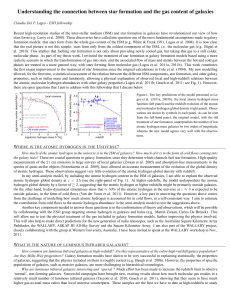
Galaxies – Island universes
... • If a small galaxy has a central collision with a larger spiral galaxy, the gravitational pulse can compress gas/dust and make a star formation burst in a ring. • Collision energy added to the central bulge can stretch it out into a very non-spherica ...
... • If a small galaxy has a central collision with a larger spiral galaxy, the gravitational pulse can compress gas/dust and make a star formation burst in a ring. • Collision energy added to the central bulge can stretch it out into a very non-spherica ...
Galaxies
... light years • Much of this gas and dust can be observed in the form of nebulae • A nebula is a cloud of gas seen in visible light • How the gas is seen depends on the stars around it ...
... light years • Much of this gas and dust can be observed in the form of nebulae • A nebula is a cloud of gas seen in visible light • How the gas is seen depends on the stars around it ...
PPT - ICRA
... 2) ``Melting’’ phase transition: the nucleon matter core, nuclei matter surroundings. 3) Super-critical electric field on the surface of collapsing core. 4) Electron-positron-photon plasma (dyadosphere) formed in gravitational collapses. 5) Hydrodynamic expansion of Electron-positron-photon plasma. ...
... 2) ``Melting’’ phase transition: the nucleon matter core, nuclei matter surroundings. 3) Super-critical electric field on the surface of collapsing core. 4) Electron-positron-photon plasma (dyadosphere) formed in gravitational collapses. 5) Hydrodynamic expansion of Electron-positron-photon plasma. ...
stars & galaxies
... The milKy Way… our home iN The sTars… • The Milky Way has a diameter of about 100,000 light years. • The nucleus is 2000 light years thick. • Our sun is located 30,000 light years from the nucleus. • It takes the sun 200 million years to ...
... The milKy Way… our home iN The sTars… • The Milky Way has a diameter of about 100,000 light years. • The nucleus is 2000 light years thick. • Our sun is located 30,000 light years from the nucleus. • It takes the sun 200 million years to ...
Our Galaxy -- The Milky Way PowerPoint
... – Gravitational bending of light has been observed • Tentatively, MACHOs account for < 40% of dark matter ...
... – Gravitational bending of light has been observed • Tentatively, MACHOs account for < 40% of dark matter ...
Cosmology - RHIG - Wayne State University
... • Connected with the quark masses • When confined quarks have a large dynamical mass constituent mass • In the small coupling limit (some) quarks have small mass current mass ...
... • Connected with the quark masses • When confined quarks have a large dynamical mass constituent mass • In the small coupling limit (some) quarks have small mass current mass ...
The Main Features of the X
... Thermal bremsstrahlung or free-free emission occurs when an e- is accelerated due to the strong electrical attraction of a positive ion in a plasma. Temperatures above 105 K are ...
... Thermal bremsstrahlung or free-free emission occurs when an e- is accelerated due to the strong electrical attraction of a positive ion in a plasma. Temperatures above 105 K are ...
Research proposal uploaded for ESO fellowship
... global star formation rate decline of the universe? Supernova feedback represents a long standing problem in galaxy formation model. Currently, toy models are used to treat supernova feedback, which are parametrized to reproduce the faint-end of the luminosity function (Cole et al. 2000; Guo et al. ...
... global star formation rate decline of the universe? Supernova feedback represents a long standing problem in galaxy formation model. Currently, toy models are used to treat supernova feedback, which are parametrized to reproduce the faint-end of the luminosity function (Cole et al. 2000; Guo et al. ...
What Do We Really Know About the Universe?
... • In a laboratory, we see an emission spectrum of bright lines against a dark background. • However, the interior of a star is so hot that the electrons are knocked completely away from the atoms. (This is called a plasma.) The star’s light is NOT from electrons jumping between specific energy level ...
... • In a laboratory, we see an emission spectrum of bright lines against a dark background. • However, the interior of a star is so hot that the electrons are knocked completely away from the atoms. (This is called a plasma.) The star’s light is NOT from electrons jumping between specific energy level ...
PH607lec12
... 6.3 Galaxy Evolution When did galaxies form? 1. Big Bang, inflation, ……expansion and cooling ……. Protons and electrons form neutral atoms: recombination epoch, the temperature was around 3000 K, the Universe was approximately 379,000 years old. Photon decoupling: relic radiation The Cosmic Microwave ...
... 6.3 Galaxy Evolution When did galaxies form? 1. Big Bang, inflation, ……expansion and cooling ……. Protons and electrons form neutral atoms: recombination epoch, the temperature was around 3000 K, the Universe was approximately 379,000 years old. Photon decoupling: relic radiation The Cosmic Microwave ...
