Chapter 2 Foundations of Individual Behavior
... c. Behaviorism and OB Mod only have an effect on human subjects when those subjects are unaware that these techniques are being used. d. The best reinforcement to use and the schedule on which it should be used varies widely between individual subjects. e. Behaviorism and OB Mod are based upon simpl ...
... c. Behaviorism and OB Mod only have an effect on human subjects when those subjects are unaware that these techniques are being used. d. The best reinforcement to use and the schedule on which it should be used varies widely between individual subjects. e. Behaviorism and OB Mod are based upon simpl ...
Learned
... • When you eat a new food, remember its taste and smell – if you don’t feel sick within a few hours it is probably safe; if you do, don’t eat it again ...
... • When you eat a new food, remember its taste and smell – if you don’t feel sick within a few hours it is probably safe; if you do, don’t eat it again ...
Ability - WordPress.com
... other way, moving from specific observations to broader generalizations and theories. Informally, we sometimes call this a "bottom up" approach (please note that it's "bottom up" and not "bottoms up" which is the kind of thing the bartender says to customers when he's trying to close for the night!) ...
... other way, moving from specific observations to broader generalizations and theories. Informally, we sometimes call this a "bottom up" approach (please note that it's "bottom up" and not "bottoms up" which is the kind of thing the bartender says to customers when he's trying to close for the night!) ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
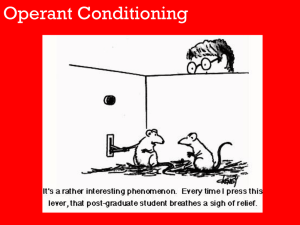
... operant conditioning the response is a set of actions that bring about an essentially equal result. Third, in classical conditioning reinforcement is dictated by the scientist or instructor. In operant conditioning reinforcement is dictated by the organism (245). Edward L. Thorndike was the first pe ...
... operant conditioning the response is a set of actions that bring about an essentially equal result. Third, in classical conditioning reinforcement is dictated by the scientist or instructor. In operant conditioning reinforcement is dictated by the organism (245). Edward L. Thorndike was the first pe ...
lecture 11
... the escape group, so the failure to learn is not simply due to having received shock in phase 1 rather, the failure to learn was due to the inability to control shock in phase 1 no matter which response they performed, their behavior was unrelated to shock offset in phase 1 according to Seligm ...
... the escape group, so the failure to learn is not simply due to having received shock in phase 1 rather, the failure to learn was due to the inability to control shock in phase 1 no matter which response they performed, their behavior was unrelated to shock offset in phase 1 according to Seligm ...
What is learned?
... better starting from that 11th day...but instead: Tolman found running was slow for 11 days, then was suddenly fast from 12th day on ...
... better starting from that 11th day...but instead: Tolman found running was slow for 11 days, then was suddenly fast from 12th day on ...
Operant Conditioning - Fleming County Schools
... This is known as: This is known as: ________________ ________________ ...
... This is known as: This is known as: ________________ ________________ ...
Day 16 (Nov 15th, chapter 6).
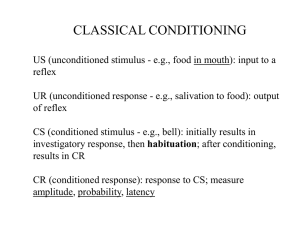
... Conditioned stimulus: An initially neutral stimulus that comes to elicit a conditioned response after being associated with an unconditioned stimulus ...
... Conditioned stimulus: An initially neutral stimulus that comes to elicit a conditioned response after being associated with an unconditioned stimulus ...
FREE Sample Here
... The proper sequence of structures a neural message passes through as it moves from one neuron to the next is ______. a. dendrite, cell body, axon c. axon, cell body, dendrite b. dendrite, axon, cell body d. cell body, dendrite, axon ...
... The proper sequence of structures a neural message passes through as it moves from one neuron to the next is ______. a. dendrite, cell body, axon c. axon, cell body, dendrite b. dendrite, axon, cell body d. cell body, dendrite, axon ...
