Classification of Crude Drugs :
... Taxonomical classification is purely a botanical classification , its based on principles of natural relationship & evolutionary developments . They are grouped in ( Kingdom , Phyllum , Order , Family , Genus & Species ) . As all the entire plants are not used as drugs , parts of plant is used as a ...
... Taxonomical classification is purely a botanical classification , its based on principles of natural relationship & evolutionary developments . They are grouped in ( Kingdom , Phyllum , Order , Family , Genus & Species ) . As all the entire plants are not used as drugs , parts of plant is used as a ...
Plants Review and Key
... 20. Which stage of the life cycle (gametophyte or sporophyte) is dominant in non vascular plants? By dominant I mean large in size, it’s the main part of the plant you see when viewing a moss. 21. Label and explain the moss life cycle on the handout. List whether the chromosome number is “n” (haploi ...
... 20. Which stage of the life cycle (gametophyte or sporophyte) is dominant in non vascular plants? By dominant I mean large in size, it’s the main part of the plant you see when viewing a moss. 21. Label and explain the moss life cycle on the handout. List whether the chromosome number is “n” (haploi ...
Fact Sheet: Nodding Thistle
... thistle has a long history as a rangeland pest. The invasive nature of this aggressive plant can lead to severe degradation of native grasslands and meadows because grazing animals focus on native vegetation giving the thistles a competitive advantage. It develops a long, fleshy taproot that becomes ...
... thistle has a long history as a rangeland pest. The invasive nature of this aggressive plant can lead to severe degradation of native grasslands and meadows because grazing animals focus on native vegetation giving the thistles a competitive advantage. It develops a long, fleshy taproot that becomes ...
Ch. 39 Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals
... ex. poinsettias, chrysanthemums, some soybeans Longday plants a plant that flowers (usually in late spring or early summer) only when the light period is longer than a critical length ex. spinach, radish, lettuce,iris Dayneutral plants plants that are unaffected by photoperiod and flower wh ...
... ex. poinsettias, chrysanthemums, some soybeans Longday plants a plant that flowers (usually in late spring or early summer) only when the light period is longer than a critical length ex. spinach, radish, lettuce,iris Dayneutral plants plants that are unaffected by photoperiod and flower wh ...
the science of spring-flowering bulbs
... plant with enough nutrients to ensure the plants survival when it’s resting or waiting to be planted, said Martha Stevens, public landscapes manager at the Delaware Center for Horticulture. Botanically speaking, a bulb is a modified stem containing a miniature plant surrounded by fleshy scales, whic ...
... plant with enough nutrients to ensure the plants survival when it’s resting or waiting to be planted, said Martha Stevens, public landscapes manager at the Delaware Center for Horticulture. Botanically speaking, a bulb is a modified stem containing a miniature plant surrounded by fleshy scales, whic ...
PowerPoint - University of Missouri Extension
... Reduced plant growth Possible early defoliation and death Thrive ...
... Reduced plant growth Possible early defoliation and death Thrive ...
Occurence of Aster amellus L. in Penza region is noted both for the
... occurs both at the lower and the upper sides of the blades. The cells of both layers densely adjoin to each other indicating that there is sufficient light on both sides of the blade. However, at the top of the leaves from steppe plants columnar mesophyll forms two layers of cells, and the bottom – ...
... occurs both at the lower and the upper sides of the blades. The cells of both layers densely adjoin to each other indicating that there is sufficient light on both sides of the blade. However, at the top of the leaves from steppe plants columnar mesophyll forms two layers of cells, and the bottom – ...
The Land Plants - Del Mar College
... Beginnings and Endings Land plants provide oxygen, food, and shelter to humans and animals, but human activities are pushing some species toward extinction ...
... Beginnings and Endings Land plants provide oxygen, food, and shelter to humans and animals, but human activities are pushing some species toward extinction ...
