Analysis of CAG and CCG repeats in Huntingtin gene
... and 31. Altogether 16 alleles were found in the normal individuals, of which the 16 repeat allele was the most frequent in every population. The overall observed heterozygosity was 0.7; the variation across populations was 0.54 in the Tripuri (TR1) to 0.78 in the Bengali Brahmin (BR2). CAG repeat di ...
... and 31. Altogether 16 alleles were found in the normal individuals, of which the 16 repeat allele was the most frequent in every population. The overall observed heterozygosity was 0.7; the variation across populations was 0.54 in the Tripuri (TR1) to 0.78 in the Bengali Brahmin (BR2). CAG repeat di ...
Complete genome sequence of the thermophilic Thermus sp
... isomerases), pulp and paper manufacturing (e.g. xylanases) as well as animal feed and human food production (amino acid and vitamin synthesis) [13, 14]. Here, we present a summary of classification and a set of features for Thermus sp. CCB_US3_UF1, together with the description of the complete genom ...
... isomerases), pulp and paper manufacturing (e.g. xylanases) as well as animal feed and human food production (amino acid and vitamin synthesis) [13, 14]. Here, we present a summary of classification and a set of features for Thermus sp. CCB_US3_UF1, together with the description of the complete genom ...
8 VARIATION IN CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE AND NUMBER
... 8.2, these mutations are categorized as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. Deletions and duplications are changes in the total amount of genetic material within a single chromosome. In Figure 8.2, human chromosomes are labeled according to their normal G-banding patterns. When ...
... 8.2, these mutations are categorized as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. Deletions and duplications are changes in the total amount of genetic material within a single chromosome. In Figure 8.2, human chromosomes are labeled according to their normal G-banding patterns. When ...
Understanding the Scurred condition in Polled Cattle
... Understanding the Scurred condition in Polled Cattle Most calves that are horned can be identified at birth or shortly after, and almost always by weaning time. Distinguishing between smooth-polled and scurred-polled is more difficult. Scurs, a rudimentary horn growth, are often not seen until cattl ...
... Understanding the Scurred condition in Polled Cattle Most calves that are horned can be identified at birth or shortly after, and almost always by weaning time. Distinguishing between smooth-polled and scurred-polled is more difficult. Scurs, a rudimentary horn growth, are often not seen until cattl ...
ABSTRACT Using a bioinformatics approach to identify genes that
... categorizations. While public users can enter a gene set into GeneWeaver, most gene sets are derived directly from experimentation (GWAS, Microarray, etc.) or publications. For example, PubMed, a database for scientific literature, can be used to find articles that describe gene sets, and these gene ...
... categorizations. While public users can enter a gene set into GeneWeaver, most gene sets are derived directly from experimentation (GWAS, Microarray, etc.) or publications. For example, PubMed, a database for scientific literature, can be used to find articles that describe gene sets, and these gene ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... – Epistasis (G X G effects between loci) – Environment (G X E effects) ...
... – Epistasis (G X G effects between loci) – Environment (G X E effects) ...
Quantitative trait loci affecting amylose, amylopectin and starch
... strongly affected by mutations. Amylose-free kernels are produced by the waxy mutation. Conversely, the amylose extender mutation leads to a higher amylose proportion than in the wild type. Sugary mutation results in a large starch deficiency and a large increase in water soluble fraction. Progress ...
... strongly affected by mutations. Amylose-free kernels are produced by the waxy mutation. Conversely, the amylose extender mutation leads to a higher amylose proportion than in the wild type. Sugary mutation results in a large starch deficiency and a large increase in water soluble fraction. Progress ...
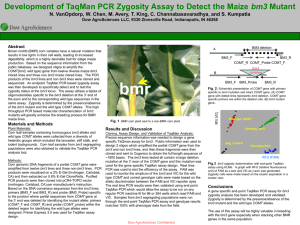
document
... used to monitor the amplicon of the bm3 and VIC for the wild type COMT and correct genotype calls were made based on the allelic discrimination between the FAM and VIC reporter dyes. The real time PCR results were then validated using end-point TaqMan PCR which would allow the assay to be run on any ...
... used to monitor the amplicon of the bm3 and VIC for the wild type COMT and correct genotype calls were made based on the allelic discrimination between the FAM and VIC reporter dyes. The real time PCR results were then validated using end-point TaqMan PCR which would allow the assay to be run on any ...