Homework Market
... Human life would be impossible without learning; it is involved in virtually everything we do. You could not communicate with other people or recognize yourself as human if you were unable to learn. In this chapter, we explore several kinds of learning. One type is learning to associate one event wi ...
... Human life would be impossible without learning; it is involved in virtually everything we do. You could not communicate with other people or recognize yourself as human if you were unable to learn. In this chapter, we explore several kinds of learning. One type is learning to associate one event wi ...
Chapter 5 Powerpoint 2
... Reinforcement after some of the behavior Very resistant to extinction More true to real life Completed in different patterns ...
... Reinforcement after some of the behavior Very resistant to extinction More true to real life Completed in different patterns ...
km.. - UMBC
... Behaviorists usually study functional questions, whereas cognitivists usually study structural questions. ...
... Behaviorists usually study functional questions, whereas cognitivists usually study structural questions. ...
Learning - Lillian McMaster
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
Unit 4 – Learning through Conditioning
... 1. Attention. You need to be paying attention to someone else’s behaviour and its consequences 2. Retention. You need to store a mental representation of what you have witnessed in your memory to be able to use later. 3. Reproduction. You have to be able to reproduce the response. 4. Motivation. You ...
... 1. Attention. You need to be paying attention to someone else’s behaviour and its consequences 2. Retention. You need to store a mental representation of what you have witnessed in your memory to be able to use later. 3. Reproduction. You have to be able to reproduce the response. 4. Motivation. You ...
Solange Amato - International Mathematical Union
... Bass, 2000). So it was necessary to help STs draw out clear connections between the symbolic ways of representing mathematics they had in their minds before starting the course and other ways of representing the subject so that different representations for the same concept or operation could be inc ...
... Bass, 2000). So it was necessary to help STs draw out clear connections between the symbolic ways of representing mathematics they had in their minds before starting the course and other ways of representing the subject so that different representations for the same concept or operation could be inc ...
research_paper_.edt_
... time it pressed the level, food pellets were delivered. That food acted as reinforcement for that behavior. This is how we learn every day. For example, when we make mistakes, we most likely tend to remember that mistake and then try doing things differently if that same situation comes up again. In ...
... time it pressed the level, food pellets were delivered. That food acted as reinforcement for that behavior. This is how we learn every day. For example, when we make mistakes, we most likely tend to remember that mistake and then try doing things differently if that same situation comes up again. In ...
reinforcement
... results, thus the learner must be free to decide for him/herself when, where his/her responses are inadequate as a means of reaching his/her goal. External reinforcement should be to encourage students to search for such signs that determine the correctness of their responses. Reliance upon external ...
... results, thus the learner must be free to decide for him/herself when, where his/her responses are inadequate as a means of reaching his/her goal. External reinforcement should be to encourage students to search for such signs that determine the correctness of their responses. Reliance upon external ...
A reinforcement learning model of joy, distress, hope and fear.
... mechanism will be much easier to understand for humans, simply because we humans know what it means to have fear when learning to adapt to an environment. So, solving the grounding problem directly helps human-robot and human-agent interaction. This means that for an emotional instrumentation to be ...
... mechanism will be much easier to understand for humans, simply because we humans know what it means to have fear when learning to adapt to an environment. So, solving the grounding problem directly helps human-robot and human-agent interaction. This means that for an emotional instrumentation to be ...
Classical Conditioning
... because it predicts another stimulus that already produces that response • Form of learning by association ...
... because it predicts another stimulus that already produces that response • Form of learning by association ...
PowerPoint Slides
... Copyright 2002 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system ...
... Copyright 2002 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system ...
assessing the use of reinforcement on primary school children
... Learning may occur as a result of habituation or classical conditioning, seen in many animal species, or as a result of more complex activities such as play, seen only in relatively intelligent animals. Learning may occur consciously or without conscious awareness. There is evidence for human behavi ...
... Learning may occur as a result of habituation or classical conditioning, seen in many animal species, or as a result of more complex activities such as play, seen only in relatively intelligent animals. Learning may occur consciously or without conscious awareness. There is evidence for human behavi ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.