Momentum and Impulse (Key)
... 1) Under what circumstances could an object initially at rest be struck and move at a greater speed after collision than the incoming object? 2) A 180-kg bumper car carrying a 70-kg driver has a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s [E]. Calculate the momentum of the car-driver system. [7.5 x 102 kgm/s] ...
... 1) Under what circumstances could an object initially at rest be struck and move at a greater speed after collision than the incoming object? 2) A 180-kg bumper car carrying a 70-kg driver has a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s [E]. Calculate the momentum of the car-driver system. [7.5 x 102 kgm/s] ...
1-5 Conservation of Angular Momentum
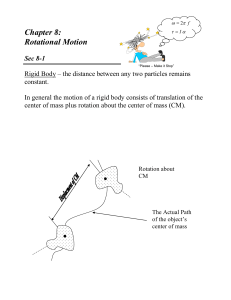
... The rotational inertia of an object with respect to a given rotation axis is a measure of the object's tendency to resist a change in its angular velocity about that axis. The rotational inertia depends on the mass of the object and how that mass is distributed. You have probably noticed that it is ...
... The rotational inertia of an object with respect to a given rotation axis is a measure of the object's tendency to resist a change in its angular velocity about that axis. The rotational inertia depends on the mass of the object and how that mass is distributed. You have probably noticed that it is ...
10.4 Newton`s Third Law of Motion and Momentum
... the ball • The reaction force is on the wrists ...
... the ball • The reaction force is on the wrists ...
Wednesday, Mar. 27, 2002
... angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
... angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics conclusion
... Right-Hand Rule: Grasp the axis of rotation with your right hand, so that your fingers circle the axis in the same sense as the rotation. ...
... Right-Hand Rule: Grasp the axis of rotation with your right hand, so that your fingers circle the axis in the same sense as the rotation. ...
CH 9
... kg and radius R = 0.5 m. The bucket is dropped and the flywheel is allowed to spin. Determine the angular velocity of the flywheel after the bucket has fallen for 5 s. ...
... kg and radius R = 0.5 m. The bucket is dropped and the flywheel is allowed to spin. Determine the angular velocity of the flywheel after the bucket has fallen for 5 s. ...
No Slide Title
... has a diameter of 1 meter. The mass of the wheel is 5 kg (assume all mass is sitting at the outside of the wheel). The friction force from the road is 25 N. If the cycle is accelerating with 0.3 m/s2, what is the force applied on each of the paddles if the paddles are 30 cm from the center of the wh ...
... has a diameter of 1 meter. The mass of the wheel is 5 kg (assume all mass is sitting at the outside of the wheel). The friction force from the road is 25 N. If the cycle is accelerating with 0.3 m/s2, what is the force applied on each of the paddles if the paddles are 30 cm from the center of the wh ...
Slide 1
... velocity (ω) is always perpendicular to the plane of motion (parallel to the axis of rotation). The direction of ω indicates whether the object is moving clockwise or counter-clockwise and is found using the right-hand-rule. We usually measure ω in radians per second and we can calculate instantaneo ...
... velocity (ω) is always perpendicular to the plane of motion (parallel to the axis of rotation). The direction of ω indicates whether the object is moving clockwise or counter-clockwise and is found using the right-hand-rule. We usually measure ω in radians per second and we can calculate instantaneo ...
Rotational Motion 3
... It describes the external influence that causes changes in the state of rotation. But what describes “the state of rotation” itself? For a particle, the state of translational motion is described by the linear momentum, p = mv . The corresponding quantity for rotational motion is the angular momentu ...
... It describes the external influence that causes changes in the state of rotation. But what describes “the state of rotation” itself? For a particle, the state of translational motion is described by the linear momentum, p = mv . The corresponding quantity for rotational motion is the angular momentu ...
Rotational Motion Objectives: After reviewing this section you should
... Remember from our discussion of Newton's Laws that objects with mass have inertia. They tend to maintain their same state of motion. Rotating objects also have inertia. The property of an object to resist changes in its rotational state of motion is called rotational inertia. In simpler terms, a ro ...
... Remember from our discussion of Newton's Laws that objects with mass have inertia. They tend to maintain their same state of motion. Rotating objects also have inertia. The property of an object to resist changes in its rotational state of motion is called rotational inertia. In simpler terms, a ro ...