- Employees
... Social Learning –Learning that occurs in the presence of one or more individuals, or as a result of interactions with another individual. There are several distinct types. Social facilitation is where one individual becomes motivated to engage in a behavior because another is doing it. Group howling ...
... Social Learning –Learning that occurs in the presence of one or more individuals, or as a result of interactions with another individual. There are several distinct types. Social facilitation is where one individual becomes motivated to engage in a behavior because another is doing it. Group howling ...
neural network
... From a technology point of view, it’s possible to use a good representation system for both. For example, a frame can be used both to store facts and to launch actors, which generate behaviour To make sensible distinctions between these things, one has to get specific about a particular representati ...
... From a technology point of view, it’s possible to use a good representation system for both. For example, a frame can be used both to store facts and to launch actors, which generate behaviour To make sensible distinctions between these things, one has to get specific about a particular representati ...
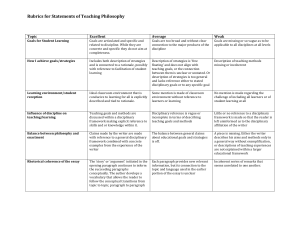
Rubrics for Statements of Teaching Philosophy
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
Classical Conditioning (Ivan Pavlov)
... Summary: Classical conditioning is a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus. Originators and Key Contributors: First described by Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), Russian physiologist, in 1903, and ...
... Summary: Classical conditioning is a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus. Originators and Key Contributors: First described by Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), Russian physiologist, in 1903, and ...
important behaviouristic theories
... In classical conditioning, conditioning of respondent behaviour occurs through a process of stimulus association and substitution. V. Extinction : The process through which a CS gradually loses ability to evoke CR, when it is no longer followed by UCS. VI. Spontaneous Recovery : Reappearance of weak ...
... In classical conditioning, conditioning of respondent behaviour occurs through a process of stimulus association and substitution. V. Extinction : The process through which a CS gradually loses ability to evoke CR, when it is no longer followed by UCS. VI. Spontaneous Recovery : Reappearance of weak ...
SBS Objectives 4
... through the use of reinforcement Positive reinforcement: giving a positive stimulus to encourage behavior Negative reinforcement: removing a negative stimulus to encourage behavior Punishment: giving a negative stimulus to discourage behavior c. Extinction: when a conditioned behavior diminish ...
... through the use of reinforcement Positive reinforcement: giving a positive stimulus to encourage behavior Negative reinforcement: removing a negative stimulus to encourage behavior Punishment: giving a negative stimulus to discourage behavior c. Extinction: when a conditioned behavior diminish ...
Social and Cognitive Learning - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... social-cognitive researchers from behaviorists • Much of what we accomplish is based on the type of goals we set – Performance goals-put focus on success in performing and failure is seen as internal and no attempt is made to improve – Mastery goals-focus is on increasing competence and skills, fail ...
... social-cognitive researchers from behaviorists • Much of what we accomplish is based on the type of goals we set – Performance goals-put focus on success in performing and failure is seen as internal and no attempt is made to improve – Mastery goals-focus is on increasing competence and skills, fail ...
Consumer Behavior
... the sitcom alone, the same music triggered a particular response—feeling sad—so it has become a conditioned stimulus (i.e., a stimulus that became associated with a particular event or feeling as a result of repetition). Feeling sad whenever you hear the music is a conditioned response (i.e., a resp ...
... the sitcom alone, the same music triggered a particular response—feeling sad—so it has become a conditioned stimulus (i.e., a stimulus that became associated with a particular event or feeling as a result of repetition). Feeling sad whenever you hear the music is a conditioned response (i.e., a resp ...
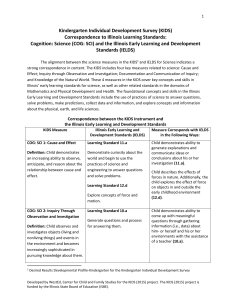
COG: SCI Correspondence to IELDS
... describe and explain factors that influence various aspects of health (22.b). Child’s level of understanding what is required for survival is emerging based on his or her understanding of events in the natural world (22.c). Child is broadly knowledgeable about the fact that people need to survive (2 ...
... describe and explain factors that influence various aspects of health (22.b). Child’s level of understanding what is required for survival is emerging based on his or her understanding of events in the natural world (22.c). Child is broadly knowledgeable about the fact that people need to survive (2 ...
Learning and Affordances 22 July draft 8 slim - learning
... sometimes makes as he moves across this broad spectrum. However, the issue in this paper is not Gibson per se, but rather an exploration of what can be called the ecological turn, as it applies to learning, and an attempt to understand learning both ontogenetically and phylogenetically, so that we c ...
... sometimes makes as he moves across this broad spectrum. However, the issue in this paper is not Gibson per se, but rather an exploration of what can be called the ecological turn, as it applies to learning, and an attempt to understand learning both ontogenetically and phylogenetically, so that we c ...
deep learning with different types of neurons
... D EEP LEARNING hypothesizes that in order to learn high-level representations of data a hierarchy of intermediate representations are needed. In the vision case the first level of representation could be gabor-like filters, the second level could be line and corner detectors, and higher level repres ...