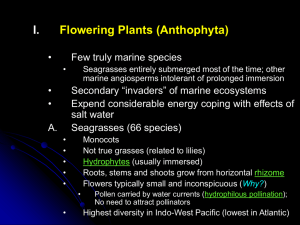
Feb 19 - University of San Diego
... Co-occur with coral reefs but more tolerant of temperature extremes than hermatypic corals and occur over a wider geographic range Maximum diversity in Indo-West Pacific ...
... Co-occur with coral reefs but more tolerant of temperature extremes than hermatypic corals and occur over a wider geographic range Maximum diversity in Indo-West Pacific ...
Investigative study of angiosperms morphology - Bij Javia
... The root system grows downwards into the soil and anchors the plant. It also absorbs water and essential minerals from the soil. On the other hand the shoot system comprising of the stem and the leaves grow upwards. It helps in synthesis of food and its translocation to various parts of the plant. T ...
... The root system grows downwards into the soil and anchors the plant. It also absorbs water and essential minerals from the soil. On the other hand the shoot system comprising of the stem and the leaves grow upwards. It helps in synthesis of food and its translocation to various parts of the plant. T ...
PLANT POLYPLOIDY AND INSECT/PLANT
... have not been designed to evaluate systematically the effect of polyploidy on the geographic pattern of attack of plant enemies across populations. Consequently, whether plant polyploidy can actually create a geographic and evolutionary barrier to enemy attack remains untested. The evolutionary barr ...
... have not been designed to evaluate systematically the effect of polyploidy on the geographic pattern of attack of plant enemies across populations. Consequently, whether plant polyploidy can actually create a geographic and evolutionary barrier to enemy attack remains untested. The evolutionary barr ...
PDF - CLIMBERS - University of Michigan
... below ground, thus the common name (3). Seedlings bear simple leaves as the first leaves to show above ground but are rapidly replaced by typical trifoliate leaves (see image). Dispersal Syndrome: Trapp (6) found that the seeds of both types of fruits are ballistically dispersed, with the aerial fru ...
... below ground, thus the common name (3). Seedlings bear simple leaves as the first leaves to show above ground but are rapidly replaced by typical trifoliate leaves (see image). Dispersal Syndrome: Trapp (6) found that the seeds of both types of fruits are ballistically dispersed, with the aerial fru ...
1 National Science Teachers Association Discovering Science
... Instruction (I/Teacher’s role) Discuss key content words (plants, root systems, erosion, tap root system, fibrous root system). Plants are living organisms. (Trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, and ferns are plants.) Plants give us food, wood, and also change carbon dioxide into oxygen, which ...
... Instruction (I/Teacher’s role) Discuss key content words (plants, root systems, erosion, tap root system, fibrous root system). Plants are living organisms. (Trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, and ferns are plants.) Plants give us food, wood, and also change carbon dioxide into oxygen, which ...
Plant Adaptations - Science.kennesaw.edu
... Carnivorous Plants Carnivorous plants have adapted to living in nutrient-poor environments. To supplement their diet they attract, capture, kill and digest animals; this is how they derive their nutrients. Carnivorous plants are not very different from other plants. They still have leaves that phot ...
... Carnivorous Plants Carnivorous plants have adapted to living in nutrient-poor environments. To supplement their diet they attract, capture, kill and digest animals; this is how they derive their nutrients. Carnivorous plants are not very different from other plants. They still have leaves that phot ...
roots lesson plan - NSTA Communities
... Instruction (I/Teacher’s role) Discuss key content words (plants, root systems, erosion, tap root system, fibrous root system). Plants are living organisms. (Trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, and ferns are plants.) Plants give us food, wood, and also change carbon dioxide into oxygen, which ...
... Instruction (I/Teacher’s role) Discuss key content words (plants, root systems, erosion, tap root system, fibrous root system). Plants are living organisms. (Trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, and ferns are plants.) Plants give us food, wood, and also change carbon dioxide into oxygen, which ...
plants.plans
... Tell students, “Roots are essential to plants. Roots anchor (hold plants in the ground and keep them from being washed away.) plants and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. When a seed begins to grow, the roots always grow first. Gravity causes the roots to grow down towards the earth and the ...
