International Rock Gardener - the Scottish Rock Garden Club
... ---International Rock Gardener--The late Joyce Carruthers sowed seed of Viola delphinantha directly in her big tufa pot and a few seedlings are prepared to show first flowers next year. Fritz Kummert had good germination from the seed and he reported that this Bulgarian clone has more rounded flowe ...
... ---International Rock Gardener--The late Joyce Carruthers sowed seed of Viola delphinantha directly in her big tufa pot and a few seedlings are prepared to show first flowers next year. Fritz Kummert had good germination from the seed and he reported that this Bulgarian clone has more rounded flowe ...
Growing Strawberries in Home Gardens
... soils that do not allow the roots to mine the soil for iron. Also, high calcium carbonate (lime) content of soils may limit iron uptake. Treating the first condition requires water drainage and change in irrigation scheduling. Lengthen the intervals between watering to allow the soil to dry. The sec ...
... soils that do not allow the roots to mine the soil for iron. Also, high calcium carbonate (lime) content of soils may limit iron uptake. Treating the first condition requires water drainage and change in irrigation scheduling. Lengthen the intervals between watering to allow the soil to dry. The sec ...
Plant Reproduction
... scented white flowers which are easy to find in dim light. Flies may pollinate flowers that smell like rotten meat. Many flowers are not pollinated primarily by insects. Red flowers may be pollinated by hummingbirds. Some large white flowers that open at night are pollinated by bats. Many flowers, s ...
... scented white flowers which are easy to find in dim light. Flies may pollinate flowers that smell like rotten meat. Many flowers are not pollinated primarily by insects. Red flowers may be pollinated by hummingbirds. Some large white flowers that open at night are pollinated by bats. Many flowers, s ...
Purple Loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria)
... Federal: The Fisheries Act10 specifies that it is an offence to harmfully alter, disrupt, or destroy fish habitat, including streamside vegetation. It is also an offence to move or introduce aquatic organisms (including plants) to new habitats. The purpose of the Fisheries Act is to conserve and pr ...
... Federal: The Fisheries Act10 specifies that it is an offence to harmfully alter, disrupt, or destroy fish habitat, including streamside vegetation. It is also an offence to move or introduce aquatic organisms (including plants) to new habitats. The purpose of the Fisheries Act is to conserve and pr ...
Monocots vs
... chloroplasts which have not been exposed to light. Instead of a large thylakoid system they have a lattice of tubules called prolamellar bodies. Their growth is very different to light sufficient cells as their vertical growth is accelerated but their leaves are usually white or yellow. What makes t ...
... chloroplasts which have not been exposed to light. Instead of a large thylakoid system they have a lattice of tubules called prolamellar bodies. Their growth is very different to light sufficient cells as their vertical growth is accelerated but their leaves are usually white or yellow. What makes t ...
04.14.10_Possumhaw Viburnum
... flowers give way to small, berries in the late summer that go through several color changes, from green to pale yellow, then pink, and finally becoming a deep blue-black. The berries are prized by wildlife, including songbirds, water birds, and small mammals. They barely have time to ripen before th ...
... flowers give way to small, berries in the late summer that go through several color changes, from green to pale yellow, then pink, and finally becoming a deep blue-black. The berries are prized by wildlife, including songbirds, water birds, and small mammals. They barely have time to ripen before th ...
Gymnosperms
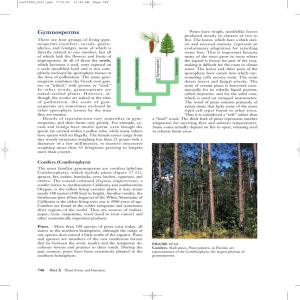
... many of the trees grow in areas where the topsoil is frozen for part of the year, making it difficult for the roots to obtain water. The leaves and other parts of the sporophyte have canals into which surrounding cells secrete resin. The resin deters insect and fungal attacks. The resin of certain p ...
... many of the trees grow in areas where the topsoil is frozen for part of the year, making it difficult for the roots to obtain water. The leaves and other parts of the sporophyte have canals into which surrounding cells secrete resin. The resin deters insect and fungal attacks. The resin of certain p ...