Idic(15)
... instead of the usual 46. The extra piece of chromosome 15 has been duplicated end-toend like a mirror image (see diagram) and is referred to as isodicentric 15 [idic(15)], inverted duplication 15 (inv dup 15), tetrasomy 15q or supernumerary marker 15 [SMC (15)]. Occasionally, a person may have two e ...
... instead of the usual 46. The extra piece of chromosome 15 has been duplicated end-toend like a mirror image (see diagram) and is referred to as isodicentric 15 [idic(15)], inverted duplication 15 (inv dup 15), tetrasomy 15q or supernumerary marker 15 [SMC (15)]. Occasionally, a person may have two e ...
Centromere Locations and Associated Chromosome
... We analyzed linkage and chromosomal positions of genes in A. lyrata ssp. petraea that are located near the centromere (CEN) regions of A. thaliana, using at least two genes from the short and long arms of each chromosome. In our map, genes from all 10 A. thaliana chromosome arms are also tightly lin ...
... We analyzed linkage and chromosomal positions of genes in A. lyrata ssp. petraea that are located near the centromere (CEN) regions of A. thaliana, using at least two genes from the short and long arms of each chromosome. In our map, genes from all 10 A. thaliana chromosome arms are also tightly lin ...
chicken.db - Bioconductor
... indicates the chromosome. Due to inconsistencies that may exist at the time the object was built, these vectors may contain more than one chromosome and/or location. If the chromosomal location is unknown, the vector will contain an NA. Chromosomal locations on both the sense and antisense strands a ...
... indicates the chromosome. Due to inconsistencies that may exist at the time the object was built, these vectors may contain more than one chromosome and/or location. If the chromosomal location is unknown, the vector will contain an NA. Chromosomal locations on both the sense and antisense strands a ...
Phylogenetic Relationships between the Western Aster Yellows
... mismatches, and gaps in the compared sequences. Distance matrix (9, 36, 54) and maximum parsimony (25, 36, 54) analyses have been used to generate phylogenetic trees from aligned 16s rRNA sequences. The plant-pathogenic mycoplasmalike organisms (MLOs) have not yet been cultured in vitro or isolated ...
... mismatches, and gaps in the compared sequences. Distance matrix (9, 36, 54) and maximum parsimony (25, 36, 54) analyses have been used to generate phylogenetic trees from aligned 16s rRNA sequences. The plant-pathogenic mycoplasmalike organisms (MLOs) have not yet been cultured in vitro or isolated ...
Introduction to GO Annotation
... GO Annotation: Strategies for Identifying Literature for Curation 1. Primary research literature with new experimental data - Mutant phenotypes – process - Activity assays – function - Localization studies – component 2. Computational analyses - Phylogenetic analysis – function (ISS) - Domain analy ...
... GO Annotation: Strategies for Identifying Literature for Curation 1. Primary research literature with new experimental data - Mutant phenotypes – process - Activity assays – function - Localization studies – component 2. Computational analyses - Phylogenetic analysis – function (ISS) - Domain analy ...
Identity-by-descent filtering of exome sequence data for disease
... cited above, it is not always applicable. Many of the thousands of Mendelian disorders listed in OMIM, whose genetic basis is unknown, are often only clinically well characterized in members of a single family. Obviously, a filtering approach that focuses on genes that are affected by variants in wh ...
... cited above, it is not always applicable. Many of the thousands of Mendelian disorders listed in OMIM, whose genetic basis is unknown, are often only clinically well characterized in members of a single family. Obviously, a filtering approach that focuses on genes that are affected by variants in wh ...
Table of Contents - Scholars` Bank
... combinations that can come from four different types of nucleotides. Crick had proposed that the interaction between the trinucleotide codon and the corresponding “adaptor” must be dictated by specific patterns of hydrogen bonds. This special type of chemical bond occurs between strands of nucleotid ...
... combinations that can come from four different types of nucleotides. Crick had proposed that the interaction between the trinucleotide codon and the corresponding “adaptor” must be dictated by specific patterns of hydrogen bonds. This special type of chemical bond occurs between strands of nucleotid ...
Quantitative analysis of SMN1 and SMN2 genes based on DHPLC
... centromeric SMN (SMN2; MIM# 601627), have been identified. These two SMN genes are highly homologous and differ in only two nucleotides in the coding region. These nucleotide differences, located in exons 7 and 8, allow the SMN1 gene to be distinguished from the SMN2 gene [Lefebvre et al., 1995]. It ...
