AGED 601
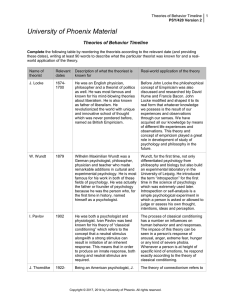
... Tuning-schemata evolve to become more consistent with experience Restructuring-creating entirely new schemata which replace or incorporate old ones Bruner o ...
... Tuning-schemata evolve to become more consistent with experience Restructuring-creating entirely new schemata which replace or incorporate old ones Bruner o ...
File
... between a conditioned stimulus and other stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus. ...
... between a conditioned stimulus and other stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus. ...
psy420r2_theories_of_behavior_timeline_1
... He has done a lot in th field of psychology that has to be remember but he is best and most known for his social cognitive theory. ...
... He has done a lot in th field of psychology that has to be remember but he is best and most known for his social cognitive theory. ...
Behavioral Ecology
... The study of animal behavior is one the oldest and most captivating fields of study in biology. Behavioral Ecology has taken on a more evolutionary view towards animal behavior... Animal behavior is an adaptation that has been favored for survival or reproduction means. Behavior has its roots in bo ...
... The study of animal behavior is one the oldest and most captivating fields of study in biology. Behavioral Ecology has taken on a more evolutionary view towards animal behavior... Animal behavior is an adaptation that has been favored for survival or reproduction means. Behavior has its roots in bo ...
Pavlov spent the rest of his life outlining his ideas. He - JMB
... to a bell (CS) then flashed a light just before you rang the bell, your dog could learn to salivate to the light without food ever being directly associated with it. ...
... to a bell (CS) then flashed a light just before you rang the bell, your dog could learn to salivate to the light without food ever being directly associated with it. ...
Analysis of Behavior Using Operant Conditioning Methods
... Basic theories of learning and memory will be discussed, with a focus on how operant conditioning methods can be utilized to gain in depth understanding of underlying cognitive processes, as pioneered by B.F. Skinner. ...
... Basic theories of learning and memory will be discussed, with a focus on how operant conditioning methods can be utilized to gain in depth understanding of underlying cognitive processes, as pioneered by B.F. Skinner. ...
ANIMAL BEHAVIORS
... – Eventually, after many repetitions, he got the dog to salivate at the sound of the bell alone ...
... – Eventually, after many repetitions, he got the dog to salivate at the sound of the bell alone ...
report
... the TCs being employed. Indeed, for example, from a tertiary teaching and learning perspective, there can be a certain freedom from micro-assessment as doctoral students learn the requisite skills of writing a dissertation using a 4 x 4 strategy: identify, articulate, discuss and plan. The question ...
... the TCs being employed. Indeed, for example, from a tertiary teaching and learning perspective, there can be a certain freedom from micro-assessment as doctoral students learn the requisite skills of writing a dissertation using a 4 x 4 strategy: identify, articulate, discuss and plan. The question ...
CX Learning Approach
... investigating classical conditioning using an infant ‘Little Albert’. Albert was 10 months old and showed little fear, the only thing that frightened him and made him cry was loud noises. Watson conditioned Albert to be afraid of his pet rat by pairing it with a loud noise. After a while, Albert wou ...
... investigating classical conditioning using an infant ‘Little Albert’. Albert was 10 months old and showed little fear, the only thing that frightened him and made him cry was loud noises. Watson conditioned Albert to be afraid of his pet rat by pairing it with a loud noise. After a while, Albert wou ...
X-Period/Learning Test
... Pavlov- starts with unlearned relationship UCS-----to-----UCR NS becomes CS ...
... Pavlov- starts with unlearned relationship UCS-----to-----UCR NS becomes CS ...
Chapter 6: Learning and Language PPT
... self-concept. Past Experiences You tend to relate what you see, hear and feel to past experiences. ...
... self-concept. Past Experiences You tend to relate what you see, hear and feel to past experiences. ...
M_5_Glossary Learning - user.meduni
... Locus of control. A personality trait that concerns whether people attribute responsibility for their own failure or success to internal factors or to external factors. Long-term memory. Components of memory where large amounts of information can be stored for long periods of time (see Module 2). Ma ...
... Locus of control. A personality trait that concerns whether people attribute responsibility for their own failure or success to internal factors or to external factors. Long-term memory. Components of memory where large amounts of information can be stored for long periods of time (see Module 2). Ma ...