Bromeliacece Q3 2013 - Bromeliad Society of Queensland
... treatment and abruptly died. He grew on some seed. Harry named it P. vargasiana. Peter is still doubtful as to what it really is, and it may be an undescribed species. He assumed at the time that Rob had collected it near Tarapoto or Moyabamba, but he also went to Tingo Maria and the Machu Picchu ar ...
... treatment and abruptly died. He grew on some seed. Harry named it P. vargasiana. Peter is still doubtful as to what it really is, and it may be an undescribed species. He assumed at the time that Rob had collected it near Tarapoto or Moyabamba, but he also went to Tingo Maria and the Machu Picchu ar ...
Plant Guide PURPLE
... flats and placed in the greenhouse or outside. Another method of cold stratification is to wrap the seeds in wet peat moss and place them in a plastic bag in the refrigerator for two to four months. Plant seeds in deep plug trays; this allows the taproot to develop straight down to a depth of six or ...
... flats and placed in the greenhouse or outside. Another method of cold stratification is to wrap the seeds in wet peat moss and place them in a plastic bag in the refrigerator for two to four months. Plant seeds in deep plug trays; this allows the taproot to develop straight down to a depth of six or ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... What is a plant? Allow students to respond. Record their thinking on the chart in the class science notebook under the “K”. 3. Distribute a piece of paper to each student. Instruct students to draw two examples of a plant. Students should label any parts that they know. Collect these pieces of paper ...
... What is a plant? Allow students to respond. Record their thinking on the chart in the class science notebook under the “K”. 3. Distribute a piece of paper to each student. Instruct students to draw two examples of a plant. Students should label any parts that they know. Collect these pieces of paper ...
Dwarf Nandinas Can Be Good Land - ifas.ufl.edu
... any gardeners have heard that news that nandinas can be invasive plants. The colorful red berries they produce are spread by birds into woodlands and other native areas where the plants continue to proliferate. However, not all nandinas are bad guys. Not only are Nandina ‘Firepower’ and Nandina ‘Har ...
... any gardeners have heard that news that nandinas can be invasive plants. The colorful red berries they produce are spread by birds into woodlands and other native areas where the plants continue to proliferate. However, not all nandinas are bad guys. Not only are Nandina ‘Firepower’ and Nandina ‘Har ...
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... towards the ovary, which contains the ovule and egg cell (female gamete). pollen tube ...
... towards the ovary, which contains the ovule and egg cell (female gamete). pollen tube ...
Plant adaptations to dry environments.
... A plant is an integrated system which: Obtains water and nutrients from the soil. Transports them through the roots and stems to leaves. Combines the H2O with CO2 entering the stomata to make sugar. Exports energy rich sugar to where it’s needed for maintenance, growth, and reproduction of the plant ...
... A plant is an integrated system which: Obtains water and nutrients from the soil. Transports them through the roots and stems to leaves. Combines the H2O with CO2 entering the stomata to make sugar. Exports energy rich sugar to where it’s needed for maintenance, growth, and reproduction of the plant ...
Leaves
... Leaves are really the digestive organs of the plant. A little like solar panels, green plants have the amazing ability to make their own food energy from sunlight, carbon dioxide, water and some essential mineral elements. A green pigment called Chlorophyll* in the leaves (and sometimes the sepals* ...
... Leaves are really the digestive organs of the plant. A little like solar panels, green plants have the amazing ability to make their own food energy from sunlight, carbon dioxide, water and some essential mineral elements. A green pigment called Chlorophyll* in the leaves (and sometimes the sepals* ...
and Growing from Seed to Maturity
... flowers, vegetables, or herbs (often shrubs and trees as well) are planted and cared for. Gardens are grown all over the world: in deserts and rainforests, on seacoasts and mountaintops, and many places in between-wherever there are people to enjoy them. In size, a garden may be as small as a tablet ...
... flowers, vegetables, or herbs (often shrubs and trees as well) are planted and cared for. Gardens are grown all over the world: in deserts and rainforests, on seacoasts and mountaintops, and many places in between-wherever there are people to enjoy them. In size, a garden may be as small as a tablet ...
Seed - DavisonScience
... – This results in a generative cell and tube cell which make up the pollen grain ...
... – This results in a generative cell and tube cell which make up the pollen grain ...
