Nerve Cells - Dr Magrann
... SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where the action potential of the neuron builds up before it transmits the signal down the axon. AXON function is to transmit signals. Some cells have many axons, some have o ...
... SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where the action potential of the neuron builds up before it transmits the signal down the axon. AXON function is to transmit signals. Some cells have many axons, some have o ...
Chapter 3 Synapses
... Postsynaptic Potentials “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with m ...
... Postsynaptic Potentials “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with m ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheaths in the CNS Have multiple processes Coil around several different axons ...
... Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheaths in the CNS Have multiple processes Coil around several different axons ...
MOTOR ph226 2015
... CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS OR PYRAMIDAL TRACTS 80 % cross in the medulla Lateral corticospinal tract 20 % do not cross in medulla Ventral or anterior (They cross in spinal cord) ...
... CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS OR PYRAMIDAL TRACTS 80 % cross in the medulla Lateral corticospinal tract 20 % do not cross in medulla Ventral or anterior (They cross in spinal cord) ...
news and views - Cortical Plasticity
... and only a few nonzero weights remaining (Fig. 1b). This means that in an optimal neural network that is operating at maximal capacity and with maximal tolerance to noise, most weights have to be zero for memory retrieval to function correctly. Because zero-valued synaptic weights translate into ine ...
... and only a few nonzero weights remaining (Fig. 1b). This means that in an optimal neural network that is operating at maximal capacity and with maximal tolerance to noise, most weights have to be zero for memory retrieval to function correctly. Because zero-valued synaptic weights translate into ine ...
Hippocampus – Why is it studied so frequently?
... and was considered cell free for exception few interneurons 13. Recently, six interneuron types and two GABA negative types were differentiated within dentate molecular layer in the rabbit hippocampus 19. The principal, granular layer, contains small granule cells with axons which form the mossy fib ...
... and was considered cell free for exception few interneurons 13. Recently, six interneuron types and two GABA negative types were differentiated within dentate molecular layer in the rabbit hippocampus 19. The principal, granular layer, contains small granule cells with axons which form the mossy fib ...
neurons - haltliappsych
... (an electrical event): Each neuron is like a tiny biological battery ready to be discharged. It takes about onethousandth of a second for a neuron to fire an impulse and return to its resting level. A maximum of 1,000 nerve impulses per second is possible. However, firing rates of 1 per second to 30 ...
... (an electrical event): Each neuron is like a tiny biological battery ready to be discharged. It takes about onethousandth of a second for a neuron to fire an impulse and return to its resting level. A maximum of 1,000 nerve impulses per second is possible. However, firing rates of 1 per second to 30 ...
Slide ()
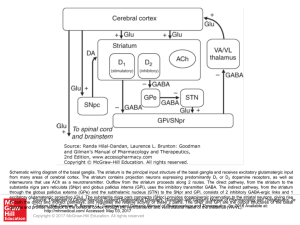
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
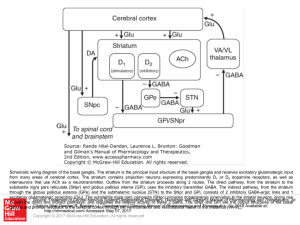
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Fridtjof Nansen Science Symposium 2011
... This talk will emphasize work dedicated to understanding the role of dendritic spines and synapse structure in learning and memory. Long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic efficacy is a model of learning and memory that is well-suited to investigate this process. A clear understanding requires the ...
... This talk will emphasize work dedicated to understanding the role of dendritic spines and synapse structure in learning and memory. Long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic efficacy is a model of learning and memory that is well-suited to investigate this process. A clear understanding requires the ...
The Nervous System
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
Photo Album
... direction of motion of a limb. For example, if cell 1 is active at half of its maximal firing rate, it is ambiguous as to whether the direction of movement is to the right or left of its preferred firing direction. However, knowing the activity of a population of neurons allows a more precise decodi ...
... direction of motion of a limb. For example, if cell 1 is active at half of its maximal firing rate, it is ambiguous as to whether the direction of movement is to the right or left of its preferred firing direction. However, knowing the activity of a population of neurons allows a more precise decodi ...
