Sample Exam Solution
... Solution: The residual flux in the magnetic material in the poles and rotor core will produce a l voltage on the armature windings when the machine is turning at rated speed (Ea = Kφω ). The small voltage will drive a small current through the field winding, which will increase E a, whic turn increa ...
... Solution: The residual flux in the magnetic material in the poles and rotor core will produce a l voltage on the armature windings when the machine is turning at rated speed (Ea = Kφω ). The small voltage will drive a small current through the field winding, which will increase E a, whic turn increa ...
EEE EE1403 - KLN College of Engineering
... (A)Find the values of main dimensions of the machine if the ratio of length to diameter is 0.2.Also calculate the value of main dimensions if (B) specific electric loadings are decreased by 10 % each with speed remaining the same;(C) speed is decreased to 150 rpm with specific loading remaining the ...
... (A)Find the values of main dimensions of the machine if the ratio of length to diameter is 0.2.Also calculate the value of main dimensions if (B) specific electric loadings are decreased by 10 % each with speed remaining the same;(C) speed is decreased to 150 rpm with specific loading remaining the ...
ir`H`/WE
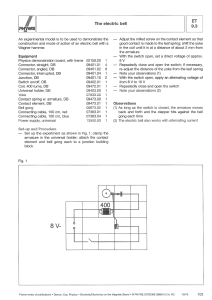
... Although the permanent load on the coil used is rated at maximally 1 A, the recommended voltage is not critical, because the current is repeatedly interrupted. Despite this, the bell should not be rung for longer than necessary, so that the area of contact of the contact screw with the leaf spring ( ...
... Although the permanent load on the coil used is rated at maximally 1 A, the recommended voltage is not critical, because the current is repeatedly interrupted. Despite this, the bell should not be rung for longer than necessary, so that the area of contact of the contact screw with the leaf spring ( ...
How real electric motors work
... which are now: S-N-S-N. The rotor is an electrical conductor, and therefore tries to follow this field. To do so it has to rotate through 90 degrees. The rotor thus takes two full cycles of the mains (40 ms) to make a complete rotation, and so revolves at 1500 rpm. At least, it would if it could kee ...
... which are now: S-N-S-N. The rotor is an electrical conductor, and therefore tries to follow this field. To do so it has to rotate through 90 degrees. The rotor thus takes two full cycles of the mains (40 ms) to make a complete rotation, and so revolves at 1500 rpm. At least, it would if it could kee ...
Multiphase Brushless DC Motor
... There are two types of stator windings: trapezoidal and sinusoidal, which refers to the shape of the back electromotive force (BEMF) signal. ...
... There are two types of stator windings: trapezoidal and sinusoidal, which refers to the shape of the back electromotive force (BEMF) signal. ...
Structures of the Energy flow system
... 2 A gear box may not be the best solution, and any alternative drive has not been investigated yet. ...
... 2 A gear box may not be the best solution, and any alternative drive has not been investigated yet. ...
Lecture_Induction Motors
... Induction motor speed So, the IM will always run at a speed lower than the synchronous speed The difference between the motor speed and the synchronous speed is called the Slip ...
... Induction motor speed So, the IM will always run at a speed lower than the synchronous speed The difference between the motor speed and the synchronous speed is called the Slip ...
Starters (Level 2) File - Totton College
... Momentum of the coil causes the coil to continue rotating. ...
... Momentum of the coil causes the coil to continue rotating. ...
electrical machines two marks
... The core is constructed by sheet steel laminations assembled to provide a continuous magnetic path with minimum of air gap included. The steel used is of high silicon content sometimes heat treated to produce a high permeability and a low hysteresis loss at the usual operating flux densities. The ed ...
... The core is constructed by sheet steel laminations assembled to provide a continuous magnetic path with minimum of air gap included. The steel used is of high silicon content sometimes heat treated to produce a high permeability and a low hysteresis loss at the usual operating flux densities. The ed ...
Lecture 16
... As the current increases, the magnetic flux through a loop due to this current also increases The increasing flux induces an emf that opposes the change in magnetic flux As the magnitude of the current increases, the rate of increase lessens and the induced emf ...
... As the current increases, the magnetic flux through a loop due to this current also increases The increasing flux induces an emf that opposes the change in magnetic flux As the magnitude of the current increases, the rate of increase lessens and the induced emf ...
5.0 Starter Motors
... When the armature rotates a half a revolution ‘A’ is positioned at the south pole “S” and ‘B’ positioned at the north pole “N”. As the magnetic field surrounding ‘A’ is in the anti-clockwise direction the magnetic field would be stronger under ‘A’ and above ‘B’, which would mean that the armature wo ...
... When the armature rotates a half a revolution ‘A’ is positioned at the south pole “S” and ‘B’ positioned at the north pole “N”. As the magnetic field surrounding ‘A’ is in the anti-clockwise direction the magnetic field would be stronger under ‘A’ and above ‘B’, which would mean that the armature wo ...
Commutator (electric)

A commutator is the moving part of a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors and electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. It consists of a cylinder composed of multiple metal contact segments on the rotating armature of the machine. The commutator is one component of a motor; there are also two or more stationary electrical contacts called ""brushes"" made of a soft conductor like carbon press against the commutator, making sliding contact with successive segments of the commutator as it rotates. The windings (coils of wire) on the armature are connected to the commutator segments. Commutators are used in direct current (DC) machines: dynamos (DC generators) and many DC motors as well as universal motors. In a motor the commutator applies electric current to the windings. By reversing the current direction in the rotating windings each half turn, a steady rotating force (torque) is produced. In a generator the commutator picks off the current generated in the windings, reversing the direction of the current with each half turn, serving as a mechanical rectifier to convert the alternating current from the windings to unidirectional direct current in the external load circuit. The first direct current commutator-type machine, the dynamo, was built by Hippolyte Pixii in 1832, based on a suggestion by André-Marie Ampère. Commutators are relatively inefficient, and also require periodic maintenance such as brush replacement. Therefore, commutated machines are declining in use, being replaced by alternating current (AC) machines, and in recent years by brushless DC motors which use semiconductor switches.