Lab 7: Plant form and function
... in duration and definitely the phase most easily noticed. However, when it begins life as a zygote and embryo, it is nutritionally dependent on the smaller, less noticeable gametophyte; as its development continues, it becomes photosynthetic and its maternal gametophyte slowly dies—resulting in an i ...
... in duration and definitely the phase most easily noticed. However, when it begins life as a zygote and embryo, it is nutritionally dependent on the smaller, less noticeable gametophyte; as its development continues, it becomes photosynthetic and its maternal gametophyte slowly dies—resulting in an i ...
Serrated Tussock - Victorian Serrated Tussock Working Party
... Rate of growth and spread Serrated Tussock is a prolific seeder with 90 per cent of the plant self pollinating. Seed heads of the plant are carried along the ground and in the air and may be blown considerable distances of up to several kilometres. The seeds of the weed are also dispersed by moving ...
... Rate of growth and spread Serrated Tussock is a prolific seeder with 90 per cent of the plant self pollinating. Seed heads of the plant are carried along the ground and in the air and may be blown considerable distances of up to several kilometres. The seeds of the weed are also dispersed by moving ...
Ch. 39 Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals
... 1. enzymes needed for photosynthesis 2. enzymes for making chemical precursors for chlorophyll production 3. affect hormone levels Hormones are chemical signals that affect different parts of an organism chemicals produced by one part of the organism and then transported to another part and ...
... 1. enzymes needed for photosynthesis 2. enzymes for making chemical precursors for chlorophyll production 3. affect hormone levels Hormones are chemical signals that affect different parts of an organism chemicals produced by one part of the organism and then transported to another part and ...
Strong, Healthy Root Systems Lead to Higher
... “Root health is a term that plant pathologists have used for many years to describe a plant root that has very little disease. Healthier, more robust root systems help plants better utilize available nutrients and moisture.” –Wayne Pedersen, Ph.D., emeritus plant pathologist, University of Illinois ...
... “Root health is a term that plant pathologists have used for many years to describe a plant root that has very little disease. Healthier, more robust root systems help plants better utilize available nutrients and moisture.” –Wayne Pedersen, Ph.D., emeritus plant pathologist, University of Illinois ...
Plant Anatomy
... The bundle cap physically protects the inner tissues of the stem. In grass leaves, the bundle sheath may extend to the epidermis, forming a bundle sheath extension. Sclerenchyma cells only become mature when the surrounding cells stop growing. They are usually dead at maturity, although the lumens o ...
... The bundle cap physically protects the inner tissues of the stem. In grass leaves, the bundle sheath may extend to the epidermis, forming a bundle sheath extension. Sclerenchyma cells only become mature when the surrounding cells stop growing. They are usually dead at maturity, although the lumens o ...
Growing and Overwintering Tender Varieties
... to the size of the plant. The larger the plant, the larger the amount of fertilizer needed. In early spring, start with a very diluted liquid fertilizer. As the amount of light and growth increases, add more fertilizer. Use the color of the foliage as an indication of the plant’s fertilizer needs. B ...
... to the size of the plant. The larger the plant, the larger the amount of fertilizer needed. In early spring, start with a very diluted liquid fertilizer. As the amount of light and growth increases, add more fertilizer. Use the color of the foliage as an indication of the plant’s fertilizer needs. B ...
Plants for Play – NRM Education B = Butterfly attracting, Tr
... their name they are not sticky – they simply look it. Best planted together at the rear of a garden or in a maze area. Plant 1 metre apart when wanting tunnels. Some minimal trimming will be required. Foliage glossy green, papery seed pods green and ripen to red. ...
... their name they are not sticky – they simply look it. Best planted together at the rear of a garden or in a maze area. Plant 1 metre apart when wanting tunnels. Some minimal trimming will be required. Foliage glossy green, papery seed pods green and ripen to red. ...
aquatic plants of texas - AgriLife Extension County Offices
... Aquatic weeds that have been introduced from other parts of the world into Texas waters can create serious environmental, economic, and public health problems. Because of their growth habits and their lack of natural controls, they often create extensive mats of vegetation which block light and gas ...
... Aquatic weeds that have been introduced from other parts of the world into Texas waters can create serious environmental, economic, and public health problems. Because of their growth habits and their lack of natural controls, they often create extensive mats of vegetation which block light and gas ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.