Learning in a neural network model in real time using real world
... neuron in the thalamic population. These synapses are subject to short-term depression [15]. Our model of the cortical circuit consists of populations of excitatory principal neurons and inhibitory interneurons where the excitatory ones project oneto-one to the inhibitory neurons. The excitatory neu ...
... neuron in the thalamic population. These synapses are subject to short-term depression [15]. Our model of the cortical circuit consists of populations of excitatory principal neurons and inhibitory interneurons where the excitatory ones project oneto-one to the inhibitory neurons. The excitatory neu ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... to several feet. Because of the length of their axons, some neurons in your legs are several feet long. Many axons are covered with __________________, a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. This myelin sheath, or casing, also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. ...
... to several feet. Because of the length of their axons, some neurons in your legs are several feet long. Many axons are covered with __________________, a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. This myelin sheath, or casing, also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. ...
Biopsychology Revision
... “The fight or flight response is a physiological reaction to a stressful or threatening situation. The ANS (autonomic nervous system) changes from a parasympathetic state to the physiologically aroused (sympathetic state). This produces changes in the body such as dilated pupils and increases hear ...
... “The fight or flight response is a physiological reaction to a stressful or threatening situation. The ANS (autonomic nervous system) changes from a parasympathetic state to the physiologically aroused (sympathetic state). This produces changes in the body such as dilated pupils and increases hear ...
Theroleofdendritesinauditory coincidence detection
... stimulus in the chick7,18 (Fig. 1a), suggesting a computational role for the dendrites. Fourth, the electrophysiological properties of these neurons have been well characterized19,20. As is appropriate for timing devices, these coincidence detectors do not respond to slowly varying inputs and fire o ...
... stimulus in the chick7,18 (Fig. 1a), suggesting a computational role for the dendrites. Fourth, the electrophysiological properties of these neurons have been well characterized19,20. As is appropriate for timing devices, these coincidence detectors do not respond to slowly varying inputs and fire o ...
Neurons - World of Teaching
... Neuron at Rest Resting Potential Occurs when the neuron is at rest. A condition where the outside of the membrane is positively(+) charged compared to the inside which is negatively(-) charged. Neuron is said to be polarized. Neuron has a voltage difference of -70 mV ...
... Neuron at Rest Resting Potential Occurs when the neuron is at rest. A condition where the outside of the membrane is positively(+) charged compared to the inside which is negatively(-) charged. Neuron is said to be polarized. Neuron has a voltage difference of -70 mV ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Neuron at Rest Resting Potential Occurs when the neuron is at rest. A condition where the outside of the membrane is positively(+) charged compared to the inside which is negatively(-) charged. Neuron is said to be polarized. Neuron has a voltage difference of -70 mV ...
... Neuron at Rest Resting Potential Occurs when the neuron is at rest. A condition where the outside of the membrane is positively(+) charged compared to the inside which is negatively(-) charged. Neuron is said to be polarized. Neuron has a voltage difference of -70 mV ...
Motor Neurons
... branching terminal fibers, through which messages are sent to other neurons or to muscles or glands ...
... branching terminal fibers, through which messages are sent to other neurons or to muscles or glands ...
1 Name: Period: _____ Laboratory Exercise and Activity: Nervous
... three basic parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. The dendrites and the single axon are extensions of the cell body called processes. Dendrites receive information from receptors or other neurons and send it as a change in membrane potential to the nerve cell body or soma (soma means body). Ne ...
... three basic parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. The dendrites and the single axon are extensions of the cell body called processes. Dendrites receive information from receptors or other neurons and send it as a change in membrane potential to the nerve cell body or soma (soma means body). Ne ...
8-Nervous tissue
... The dendrites are characterized by the fact that they terminate near the cell body. They are irregular in thickness, and Nissl granules extend into them. They bear numerous small spines which are of variable shape. ...
... The dendrites are characterized by the fact that they terminate near the cell body. They are irregular in thickness, and Nissl granules extend into them. They bear numerous small spines which are of variable shape. ...
neurons
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...