Lecture 15
... state ψ100(r) the energy is -13.6 eV = -ħ2 / 2 m a02 = - mk2e4/ħ2 Now look at the He+ ion. It has an energy E = -54.4 eV since if we let e → 2e in the expression for the energy, this is what we get. Now put the second electron in. We might expect that it should also go into the 1s state. However, th ...
... state ψ100(r) the energy is -13.6 eV = -ħ2 / 2 m a02 = - mk2e4/ħ2 Now look at the He+ ion. It has an energy E = -54.4 eV since if we let e → 2e in the expression for the energy, this is what we get. Now put the second electron in. We might expect that it should also go into the 1s state. However, th ...
RES9_phys_flash_card..
... repulsion (Coulomb’s law) and a weak gravitational attraction (Newton’s law of gravitation). There must therefore be a very strong short-range attractive force (the strong nuclear interaction) between nucleons. For a nuclide is the nucleon number or mass number, the number of nucleons in the nuc ...
... repulsion (Coulomb’s law) and a weak gravitational attraction (Newton’s law of gravitation). There must therefore be a very strong short-range attractive force (the strong nuclear interaction) between nucleons. For a nuclide is the nucleon number or mass number, the number of nucleons in the nuc ...
Ch3 Video 2 pdf file
... In the nucleus, a neutron becomes a proton and ejects an electron Daughter nuclide has the same mass, but one less neutron ...
... In the nucleus, a neutron becomes a proton and ejects an electron Daughter nuclide has the same mass, but one less neutron ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... The mass of an atom is mostly from the __protons___ and ____neutrons________. Find O on the periodic table. It’s mass is _16.00___ amu. It has _8_ protons. It must have _8_ neutrons. Electrically neutral atoms (as opposed to ions) have one electron for every proton. Fill in this chart for these neut ...
... The mass of an atom is mostly from the __protons___ and ____neutrons________. Find O on the periodic table. It’s mass is _16.00___ amu. It has _8_ protons. It must have _8_ neutrons. Electrically neutral atoms (as opposed to ions) have one electron for every proton. Fill in this chart for these neut ...
CHAPTER 4: ABUNDANCE AND RADIOACTIVITY OF UNSTABLE
... the emission of an electron and an anti-neutrino. A (anti)neutrino is a particle with mainly a relativistic mass, i.e. mass because of its motion. (Neutrino's and negatrons have their spin anti-parallel to their direction of motion and anti-neutrino's and positrons parallel). The total reaction ener ...
... the emission of an electron and an anti-neutrino. A (anti)neutrino is a particle with mainly a relativistic mass, i.e. mass because of its motion. (Neutrino's and negatrons have their spin anti-parallel to their direction of motion and anti-neutrino's and positrons parallel). The total reaction ener ...
Nuclear Forces and Quarks
... Quarks and Radioactive Decay Beta (β) radioactive decay occurs when the weak force changes the spin on one of the quarks in a proton or neutron. In β− decay (the more wellknown form), the spin goes from “down” to “up,” which turns a neutron into a proton. In β+ decay, the spin goes from “up” to “dow ...
... Quarks and Radioactive Decay Beta (β) radioactive decay occurs when the weak force changes the spin on one of the quarks in a proton or neutron. In β− decay (the more wellknown form), the spin goes from “down” to “up,” which turns a neutron into a proton. In β+ decay, the spin goes from “up” to “dow ...
Chapter 14
... When a neutron is converted into a proton, this is an example of _________. This is the process by which one element changes into another element. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are called _. The atomic number of an element is equal to _____________. This is the smalle ...
... When a neutron is converted into a proton, this is an example of _________. This is the process by which one element changes into another element. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are called _. The atomic number of an element is equal to _____________. This is the smalle ...
Words for Matter Chapter 2
... characteristics that can be measured or detected by the senses – For example color, size, odor, and density describes how matter changes when it reacts with other matter – For example, does it burn? Will it rust? Will it react with acid? Will it rot? is a material that always has the same makeup and ...