Spiral Galaxies - Astronomy Centre
... Nature of the Nebulae • We now know that Kant was correct • Our Milky Way Galaxy is just one of Kant’s island universes, which are now referred to as galaxies • The word Universe now refers to the full expanse of space and its contents • While most diffuse nebulae are nearby clouds of gas and dust ...
... Nature of the Nebulae • We now know that Kant was correct • Our Milky Way Galaxy is just one of Kant’s island universes, which are now referred to as galaxies • The word Universe now refers to the full expanse of space and its contents • While most diffuse nebulae are nearby clouds of gas and dust ...
How Big is the Universe
... Andromeda. One particular type of star allowed him to calculate its distance. He showed that the Andromeda Nebula was far outside our Milky Way Galaxy. Hubble realized that many of the objects that astronomers called nebulae were not actually clouds of gas. They were what we now call galaxies – a co ...
... Andromeda. One particular type of star allowed him to calculate its distance. He showed that the Andromeda Nebula was far outside our Milky Way Galaxy. Hubble realized that many of the objects that astronomers called nebulae were not actually clouds of gas. They were what we now call galaxies – a co ...
Galaxies Powerpoint
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Main Types of Galaxies
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Assignment 10
... b. long jets of radio emissions c. two lobes (regions of radio emission) that can be quite far from the galaxy's center d. all of the above e. none of the above ____ 24. A friend of yours who is a science fiction fan hears you talk about the fact that astronomers now believe that the mechanism for ...
... b. long jets of radio emissions c. two lobes (regions of radio emission) that can be quite far from the galaxy's center d. all of the above e. none of the above ____ 24. A friend of yours who is a science fiction fan hears you talk about the fact that astronomers now believe that the mechanism for ...
Pistol Star - University of Dayton
... Earth is only one planet orbiting one star among roughly a hundred billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way is only one galaxy of billions in the universe. Looking beyond the solar system into galactic and intergalactic space, we must stretch our minds to nearly unimaginable distances t ...
... Earth is only one planet orbiting one star among roughly a hundred billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way is only one galaxy of billions in the universe. Looking beyond the solar system into galactic and intergalactic space, we must stretch our minds to nearly unimaginable distances t ...
relativistic time correction on movement of distant galaxies
... stars. Suppose there is a Sun like star of about 5 billion years old, then that star was formed at about 13.4+5=18.4 billion years ago. (In fact, present age of this star is to be multiplied by 1+z =1.98. So it is 5x1.98= 9.9 billion light years. But we have just received light from that galaxy and ...
... stars. Suppose there is a Sun like star of about 5 billion years old, then that star was formed at about 13.4+5=18.4 billion years ago. (In fact, present age of this star is to be multiplied by 1+z =1.98. So it is 5x1.98= 9.9 billion light years. But we have just received light from that galaxy and ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... – The farthest that any light could have travelled is 13.7 billion light years. cosmic horizon ...
... – The farthest that any light could have travelled is 13.7 billion light years. cosmic horizon ...
Answers for the HST Scavenger Hunt
... The spherical outer boundary of a black hole. Once matter crosses this threshold, the speed required for it to escape the black hole’s gravitational grip is greater than the speed of light. When scientists used the HST to study Cygnus X-1, they were able to observe two of these events, which defines ...
... The spherical outer boundary of a black hole. Once matter crosses this threshold, the speed required for it to escape the black hole’s gravitational grip is greater than the speed of light. When scientists used the HST to study Cygnus X-1, they were able to observe two of these events, which defines ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 24 Galaxies
... Hot intergalactic gases in rich clusters account for a small part of the unobserved mass. These gases are detected by their X-ray emission. The remaining unobserved mass is probably in the form of dark-matter halos that surround the galaxies in these clusters. Gravitational lensing of remote galaxie ...
... Hot intergalactic gases in rich clusters account for a small part of the unobserved mass. These gases are detected by their X-ray emission. The remaining unobserved mass is probably in the form of dark-matter halos that surround the galaxies in these clusters. Gravitational lensing of remote galaxie ...
The Bible and big bang cosmology
... “The stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, rotate about the galactic center with different speeds, the inner ones rotating faster than the outer ones. The observed rotation speeds are so fast that if our galaxy were more than a few hundred million years old, it would be a featureless disc of stars ...
... “The stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, rotate about the galactic center with different speeds, the inner ones rotating faster than the outer ones. The observed rotation speeds are so fast that if our galaxy were more than a few hundred million years old, it would be a featureless disc of stars ...
(Mike Riddle CTI)-84_eng_cr_v4.0
... “The stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, rotate about the galactic center with different speeds, the inner ones rotating faster than the outer ones. The observed rotation speeds are so fast that if our galaxy were more than a few hundred million years old, it would be a featureless disc of stars ...
... “The stars of our own galaxy, the Milky Way, rotate about the galactic center with different speeds, the inner ones rotating faster than the outer ones. The observed rotation speeds are so fast that if our galaxy were more than a few hundred million years old, it would be a featureless disc of stars ...