... centromeric SMN (SMN2; MIM# 601627), have been identified. These two SMN genes are highly homologous and differ in only two nucleotides in the coding region. These nucleotide differences, located in exons 7 and 8, allow the SMN1 gene to be distinguished from the SMN2 gene [Lefebvre et al., 1995]. It ...
Robust gene silencing mediated by antisense small RNAs in the
... knockdown efficiency varies, (ii) not all genes appear to be amenable to silencing, (iii) the small hairpin RNA (shRNA) approach is labor intensive and (iv) reversal of gene silencing mediated by both double stranded RNA and shRNA has been reported (24) [W. A. Petri Jr. (personal communication)]. Add ...
... knockdown efficiency varies, (ii) not all genes appear to be amenable to silencing, (iii) the small hairpin RNA (shRNA) approach is labor intensive and (iv) reversal of gene silencing mediated by both double stranded RNA and shRNA has been reported (24) [W. A. Petri Jr. (personal communication)]. Add ...
Comparative gene mapping in Arabidopsis lyrata chromosomes 6
... regions of A. thaliana chromosomes IV and V, we localize the AL6 centromere, and can localize the breakpoints of these chromosome rearrangements more precisely than previously. One translocation breakpoint was close to the centromere, and the other coincided with one end of the inversion, suggesting ...
... regions of A. thaliana chromosomes IV and V, we localize the AL6 centromere, and can localize the breakpoints of these chromosome rearrangements more precisely than previously. One translocation breakpoint was close to the centromere, and the other coincided with one end of the inversion, suggesting ...
An Introduction to Streptomyces
... In the early steps of microbiology, many organisms now belonging to the class of Actinobacteria, such as Mycobacterium leprae were considered as species somewhere between fungi and bacteria (Hopwood, 1999). In the light of new discoveries such as the: composition of the Actinobacteria cell wall (lik ...
... In the early steps of microbiology, many organisms now belonging to the class of Actinobacteria, such as Mycobacterium leprae were considered as species somewhere between fungi and bacteria (Hopwood, 1999). In the light of new discoveries such as the: composition of the Actinobacteria cell wall (lik ...
Cytogenetics with special reference to domestic animals
... Sheep: (Differences between species often involve Roberstonian fusions) ...
... Sheep: (Differences between species often involve Roberstonian fusions) ...
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Regulation of Gene Expression in
... parental alleles and provides an opportunity to examine variation in transcript abundance within the RILs and the relationship between the population and the parents. We first focused on the expression levels of 22,242 genes that were detected in both parents and at least 90% of the IBM RILs. The me ...
... parental alleles and provides an opportunity to examine variation in transcript abundance within the RILs and the relationship between the population and the parents. We first focused on the expression levels of 22,242 genes that were detected in both parents and at least 90% of the IBM RILs. The me ...
Part 4 - URMC - University of Rochester
... Narrator: Jenny, Jeremy, and their father have decided to undergo genetic testing for Huntington’s disease. Today, our lab groups will act as gene testing laboratory technicians. We will use the gel electrophoresis laboratory procedure to analyze the results of the simulated DNA samples from Jenny, ...
... Narrator: Jenny, Jeremy, and their father have decided to undergo genetic testing for Huntington’s disease. Today, our lab groups will act as gene testing laboratory technicians. We will use the gel electrophoresis laboratory procedure to analyze the results of the simulated DNA samples from Jenny, ...
Family Secrets Part 4 - University of Rochester Medical Center
... Narrator: Jenny, Jeremy, and their father have decided to undergo genetic testing for Huntington’s disease. Today, our lab groups will act as gene testing laboratory technicians. We will use the gel electrophoresis laboratory procedure to analyze the results of the simulated DNA samples from Jenny, ...
... Narrator: Jenny, Jeremy, and their father have decided to undergo genetic testing for Huntington’s disease. Today, our lab groups will act as gene testing laboratory technicians. We will use the gel electrophoresis laboratory procedure to analyze the results of the simulated DNA samples from Jenny, ...
Copy-number variation

Copy-number variations (CNVs)—a form of structural variation—are alterations of the DNA of a genome that results in the cell having an abnormal or, for certain genes, a normal variation in the number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA. CNVs correspond to relatively large regions of the genome that have been deleted (fewer than the normal number) or duplicated (more than the normal number) on certain chromosomes. For example, the chromosome that normally has sections in order as A-B-C-D might instead have sections A-B-C-C-D (a duplication of ""C"") or A-B-D (a deletion of ""C"").This variation accounts for roughly 13% of human genomic DNA and each variation may range from about one kilobase (1,000 nucleotide bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which affect only one single nucleotide base.