...
Gi Embryology 3
... expansion of the abdominal cavity play important roles. • The proximal portion of the jejunum, the first part to reenter the abdominal cavity, comes to lie on the left side • The later returning loops gradually settle more and more to the right. ...
... expansion of the abdominal cavity play important roles. • The proximal portion of the jejunum, the first part to reenter the abdominal cavity, comes to lie on the left side • The later returning loops gradually settle more and more to the right. ...
19. oral cavity by girls antomy teame2010-10
... mouth below tongue, contains : 1-The frenulum of the tongue is a fold of mucous membrane in the midline connects undersurface of tongue to floor of mouth. 2-Duct of submandibular gland opens on each side of frenulum. 3Sublingual gland is covered by m.m called sublingual fold, which extends laterally ...
... mouth below tongue, contains : 1-The frenulum of the tongue is a fold of mucous membrane in the midline connects undersurface of tongue to floor of mouth. 2-Duct of submandibular gland opens on each side of frenulum. 3Sublingual gland is covered by m.m called sublingual fold, which extends laterally ...
lecture 15
... Pharyngeal Cavity • Pharynx (3 regions) – 12 cm in length – Extends from the vocal folds blow to the region behind the nasal cavities, above – Tube is lined with muscle capable of constricting to facilitate deglutition (also closes velopharyngeal port) • Velopharyngeal port- Opening between the oro ...
... Pharyngeal Cavity • Pharynx (3 regions) – 12 cm in length – Extends from the vocal folds blow to the region behind the nasal cavities, above – Tube is lined with muscle capable of constricting to facilitate deglutition (also closes velopharyngeal port) • Velopharyngeal port- Opening between the oro ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.