Chapter 4 - Marketing Club UMT
... best done as a method of creating short cut to solving problems, the more consumers learn to use the marketers product, the faster the decision process becomes, which in turn results in greater brand loyalty. ...
... best done as a method of creating short cut to solving problems, the more consumers learn to use the marketers product, the faster the decision process becomes, which in turn results in greater brand loyalty. ...
Setting Up Interesting Learning Opportunities
... challenging. Some children have limited interests in their classrooms. They may be children who tend to wander around the classroom and don’t often play with peers, toys, or materials. How can teachers find interesting and meaningful opportunities to help children practice skills when children don’t ...
... challenging. Some children have limited interests in their classrooms. They may be children who tend to wander around the classroom and don’t often play with peers, toys, or materials. How can teachers find interesting and meaningful opportunities to help children practice skills when children don’t ...
Word format
... ii. This indicates that learning had occurred, but that it remained hidden or unexpressed. (From Tolman & Honzik, 1930.) 41. Social Learning (Cognitive) Theory a. S—R—Sr b. Imitation i. ...
... ii. This indicates that learning had occurred, but that it remained hidden or unexpressed. (From Tolman & Honzik, 1930.) 41. Social Learning (Cognitive) Theory a. S—R—Sr b. Imitation i. ...
Effects on cognitive development and academic achievement
... Word skills and IQs higher than performance skills Consistent evidence of visuomotor and visuoperceptual deficits in children with hydrocephalus ...
... Word skills and IQs higher than performance skills Consistent evidence of visuomotor and visuoperceptual deficits in children with hydrocephalus ...
2) Speech, Language, Communication and Neuro
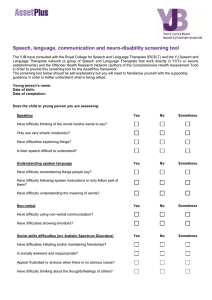
... Speech, language, communication and neuro-disability screening tool The YJB have consulted with the Royal College for Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT) and the YJ Speech and Language Therapists network (a group of Speech and Language Therapists that work directly in YOTs or secure establishment ...
... Speech, language, communication and neuro-disability screening tool The YJB have consulted with the Royal College for Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT) and the YJ Speech and Language Therapists network (a group of Speech and Language Therapists that work directly in YOTs or secure establishment ...
Family Name: Name: Chapter 1 Studying learning What is the
... Are there parallels between human causal learning and animal conditioning? What is the difference between associative models of learning and rule models? Illustrate and explain the essential part of the formula of Rescorla & Wagner (1972) model. According to Rescorla & Wagner (1972) model, what is t ...
... Are there parallels between human causal learning and animal conditioning? What is the difference between associative models of learning and rule models? Illustrate and explain the essential part of the formula of Rescorla & Wagner (1972) model. According to Rescorla & Wagner (1972) model, what is t ...
Ch01
... food. Initially, only presentation of the food caused the dog to salivate, but after a number of pairings of bell and food, the bell alone caused salivation. This principle of learning by pairing, which came to be called classical conditioning, was the basis of Watson’s “Little Albert” experiment. ...
... food. Initially, only presentation of the food caused the dog to salivate, but after a number of pairings of bell and food, the bell alone caused salivation. This principle of learning by pairing, which came to be called classical conditioning, was the basis of Watson’s “Little Albert” experiment. ...
copy - Altoona School District
... A large portion of psychology is learning various terms and concepts. One way to help learn the items is to create vocabulary flashcards on 3x5 index cards. On one side write the term, name, or concept, on the other write the definition or explanation, an example, and the page number from the text. ...
... A large portion of psychology is learning various terms and concepts. One way to help learn the items is to create vocabulary flashcards on 3x5 index cards. On one side write the term, name, or concept, on the other write the definition or explanation, an example, and the page number from the text. ...
my notes - Amazon Web Services
... Customer!value!is!the!difference!between!all!the!benefits!derived!from!the!total! product!and!all!the!costs!of!acquiring!these!benefits.!Providing!superior!customer!value! requires!the!business!to!anticipate!and!react!to!customer!needs!faster!and!better!than! its!competitors.!Today’s!consumers!hold! ...
... Customer!value!is!the!difference!between!all!the!benefits!derived!from!the!total! product!and!all!the!costs!of!acquiring!these!benefits.!Providing!superior!customer!value! requires!the!business!to!anticipate!and!react!to!customer!needs!faster!and!better!than! its!competitors.!Today’s!consumers!hold! ...