... D EEP LEARNING hypothesizes that in order to learn high-level representations of data a hierarchy of intermediate representations are needed. In the vision case the first level of representation could be gabor-like filters, the second level could be line and corner detectors, and higher level repres ...
Memory - Psychological Associates of South Florida
... philosophical theories. However, it was the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov who elucidated classical conditioning. His work provided a basis for later behaviorists like John Watson. ...
... philosophical theories. However, it was the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov who elucidated classical conditioning. His work provided a basis for later behaviorists like John Watson. ...
Operant Conditioning Powerpoint
... associated with their natural behaviors – Example – can use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to rear up, more difficult to use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to wash its face ...
... associated with their natural behaviors – Example – can use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to rear up, more difficult to use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to wash its face ...
Input Hypothesis
... a “nurture”position: later education is stressed. 2. The mentalism model:语法天生说 (“nature”position /innateness position / innateness hypothesis) : stress that human beings, equipped with language acquisition device (LAD), are capable of language learning if provided with ...
... a “nurture”position: later education is stressed. 2. The mentalism model:语法天生说 (“nature”position /innateness position / innateness hypothesis) : stress that human beings, equipped with language acquisition device (LAD), are capable of language learning if provided with ...
Os textos são da exclusiva responsabilidade dos autores
... multiple brain areas, including the posterior parietal cortex (PPC). Functional neuroimaging studies have found that the initial, more attentionally demanding stage of skill learning is associated with greater activity on the PPC. This activation tends to decrease with extensive practice. To date, n ...
... multiple brain areas, including the posterior parietal cortex (PPC). Functional neuroimaging studies have found that the initial, more attentionally demanding stage of skill learning is associated with greater activity on the PPC. This activation tends to decrease with extensive practice. To date, n ...
CLEreg
... Teleconferencing: Two-way electronic communication between two or more groups in separate locations via audio, video, and/or computer systems. Videoconferencing: Using video and audio signals to link participants at different and remote locations. Vodcast: or Vidcast is a method of publishing video/ ...
... Teleconferencing: Two-way electronic communication between two or more groups in separate locations via audio, video, and/or computer systems. Videoconferencing: Using video and audio signals to link participants at different and remote locations. Vodcast: or Vidcast is a method of publishing video/ ...
The Behavioural Model
... the patient observes others (the “model(s)”) in the presence of the phobic stimulus who are responding with relaxation rather that fear to the phobic stimulus. In this way, the patient is encouraged to imitate the model(s) and thereby relieve their phobia. ...
... the patient observes others (the “model(s)”) in the presence of the phobic stimulus who are responding with relaxation rather that fear to the phobic stimulus. In this way, the patient is encouraged to imitate the model(s) and thereby relieve their phobia. ...
LEARNING
... the dog with meat powder. This pairing, carefully planned so that exactly the same amount of time elapsed between the presentation of the sound and the meat occurred repeatedly. At first the dog would salivate only when the meat powder itself was presented, but soon it began to salivate at the sound ...
... the dog with meat powder. This pairing, carefully planned so that exactly the same amount of time elapsed between the presentation of the sound and the meat occurred repeatedly. At first the dog would salivate only when the meat powder itself was presented, but soon it began to salivate at the sound ...
Document
... engagement with learning. Therefore it may be beneficial to maturation for young people to spend time on social networking sites and instant messaging rather than in face-to-face interactions. Young people make use of digital technologies in their personal and out-of-school activities, some of which ...
... engagement with learning. Therefore it may be beneficial to maturation for young people to spend time on social networking sites and instant messaging rather than in face-to-face interactions. Young people make use of digital technologies in their personal and out-of-school activities, some of which ...
Document
... All the new learning depends to a large extent on what has been learned before, students do not always call the mind and use relevant information when faced with a new learning task. ...
... All the new learning depends to a large extent on what has been learned before, students do not always call the mind and use relevant information when faced with a new learning task. ...
LEARNING
... Operant conditioning was coined by behaviorist B.F. Skinner which is why it is referred to as Skinnerian conditioning. As a behaviorist, Skinner believed that internal thoughts and motivations could not be used to explain behavior. Instead, he suggested, we should look only at the external, observa ...
... Operant conditioning was coined by behaviorist B.F. Skinner which is why it is referred to as Skinnerian conditioning. As a behaviorist, Skinner believed that internal thoughts and motivations could not be used to explain behavior. Instead, he suggested, we should look only at the external, observa ...
Chapter 6: Learning (Classical Conditioning)
... WHY? In real life, organisms should be “tuned” to associate pain from a shock with external stimuli such as sights or sounds rather than with something eaten. In sum, animals (including humans) are prone to learn the type of associations that are most common or relevant to their environment. ...
... WHY? In real life, organisms should be “tuned” to associate pain from a shock with external stimuli such as sights or sounds rather than with something eaten. In sum, animals (including humans) are prone to learn the type of associations that are most common or relevant to their environment. ...
Educating Students with Significant Disabilites
... Strengthening the interactive relationship between the caregiver and the child Beliefs All young children learn through play They need to be encouraged to explore their environment and objects in their environment That all very young children learn by being active, rather than passive recipi ...
... Strengthening the interactive relationship between the caregiver and the child Beliefs All young children learn through play They need to be encouraged to explore their environment and objects in their environment That all very young children learn by being active, rather than passive recipi ...