... Tell students, “Roots are essential to plants. Roots anchor (hold plants in the ground and keep them from being washed away.) plants and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. When a seed begins to grow, the roots always grow first. Gravity causes the roots to grow down towards the earth and the ...
Chp 14 Plant tropisms - AdventuresinScienceEducation
... Plant hormones are less specific than animal hormones. Some hormones work together to produce an effect. Hormones are slow to act as they need to travel via the phloem. The effect of hormones are long lasting. ...
... Plant hormones are less specific than animal hormones. Some hormones work together to produce an effect. Hormones are slow to act as they need to travel via the phloem. The effect of hormones are long lasting. ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... plants that produce flowers and fruits. They are the most diverse and geographically widespread of all plants, including more than 90% of plant species. There are about 250,000 known species of angiosperms. All angiosperms are placed in a single phylum, the phylum Anthophyta. The flower is the ...
... plants that produce flowers and fruits. They are the most diverse and geographically widespread of all plants, including more than 90% of plant species. There are about 250,000 known species of angiosperms. All angiosperms are placed in a single phylum, the phylum Anthophyta. The flower is the ...
Weed Identification Poster
... Fact Sheet: http://www.dpi.qld.gov.au/documents/Biosecurity_EnvironmentalPests/IPA-African-BoxthornPP8.pdf ...
... Fact Sheet: http://www.dpi.qld.gov.au/documents/Biosecurity_EnvironmentalPests/IPA-African-BoxthornPP8.pdf ...
Plant Diversity II - The Evolution of Seed Plants
... plants that produce flowers and fruits. They are the most diverse and geographically widespread of all plants, including more than 90% of plant species. There are about 250,000 known species of angiosperms. All angiosperms are placed in a single phylum, the phylum Anthophyta. The flower is the ...
... plants that produce flowers and fruits. They are the most diverse and geographically widespread of all plants, including more than 90% of plant species. There are about 250,000 known species of angiosperms. All angiosperms are placed in a single phylum, the phylum Anthophyta. The flower is the ...
Web link - Biobits
... economic value. In recent years soil bacteria have garnered attention in the context of plant-fungal symbioses, as many bacterial populations have been found to be loosely or tightly associated with mycorrhizal fungi, most likely playing a role in mycorrhizal function. They seem therefore to represe ...
... economic value. In recent years soil bacteria have garnered attention in the context of plant-fungal symbioses, as many bacterial populations have been found to be loosely or tightly associated with mycorrhizal fungi, most likely playing a role in mycorrhizal function. They seem therefore to represe ...
Cotton: non-chemical pest control
... An especially important aspect is the crop rotation. Crop rotation ensures that on one and the same field different crops are grown for a period of two to three consecutive years. Monoculture, which makes it easy for so-called pests to find their favourite source of food regularly in the same place, ...
... An especially important aspect is the crop rotation. Crop rotation ensures that on one and the same field different crops are grown for a period of two to three consecutive years. Monoculture, which makes it easy for so-called pests to find their favourite source of food regularly in the same place, ...
Plant Form and Function Intro
... – Some plants have to have less than some specific number of hours of light to flower. – These plants are called Short Day Plants. SDP. – Others have to be more than some minimum numbers of hours. – These plants are referred to as Long Day Plants. LDP. ...
... – Some plants have to have less than some specific number of hours of light to flower. – These plants are called Short Day Plants. SDP. – Others have to be more than some minimum numbers of hours. – These plants are referred to as Long Day Plants. LDP. ...
Section 1-Maggie-final_AM
... At Group 5, you will have another key which includes all those plants fitting the above description, but this key now includes letters as well as numerals on the right hand side. These represent the subgroups. Thus the hypothetical tree would be found under Group 5.D or Group 5.E depending on whethe ...
... At Group 5, you will have another key which includes all those plants fitting the above description, but this key now includes letters as well as numerals on the right hand side. These represent the subgroups. Thus the hypothetical tree would be found under Group 5.D or Group 5.E depending on whethe ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.