EXAMINATION REVISION GUIDE FIRST: READ THE UNIT
... Behaviour is determined by the environment, since we are the total of all our past learning experiences, free will is an illusion. Only observable behaviours should be studied if psychology is to be objective. There is an innate predisposition to learning. Learning can take place in the abse ...
... Behaviour is determined by the environment, since we are the total of all our past learning experiences, free will is an illusion. Only observable behaviours should be studied if psychology is to be objective. There is an innate predisposition to learning. Learning can take place in the abse ...
Bild 1 - Karlstads universitetsbibliotek
... How does learning occur? What is the role of memory? What is the role of motivation? How does transfer occur? Which processes are involved in self-regulation? What are the implications for instruction? ...
... How does learning occur? What is the role of memory? What is the role of motivation? How does transfer occur? Which processes are involved in self-regulation? What are the implications for instruction? ...
- W.W. Norton
... associations. Through the Little Albert study, John Watson became one of the first researchers to demonstrate the role of classical conditioning in the learning of phobias. Counterconditioning is a technique that can help overcome phobias. Adaptation and Cognition Influence Classical Conditioning. A ...
... associations. Through the Little Albert study, John Watson became one of the first researchers to demonstrate the role of classical conditioning in the learning of phobias. Counterconditioning is a technique that can help overcome phobias. Adaptation and Cognition Influence Classical Conditioning. A ...
Name: Period: Learning Reading Guide 1. What is classical
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
AP PSYCH 1
... bop-it doll. Therefore, in return, the child would respond in the same way if he/she was in the past violent or they would not act in such a way if they were not violent in the past. This showed that most children lead by example or observational learning. ...
... bop-it doll. Therefore, in return, the child would respond in the same way if he/she was in the past violent or they would not act in such a way if they were not violent in the past. This showed that most children lead by example or observational learning. ...
The 2016 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence
... may be unknown) (with almost any nonlinear piecewise activation functions) can be randomly generated independent of training data and application environments, which has recently been confirmed with concrete biological evidences. ELM theories and algorithms argue t ...
... may be unknown) (with almost any nonlinear piecewise activation functions) can be randomly generated independent of training data and application environments, which has recently been confirmed with concrete biological evidences. ELM theories and algorithms argue t ...
Learning Experience Learning is characterized as the method of
... when an unbiased stimulus is joined with an unconditioned stimulus, it becomes trained stimulus that conveys up a trained reaction. An unconditioned stimulus is one that unreservedly fallout in a reaction. An unconditioned reaction is a reaction which happens involuntarily when a trained stimulus is ...
... when an unbiased stimulus is joined with an unconditioned stimulus, it becomes trained stimulus that conveys up a trained reaction. An unconditioned stimulus is one that unreservedly fallout in a reaction. An unconditioned reaction is a reaction which happens involuntarily when a trained stimulus is ...
instruction and learning in teacher education
... questions that create dilemmas for students. The children work through these dilemmas and as a result knowledge is constructed. Therefore, the instructional practices include discovery learning. Children are given hands-on activities. Students challenge existing concepts. Students challenge present ...
... questions that create dilemmas for students. The children work through these dilemmas and as a result knowledge is constructed. Therefore, the instructional practices include discovery learning. Children are given hands-on activities. Students challenge existing concepts. Students challenge present ...
Components of Motivation
... Attribution theory: how humans come to perceive the causes of behavior; reasonable explanations. Locus of control theory (internal vs. external causes of behavior): Internals: cause of behavior lies within self Externals: cause of behavior lies outside self ...
... Attribution theory: how humans come to perceive the causes of behavior; reasonable explanations. Locus of control theory (internal vs. external causes of behavior): Internals: cause of behavior lies within self Externals: cause of behavior lies outside self ...
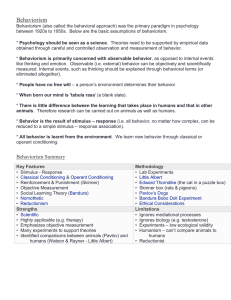
Behaviorism
... * Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. * Behaviorism is primarily concerned with observable behavior, as opposed to internal events like thinking and emotion. Observabl ...
... * Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. * Behaviorism is primarily concerned with observable behavior, as opposed to internal events like thinking and emotion. Observabl ...
Behaviorism
... Classical conditioning was the first type of For example, if a child is constantly corrected during a reading exercise, the child’s feelings of humiliation may learning to be discovered and studied within ultimately be replaced by a fear of reading aloud. the behaviorist tradition (hence the na ...
... Classical conditioning was the first type of For example, if a child is constantly corrected during a reading exercise, the child’s feelings of humiliation may learning to be discovered and studied within ultimately be replaced by a fear of reading aloud. the behaviorist tradition (hence the na ...
