Unit 6 Ecology Ecology – How organisms interact with both living
... • Diversity is essential in ecosystems since all populations are linked directly or indirectly. Ecological niche – The role or part of the ecosystem a species occupies. • only one or two species can occupy a niche • Competiton and the species best suited will occupy the particular niche. • Sometimes ...
... • Diversity is essential in ecosystems since all populations are linked directly or indirectly. Ecological niche – The role or part of the ecosystem a species occupies. • only one or two species can occupy a niche • Competiton and the species best suited will occupy the particular niche. • Sometimes ...
Ecology HARDCOPY - New Hartford Central Schools
... 2. What would happen if all the producers became extinct? All other forms of life that depend on them would also die. ...
... 2. What would happen if all the producers became extinct? All other forms of life that depend on them would also die. ...
Subtopic (b) How it works
... A Pyramid of Numbers shows the number of living things at each level in a food chain. A Pyramid of Biomass shows the total mass ( weight) of living material at each level in the food chain. A Pyramid of Biomass is the more accurate way of displaying how much energy is available at each level because ...
... A Pyramid of Numbers shows the number of living things at each level in a food chain. A Pyramid of Biomass shows the total mass ( weight) of living material at each level in the food chain. A Pyramid of Biomass is the more accurate way of displaying how much energy is available at each level because ...
Section 1
... Tip: Foxfire is a mushroom. Mushrooms are organisms classified as fungi (singular- fungus). They are not plants as they have no leaves and no chlorophyll to make their own food by photosynthesis. They depend on other organisms for their food so can be found growing on plants and animals. 6. B. attra ...
... Tip: Foxfire is a mushroom. Mushrooms are organisms classified as fungi (singular- fungus). They are not plants as they have no leaves and no chlorophyll to make their own food by photosynthesis. They depend on other organisms for their food so can be found growing on plants and animals. 6. B. attra ...
9_foraging - WordPress.com
... Researchers at Vanderbilt University have found that the star-nosed mole can eat 10 mouthful-size chunks of earthworm, one at a time, in 2.3 seconds, or 0.23 second a chunk. It is the fastest eating ever measured in any mammal. ...
... Researchers at Vanderbilt University have found that the star-nosed mole can eat 10 mouthful-size chunks of earthworm, one at a time, in 2.3 seconds, or 0.23 second a chunk. It is the fastest eating ever measured in any mammal. ...
TAKS Objective 3
... Which of these is the best example of a mutualistic relationship in an aquatic environment? F Some fish can survive repeated infections by harmful bacteria. • G Some fish have bacteria living in their digestive tract that help the fish digest food. • H Some bacteria are present in aquatic food chain ...
... Which of these is the best example of a mutualistic relationship in an aquatic environment? F Some fish can survive repeated infections by harmful bacteria. • G Some fish have bacteria living in their digestive tract that help the fish digest food. • H Some bacteria are present in aquatic food chain ...
Food chains and food webs
... Food webs are more complex, showing more interrelationships. They give a more accurate picture of the ecosystem. They are made of many food chains and have multiple energy paths. ...
... Food webs are more complex, showing more interrelationships. They give a more accurate picture of the ecosystem. They are made of many food chains and have multiple energy paths. ...
NOTES_Ecology Student version
... chemicals and acid rain from factory smoke Toxic wastes in water moves through the food chain and become most concentrated in organisms at the top of the chain (like humans) Air – releasing harmful substances into the air ...
... chemicals and acid rain from factory smoke Toxic wastes in water moves through the food chain and become most concentrated in organisms at the top of the chain (like humans) Air – releasing harmful substances into the air ...
Digestive and Circulatory Systems
... 6. Discuss the impact of change of diet on Aboriginal populations and other peoples from traditional foods to diets high in starch, refined sugars and trans fats. ...
... 6. Discuss the impact of change of diet on Aboriginal populations and other peoples from traditional foods to diets high in starch, refined sugars and trans fats. ...
Part I: The Chain vs. the Web Fundamental Question: How does
... Fundamental Question: How does energy flow in a food chain and food web? The example on the right is a food chain. The arrows show how energy flows through the food chain by indicating what organism is eaten by another organism. The base of the food chain is the producer, grass. The grass obtained g ...
... Fundamental Question: How does energy flow in a food chain and food web? The example on the right is a food chain. The arrows show how energy flows through the food chain by indicating what organism is eaten by another organism. The base of the food chain is the producer, grass. The grass obtained g ...
Trophic Levels
... • Blocks are stacked on top of one another, with the lowest trophic level on the bottom. The width of each block is determined by the amount of energy stored in the organisms at that trophic level. Because the energy stored by the organisms at each trophic level is about one-tenth the energy stored ...
... • Blocks are stacked on top of one another, with the lowest trophic level on the bottom. The width of each block is determined by the amount of energy stored in the organisms at that trophic level. Because the energy stored by the organisms at each trophic level is about one-tenth the energy stored ...
Chapter 2.2 – Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem
... start with energy from Carnivore the sun Level 2 Primary consumer first level of all food chains is plants Herbivore most food chains Level 1 Producer usually go up only 4 or 5 levels all levels connect to Decomposers decomposers Bacteria ...
... start with energy from Carnivore the sun Level 2 Primary consumer first level of all food chains is plants Herbivore most food chains Level 1 Producer usually go up only 4 or 5 levels all levels connect to Decomposers decomposers Bacteria ...
