1 Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field
... potential. If we realise that the derivative is nothing but the limit of the difference of the vector potential between neighboring points and at the same time, we can argue that the magnetic field is the limit of a linear combination of vector potentials at different points. Since the vector poten ...
... potential. If we realise that the derivative is nothing but the limit of the difference of the vector potential between neighboring points and at the same time, we can argue that the magnetic field is the limit of a linear combination of vector potentials at different points. Since the vector poten ...
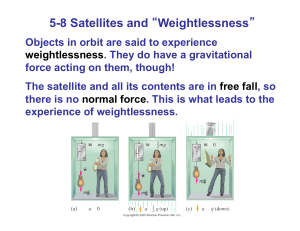
5-8 Satellites and “Weightlessness”
... • Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular position. • Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity. • The angular velocity and acceleration can be related to the linear velocity and acceleration. • The frequency is the number of full revolutions per second; the period ...
... • Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular position. • Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity. • The angular velocity and acceleration can be related to the linear velocity and acceleration. • The frequency is the number of full revolutions per second; the period ...
15. Parallel Axis Theorem and Torque A) Overview B) Parallel Axis
... A point mass costrained to move on a force is equal to the product of the moment of circle of radius r is acted upon by a inertia of the object about the rotation axis and force F. The tangential component of the angular acceleration. this force, Fθ, gives rise to an angular rFθ = Iα acceleration α. ...
... A point mass costrained to move on a force is equal to the product of the moment of circle of radius r is acted upon by a inertia of the object about the rotation axis and force F. The tangential component of the angular acceleration. this force, Fθ, gives rise to an angular rFθ = Iα acceleration α. ...
chap 6 momentum
... Momentum Defined The quantity of motion, momentum, as being directly proportional to the object's mass and velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity……. ……..because it is a scalar (mass) of the vector ...
... Momentum Defined The quantity of motion, momentum, as being directly proportional to the object's mass and velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity……. ……..because it is a scalar (mass) of the vector ...
I = m • Δ v - CUSDPhysics
... Impulse is the reason behind innovative designs in practical life. When we look at Impulse = Force * time, and this is also the change an object experiences, we can see that if we extend the time over which a force is applied, we can change how much momentum we feel. Take some time now and talk wit ...
... Impulse is the reason behind innovative designs in practical life. When we look at Impulse = Force * time, and this is also the change an object experiences, we can see that if we extend the time over which a force is applied, we can change how much momentum we feel. Take some time now and talk wit ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
... Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
... Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
Slides for Chapters 9, 10, 11 and Review
... Example 9.5. You are designing an airplane propeller that is to turn at 2400 rpm (or revolutions per minute). The forward airspeed of the plane is to be 75.0 m/s, and the speed of the tips of the propeller blades through the air must not exceed 270 m/s. (This is about 80% of the speed of the sound i ...
... Example 9.5. You are designing an airplane propeller that is to turn at 2400 rpm (or revolutions per minute). The forward airspeed of the plane is to be 75.0 m/s, and the speed of the tips of the propeller blades through the air must not exceed 270 m/s. (This is about 80% of the speed of the sound i ...
Momentum
... This is called the law of conservation of linear momentum for a closed system with no external forces acting on it. Note that the above is a set of three equations (one for each direction). It is useful to observe that if there is no external force along some particular direction, then the linear mo ...
... This is called the law of conservation of linear momentum for a closed system with no external forces acting on it. Note that the above is a set of three equations (one for each direction). It is useful to observe that if there is no external force along some particular direction, then the linear mo ...
Momentum and Impulse
... The conservation of kinetic energy tells us how the distribution between mass and velocity by considering the elastic properties of the colliding objects. The conservation of energy puts an upper limit of the velocity of the impacted object and how close you get to this upper limit depends on the ...
... The conservation of kinetic energy tells us how the distribution between mass and velocity by considering the elastic properties of the colliding objects. The conservation of energy puts an upper limit of the velocity of the impacted object and how close you get to this upper limit depends on the ...
5, 6, 10, 13, 14, 18, 23 / 5, 7, 16, 23, 31, 34, 39, 43, 45
... 18. REASONING AND SOLUTION Let each object have mass M and radius R. The objects are initially at rest. In rolling down the incline, the objects lose gravitational potential energy Mgh , where h is the height of the incline. The objects gain kinetic energy equal to (1 / 2 ) I 2 (1 / 2 ) Mv 2 , wh ...
... 18. REASONING AND SOLUTION Let each object have mass M and radius R. The objects are initially at rest. In rolling down the incline, the objects lose gravitational potential energy Mgh , where h is the height of the incline. The objects gain kinetic energy equal to (1 / 2 ) I 2 (1 / 2 ) Mv 2 , wh ...
7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem
... TRSP Fig. 7-1b: Force on a baseball. Definition of Impulse: the impulse of a force is the product of the average force F and the time interval ∆t during which the force acts: ...
... TRSP Fig. 7-1b: Force on a baseball. Definition of Impulse: the impulse of a force is the product of the average force F and the time interval ∆t during which the force acts: ...
CfE Advanced Higher Physics – Unit 1 – Rotational Motion
... Notice that the angular momentum of a rigid object about a fixed axis depends on the moment of inertia. Angular momentum is a vector quantity. The direction of this vector is at right angles to the plane containing v (since p = m v and mass is scalar) and r and lies along the axis of rotation. For i ...
... Notice that the angular momentum of a rigid object about a fixed axis depends on the moment of inertia. Angular momentum is a vector quantity. The direction of this vector is at right angles to the plane containing v (since p = m v and mass is scalar) and r and lies along the axis of rotation. For i ...