Learning
... Neither habituation nor classical conditioning teaches the organism a new response. You just learn to associate an existing response (salivating) with a new stimulus (the bell) Key difference from Classical Conditioning: subject’s behavior determines an outcome and is subsequently impacted by that o ...
... Neither habituation nor classical conditioning teaches the organism a new response. You just learn to associate an existing response (salivating) with a new stimulus (the bell) Key difference from Classical Conditioning: subject’s behavior determines an outcome and is subsequently impacted by that o ...
Negative Reinforcement
... Behaviorist: Only cares about behavior – what a person does – what can be observed or proven Learning is mechanical – you behave the way you do because of external stimuli – no internal processes are required (learning by thinking about something or watching it) ...
... Behaviorist: Only cares about behavior – what a person does – what can be observed or proven Learning is mechanical – you behave the way you do because of external stimuli – no internal processes are required (learning by thinking about something or watching it) ...
Behaviorism - N. Schollmeier`s Educational Research
... Written goals or job descriptions are considered stimuli, which improves production, skill, etc. (the desired response). The largest strength! Motivation, motivation, ...
... Written goals or job descriptions are considered stimuli, which improves production, skill, etc. (the desired response). The largest strength! Motivation, motivation, ...
IMPORTANT PEOPLE IN PSYCHOLOGY
... imprinting which is defined as learning occurring at a particular age or a particular life stage) that is rapid and apparently independent of the consequences of behavior. It was first used to describe situations in which an animal or person learns the characteristics of some stimulus, which is ther ...
... imprinting which is defined as learning occurring at a particular age or a particular life stage) that is rapid and apparently independent of the consequences of behavior. It was first used to describe situations in which an animal or person learns the characteristics of some stimulus, which is ther ...
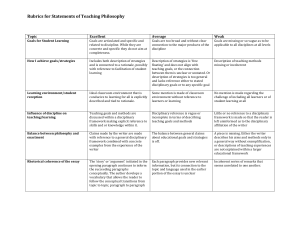
Rubrics for Statements of Teaching Philosophy
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
caroddo power point - Doral Academy Preparatory
... -classical conditioning-how all organism learn to adapt to their environment -practical applications for fears, phobias etc. Skinner -definitive insight into learned behavior -practical applications abound Both asserted that learning occurs w/o though (cognition) Only focused on observable beh ...
... -classical conditioning-how all organism learn to adapt to their environment -practical applications for fears, phobias etc. Skinner -definitive insight into learned behavior -practical applications abound Both asserted that learning occurs w/o though (cognition) Only focused on observable beh ...
Name two scientists famous for their studies of classical conditioning 2
... 12 – Jack finally takes out the garbage in order to get his father to stop pestering him. This is an example of _________________. 13 – Give an example of positive reinforcement. 14 – Which will lead to faster learning – immediate or delayed reinforcement? 15 – What is secondary (or conditioned) rei ...
... 12 – Jack finally takes out the garbage in order to get his father to stop pestering him. This is an example of _________________. 13 – Give an example of positive reinforcement. 14 – Which will lead to faster learning – immediate or delayed reinforcement? 15 – What is secondary (or conditioned) rei ...
M O D U L E 1 0
... 18 an accidental pairing of a reinforcer and a behavior causes that behavior to occur again. 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinfor ...
... 18 an accidental pairing of a reinforcer and a behavior causes that behavior to occur again. 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinfor ...
Chapter one - Forensic Consultation
... Negative: taking away something the person does not like (aversive event) ...
... Negative: taking away something the person does not like (aversive event) ...
Unit 1: Psychology*s History and Approaches
... • Results showed that boys exhibited more aggression when exposed to aggressive male models than boys exposed to aggressive female models. When exposed to aggressive male models, the number of aggressive instances exhibited by boys averaged 104 compared to 48.4 aggressive instances exhibited by boys ...
... • Results showed that boys exhibited more aggression when exposed to aggressive male models than boys exposed to aggressive female models. When exposed to aggressive male models, the number of aggressive instances exhibited by boys averaged 104 compared to 48.4 aggressive instances exhibited by boys ...
cognitive psychology: part 2: learning
... Learning is a permanent change in the nervous system of an organism that changes the way it responds to its environment, usually as a result of an experience that the organism went through. (Note: By learning here we do not mean the acquisition of knowledge like in school but the acquisition of beha ...
... Learning is a permanent change in the nervous system of an organism that changes the way it responds to its environment, usually as a result of an experience that the organism went through. (Note: By learning here we do not mean the acquisition of knowledge like in school but the acquisition of beha ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.