Interactions and Ecosystems Study Guide 1. Describe the difference
... Is the first species to arrive to an ecosystem that was devoid of life before it arrived. These species tend to be plants that can survive in harsh conditions and have adaptations that allow to grow when little soil is present 18. Explain how things like pesticides can have ‘unintended consequences’ ...
... Is the first species to arrive to an ecosystem that was devoid of life before it arrived. These species tend to be plants that can survive in harsh conditions and have adaptations that allow to grow when little soil is present 18. Explain how things like pesticides can have ‘unintended consequences’ ...
Notes
... nutrients made by autotrophs is passed on to heterotrophs, and only a small amount is passed to each succeeding consumer; much energy is used at each level for cellular respiration and much is lost as heat. Ecosystems are dependent on a continual supply of solar energy. The laws of thermodynamics su ...
... nutrients made by autotrophs is passed on to heterotrophs, and only a small amount is passed to each succeeding consumer; much energy is used at each level for cellular respiration and much is lost as heat. Ecosystems are dependent on a continual supply of solar energy. The laws of thermodynamics su ...
Ecology Terms
... Parasite: a living organism that lives with and feeds off another living organism causing it harm. Pollution: is any human addition to the environment that leaves it less able to sustain life. It is the most harmful human impact and affects air, fresh water, sea and land. Chemicals of human origin t ...
... Parasite: a living organism that lives with and feeds off another living organism causing it harm. Pollution: is any human addition to the environment that leaves it less able to sustain life. It is the most harmful human impact and affects air, fresh water, sea and land. Chemicals of human origin t ...
Ecology Dictionary
... Parasite: a living organism that lives with and feeds off another living organism causing it harm. Pollution: is any human addition to the environment that leaves it less able to sustain life. It is the most harmful human impact and affects air, fresh water, sea and land. Chemicals of human origin t ...
... Parasite: a living organism that lives with and feeds off another living organism causing it harm. Pollution: is any human addition to the environment that leaves it less able to sustain life. It is the most harmful human impact and affects air, fresh water, sea and land. Chemicals of human origin t ...
Food and Agriculture Section 1 The Green Revolution
... • Yield is the amount of crops produced per unit area. • Researchers are interested in organisms that can thrive in various climates and that do not require large amounts of fertilizer, pesticides, or fresh water. Some organisms have been a source of food for centuries, while other sources are just ...
... • Yield is the amount of crops produced per unit area. • Researchers are interested in organisms that can thrive in various climates and that do not require large amounts of fertilizer, pesticides, or fresh water. Some organisms have been a source of food for centuries, while other sources are just ...
The Ecosystem
... An abiotic factor can limit the population size if there is too much or too little of it. Even if there is the right amount of other factors Examples to consider: ...
... An abiotic factor can limit the population size if there is too much or too little of it. Even if there is the right amount of other factors Examples to consider: ...
Feeding Relationships
... Organism that obtains food by consuming other living things, also called a consumer. ...
... Organism that obtains food by consuming other living things, also called a consumer. ...
Living things are . . .
... 35 Clown fish are small reef fish that seek protection from predators by sheltering themselves among the stinging tentacles of sea anemones. Clown fish are very territorial and can potentially scare off predators of sea anemones. This relationship is an example of -A neutralism This is not a type o ...
... 35 Clown fish are small reef fish that seek protection from predators by sheltering themselves among the stinging tentacles of sea anemones. Clown fish are very territorial and can potentially scare off predators of sea anemones. This relationship is an example of -A neutralism This is not a type o ...
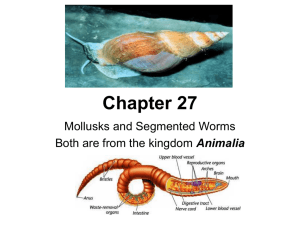
Chapter 27
... Mouth-takes in food Crop-stores food until it can be broken down Gizzard-has stone-like structures that grind up soil/food until tiny pieces can be absorbed by the intestines Nephridia-structures that eliminate waste found on each segment Setae-tiny hairs that extend from each segment – Anchors worm ...
... Mouth-takes in food Crop-stores food until it can be broken down Gizzard-has stone-like structures that grind up soil/food until tiny pieces can be absorbed by the intestines Nephridia-structures that eliminate waste found on each segment Setae-tiny hairs that extend from each segment – Anchors worm ...
The Biosphere Summary
... 11. * When growing crops a farmer is creating and controlling an artificial ecosystem. 1. The soil must be kept fertile and with good structure, for this fertilisers are used. 2. Pests and pesticides must be kept at bay, for this pesticides are used. 3. Weeds that compete with the crop species must ...
... 11. * When growing crops a farmer is creating and controlling an artificial ecosystem. 1. The soil must be kept fertile and with good structure, for this fertilisers are used. 2. Pests and pesticides must be kept at bay, for this pesticides are used. 3. Weeds that compete with the crop species must ...
Local food

Local food or the local food movement is a movement which aims to connect food producers and food consumers in the same geographic region; in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks, improve local economies, or for health, environmental, community, or social impact in a particular place. The term has also been extended to include not only geographic location of supplier and consumer but can also be ""defined in terms of social and supply chain characteristics."" For example, local food initiatives often promote sustainable and organic farming practices, although these are not explicitly related to the geographic proximity of the producer and consumer.Local food represents an alternative to the global food model, a model which often sees food travelling long distances before it reaches the consumer. A local food network involves relationships between food producers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a particular place where they work together to increase food security and ensure economic, ecological and social sustainability of a community