Butale and Nyoni
... another place.’ • “the experience of being in one place while located physically in another place during one’s normal state of consciousness.” ...
... another place.’ • “the experience of being in one place while located physically in another place during one’s normal state of consciousness.” ...
Lecture8a_blanks_101
... How do we learn? Learning A relatively _____________________________ in an organism’s behavior due to experience 3 main types _____________________________ conditioning Operant conditioning _____________________________ learning Association Learning Learning a basic _____________________________ bet ...
... How do we learn? Learning A relatively _____________________________ in an organism’s behavior due to experience 3 main types _____________________________ conditioning Operant conditioning _____________________________ learning Association Learning Learning a basic _____________________________ bet ...
Unit 6 FRQ
... teens’ committing violent crimes in New City. Do you support her conclusion? Explain your response using the psychological research we have investigated. ...
... teens’ committing violent crimes in New City. Do you support her conclusion? Explain your response using the psychological research we have investigated. ...
The current Modern Perspectives in Psychology include
... Piaget's Theory of child Cognitive Development has different stages: a- Sensor motor (0 to 2 years) b- Preoperational (2 to 7 years) c- Concrete operational (7 to 11 or 12 years) d- Formal operational (11 or 12 years and beyond) Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial Development has: a- five psychosocial ...
... Piaget's Theory of child Cognitive Development has different stages: a- Sensor motor (0 to 2 years) b- Preoperational (2 to 7 years) c- Concrete operational (7 to 11 or 12 years) d- Formal operational (11 or 12 years and beyond) Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial Development has: a- five psychosocial ...
cognitive learning
... to get food. When placed on opposite side instead of turning right, rat moved towards food. So, rat formed a cognitive map to get food and reinforcement was not a precondition for learning to take place. ...
... to get food. When placed on opposite side instead of turning right, rat moved towards food. So, rat formed a cognitive map to get food and reinforcement was not a precondition for learning to take place. ...
Module 22 Powerpoint
... rewards from others. Intrinsic motivation can sometimes be reduced by external rewards, and can be prevented by using continuous reinforcement. One principle for maintaining behavior is to use as few rewards as possible, and fade the rewards over time. ...
... rewards from others. Intrinsic motivation can sometimes be reduced by external rewards, and can be prevented by using continuous reinforcement. One principle for maintaining behavior is to use as few rewards as possible, and fade the rewards over time. ...
Key Terms - Ms. Paras
... Tentative Quest Date: 11/17 This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning. The biological bases ...
... Tentative Quest Date: 11/17 This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning. The biological bases ...
missing slide slide 7
... invoke prior beliefs. This can lead to the detection of relationships that are not objectively present ,having a prior belief about it can lead to objective relationships conflicts with a prior belief . These effects demonstrate top-down processing in learning. ...
... invoke prior beliefs. This can lead to the detection of relationships that are not objectively present ,having a prior belief about it can lead to objective relationships conflicts with a prior belief . These effects demonstrate top-down processing in learning. ...
LEARNING
... invoke prior beliefs. This can lead to the detection of relationships that are not objectively present ,having a prior belief about it can lead to objective relationships conflicts with a prior belief . These effects demonstrate top-down processing in learning. ...
... invoke prior beliefs. This can lead to the detection of relationships that are not objectively present ,having a prior belief about it can lead to objective relationships conflicts with a prior belief . These effects demonstrate top-down processing in learning. ...
Psychology People Test Version A
... environment of the lab experiment does not necessarily mean that other forms of stimulation will increase the dendrites of neurons. (Greenough) c. Sigmund Freud’s assertion that most of our behavior can be explained by unconscious drives is difficult to prove. d. Carl Rogers’ assertion that Conformi ...
... environment of the lab experiment does not necessarily mean that other forms of stimulation will increase the dendrites of neurons. (Greenough) c. Sigmund Freud’s assertion that most of our behavior can be explained by unconscious drives is difficult to prove. d. Carl Rogers’ assertion that Conformi ...
An Overview of Psychological Theories of Crime Causation
... Psychoanalytic Theories Psychoanalytic theorists, such as Sigmund Freud (1856- 1939), explain criminal behavior as follows: "(1)The actions and behavior of an adult are understood in terms of childhood development. (2)Behavior and unconscious motives are intertwined, and their interaction mus ...
... Psychoanalytic Theories Psychoanalytic theorists, such as Sigmund Freud (1856- 1939), explain criminal behavior as follows: "(1)The actions and behavior of an adult are understood in terms of childhood development. (2)Behavior and unconscious motives are intertwined, and their interaction mus ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.