Chapter 8: Learning Learning - relatively in an organism`s behavior
... Discrimination in classical conditioning, the learned ability ___________________ between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal a UCS Nausea Conditioning in Cancer Patients Operant Conditioning type of learning in which behavior is ____________________ if followed by reinforcement or ___________ ...
... Discrimination in classical conditioning, the learned ability ___________________ between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal a UCS Nausea Conditioning in Cancer Patients Operant Conditioning type of learning in which behavior is ____________________ if followed by reinforcement or ___________ ...
Psychological Foundations
... • Responses that cause satisfaction strengthen connections and discomfort weakens connections. • Justifies use of rewards and punishments, especially Skinner’s ...
... • Responses that cause satisfaction strengthen connections and discomfort weakens connections. • Justifies use of rewards and punishments, especially Skinner’s ...
Operant Conditioning
... steps, leading to a desired complex behavior – Successive approximation: small steps, one after another, that lead to a particular goal behavior ...
... steps, leading to a desired complex behavior – Successive approximation: small steps, one after another, that lead to a particular goal behavior ...
Chapter 2 LEARNING: Principals and Applications
... Hypothesis #1 Did the results of the experiment support the hypothesis……. ...
... Hypothesis #1 Did the results of the experiment support the hypothesis……. ...
Classical Conditioning - Cedar Bluffs Public Schools
... Hypothesis #1 Did the results of the experiment support the hypothesis……. ...
... Hypothesis #1 Did the results of the experiment support the hypothesis……. ...
File
... Associative Learning: Learning that certain events occur together the events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning). Ex.) Two related events: ...
... Associative Learning: Learning that certain events occur together the events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning). Ex.) Two related events: ...
True or False?
... • Bandura Social Learning Theory •Focus on observation and imitation as learning mechanism. •Learning mostly social. Reinforcement increases likelihood of imitation, but it is not necessary for learning. •Reciprocal Determinism: child-environment influences operate in both directions. ...
... • Bandura Social Learning Theory •Focus on observation and imitation as learning mechanism. •Learning mostly social. Reinforcement increases likelihood of imitation, but it is not necessary for learning. •Reciprocal Determinism: child-environment influences operate in both directions. ...
4xpage
... Social Learning Theory on Gender Typing Differential reinforcement - children are rewarded for sex-appropriate behaviors, punished for behaviors appropriate for the other sex. Observational learning - children adopt the attitudes and behaviors of same-sex models. Consistent evidence? Inconsisten ...
... Social Learning Theory on Gender Typing Differential reinforcement - children are rewarded for sex-appropriate behaviors, punished for behaviors appropriate for the other sex. Observational learning - children adopt the attitudes and behaviors of same-sex models. Consistent evidence? Inconsisten ...
observational learning
... children with developmental delays, physical disabilities, and poor language skills; and children with hyperactivity and poor cognitive and social abilities. ...
... children with developmental delays, physical disabilities, and poor language skills; and children with hyperactivity and poor cognitive and social abilities. ...
Affective Models - Cognitive Systems Lab
... • Today, learning is mainly seen as cognitive process, however behaviorist ideas and principles are still important and valid and still vitally researched ...
... • Today, learning is mainly seen as cognitive process, however behaviorist ideas and principles are still important and valid and still vitally researched ...
Organizational Behavior 11e
... A type of conditioning in which an individual responds to some stimulus that would not ordinarily produce such a response. Key Concepts ...
... A type of conditioning in which an individual responds to some stimulus that would not ordinarily produce such a response. Key Concepts ...
Chapter 8 PowerPoint
... Cognition & Operant Conditioning Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze (environment). ...
... Cognition & Operant Conditioning Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze (environment). ...
Nevid session - Society for the Teaching of Psychology
... Instructional techniques: •Use of anecdotes, personal stories, case examples, etc., to bring concepts to life •Use of video clips, with guided questions to illustrate key psychological concepts •Practice in retelling, reciting, or rehearsing acquired knowledge within ...
... Instructional techniques: •Use of anecdotes, personal stories, case examples, etc., to bring concepts to life •Use of video clips, with guided questions to illustrate key psychological concepts •Practice in retelling, reciting, or rehearsing acquired knowledge within ...
Learning Objectives
... 15. Define discriminative stimulus and stimulus control. Give an example of stimulus control. Explain how stimulus discrimination and stimulus generalization can work together. (see Basic Components of Operant Conditioning) 16. Define shaping. Explain when it is used in operant conditioning. (see F ...
... 15. Define discriminative stimulus and stimulus control. Give an example of stimulus control. Explain how stimulus discrimination and stimulus generalization can work together. (see Basic Components of Operant Conditioning) 16. Define shaping. Explain when it is used in operant conditioning. (see F ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.