... characteristics that can be measured or detected by the senses – For example color, size, odor, and density describes how matter changes when it reacts with other matter – For example, does it burn? Will it rust? Will it react with acid? Will it rot? is a material that always has the same makeup and ...
Practice_Final_B
... water is 1.0 cal/g C°. Assuming the cup doesn't exchange any heat, the final temperature of the system will be which of the following? A) +5.0oC. B) 0oC. C) 4oC. D) +2.5oC. E) -10oC. 4. Three blocks are being pulled across a frictionless horizontal floor as shown in the diagram. What is the tension ...
... water is 1.0 cal/g C°. Assuming the cup doesn't exchange any heat, the final temperature of the system will be which of the following? A) +5.0oC. B) 0oC. C) 4oC. D) +2.5oC. E) -10oC. 4. Three blocks are being pulled across a frictionless horizontal floor as shown in the diagram. What is the tension ...
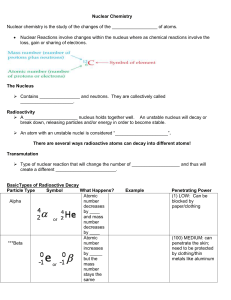
Nuclear Chemistry – Chapter 25, chapter 4, section 4
... There are several ways radioactive atoms can decay into different atoms! Transmutation Type of nuclear reaction that will change the number of ___________________ and thus will create a different ________________________. ...
... There are several ways radioactive atoms can decay into different atoms! Transmutation Type of nuclear reaction that will change the number of ___________________ and thus will create a different ________________________. ...
Helical Particle Waves
... The more energy a relativistic particle absorbs, the higher its spin moment becomes and thus gains higher resistance to directional change. That is, a stream of relativistic particles (a helical particle wave) starts to lose amplitude as the velocity at which it propagates through space approaches c ...
... The more energy a relativistic particle absorbs, the higher its spin moment becomes and thus gains higher resistance to directional change. That is, a stream of relativistic particles (a helical particle wave) starts to lose amplitude as the velocity at which it propagates through space approaches c ...
NW3424392440
... its constituents. Potential of quark-anti-quark can be considered in different ways. In some practical uses, a harmonic oscillator potential, as it is determined in QCD theory, is used. This model of harmonic oscillator has simple mathematics and most of the time is used. Otherwise the colony is not ...
... its constituents. Potential of quark-anti-quark can be considered in different ways. In some practical uses, a harmonic oscillator potential, as it is determined in QCD theory, is used. This model of harmonic oscillator has simple mathematics and most of the time is used. Otherwise the colony is not ...
Name Class Date assigned Due date Nuclear chemistry ws – part 1
... 22. In negative Beta radiation, the actual Beta particle is an _________________. 23. Does Gamma radiation emit a particle or energy only? 24. In positive Beta radiation, a proton splits into a __________________ and a ___________________. 25. In positive Beta radiation, the actual Beta particle is ...
... 22. In negative Beta radiation, the actual Beta particle is an _________________. 23. Does Gamma radiation emit a particle or energy only? 24. In positive Beta radiation, a proton splits into a __________________ and a ___________________. 25. In positive Beta radiation, the actual Beta particle is ...
Document
... Adopt realistic NN (and NNN) interaction(s) & renormalize as needed - retain induced many-body interactions: Chiral EFT interactions and JISP16 Adopt the 3-D Harmonic Oscillator (HO) for the single-nucleon basis states, , ,… nuclear Hamiltonian, H, in basis space of HO (Slater) determinants ...
... Adopt realistic NN (and NNN) interaction(s) & renormalize as needed - retain induced many-body interactions: Chiral EFT interactions and JISP16 Adopt the 3-D Harmonic Oscillator (HO) for the single-nucleon basis states, , ,… nuclear Hamiltonian, H, in basis space of HO (Slater) determinants ...
The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... Matter as a wave! • If light is both particles and waves and • quantum mechanics is the theory of the very small, • then, maybe small particles act as waves. • This was shown by Prince Louis de Broglie! ...
... Matter as a wave! • If light is both particles and waves and • quantum mechanics is the theory of the very small, • then, maybe small particles act as waves. • This was shown by Prince Louis de Broglie! ...