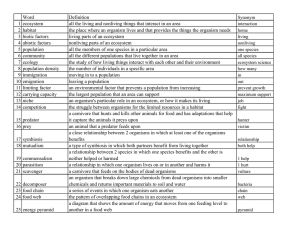
Ecology Review Sheet. KEY
... Using the food web above, decide which organisms are a. Producers (1): algae b. primary consumers (3): fish, krill, blue whales c. secondary consumers (5): fish, blue whales, birds, killer whales, seals d. both primary and secondary consumers (2): fish, blue whales Using the food web above answer th ...
... Using the food web above, decide which organisms are a. Producers (1): algae b. primary consumers (3): fish, krill, blue whales c. secondary consumers (5): fish, blue whales, birds, killer whales, seals d. both primary and secondary consumers (2): fish, blue whales Using the food web above answer th ...
The Needs of Living Things
... • All organisms need a place to live and get food, water, and shelter. • No matter where an organism lives, it must provide what it needs to survive. • Because there is a limited amount of space on Earth, some organisms compete for space. • Trees in a forest complete for sunlight above ground. • Bel ...
... • All organisms need a place to live and get food, water, and shelter. • No matter where an organism lives, it must provide what it needs to survive. • Because there is a limited amount of space on Earth, some organisms compete for space. • Trees in a forest complete for sunlight above ground. • Bel ...
Ecosystem Interaction Practice
... 1 a) The following organisms in the food web are producers: ______________________ b) Producers are also known as ___________________________ c) The field mice in this food web are classified as ______________ consumers and occupy the ________ trophic level. d) The highest trophic level a bass could ...
... 1 a) The following organisms in the food web are producers: ______________________ b) Producers are also known as ___________________________ c) The field mice in this food web are classified as ______________ consumers and occupy the ________ trophic level. d) The highest trophic level a bass could ...
Life Science Study Guide Environment – Everything that surrounds
... Decomposer – An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals and returns the nutrients to the soil. Bacteria, fungi (mushrooms and yeast), termites, and earthworms are examples of decomposers. Plants then use the nutrients in the soil to help them grow. Herbivore – An herbivore is an organism t ...
... Decomposer – An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals and returns the nutrients to the soil. Bacteria, fungi (mushrooms and yeast), termites, and earthworms are examples of decomposers. Plants then use the nutrients in the soil to help them grow. Herbivore – An herbivore is an organism t ...
Ecology Test Review - DanaFrank
... a food web? Toxins increase in concentration as You move up a food chain/web. At each level the consumer gets a bigger dose with each meal. This is Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification ...
... a food web? Toxins increase in concentration as You move up a food chain/web. At each level the consumer gets a bigger dose with each meal. This is Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification ...
pdf
... indicators in an effort to build a process of understanding of lower food web components and their use as ecosystem indicators. A oneday workshop, featuring presentations from top scientists from the U.S. and Canada was organized to present this information to the public. Fifty attendees were educat ...
... indicators in an effort to build a process of understanding of lower food web components and their use as ecosystem indicators. A oneday workshop, featuring presentations from top scientists from the U.S. and Canada was organized to present this information to the public. Fifty attendees were educat ...
Lesson 1: Make the Connection - Michigan Sea Grant
... In reality, food chains overlap at many points—because animals often feed on multiple species—forming complex food webs. Food web diagrams depict all feeding interactions among species in real communities. These complex diagrams often appear as intricate spider webs connecting the species. See: Uni ...
... In reality, food chains overlap at many points—because animals often feed on multiple species—forming complex food webs. Food web diagrams depict all feeding interactions among species in real communities. These complex diagrams often appear as intricate spider webs connecting the species. See: Uni ...
Organisms and Their Environment
... • Energy originally comes from the sun • flows from producers to consumers – Producers (make food) – Consumers (use food by eating producers or other consumers) ...
... • Energy originally comes from the sun • flows from producers to consumers – Producers (make food) – Consumers (use food by eating producers or other consumers) ...
Who is the producer in this food web?
... Create a table like the one above in your biology notebook. Using your filled-in pyramid, write the name of the organism on each food chain card in the appropriate column in the table. ...
... Create a table like the one above in your biology notebook. Using your filled-in pyramid, write the name of the organism on each food chain card in the appropriate column in the table. ...
Ecology Definitions
... factors in a particular area; these factors are interacting and interdependent; they make up a self-contained system which is self supporting in terms of energy flow. ...
... factors in a particular area; these factors are interacting and interdependent; they make up a self-contained system which is self supporting in terms of energy flow. ...
The Marine Food Web
... third trophic level includes molluscan bivalves, amphipods, and larval forms of many fish and crustaceans as well as small fish such as alewife and menhaden. These finfish are schooling fish, and they can make a significant dent in the zooplankton population. A single adult menhaden, for example, ca ...
... third trophic level includes molluscan bivalves, amphipods, and larval forms of many fish and crustaceans as well as small fish such as alewife and menhaden. These finfish are schooling fish, and they can make a significant dent in the zooplankton population. A single adult menhaden, for example, ca ...
8 th Grade Health Unit 3 Study Guide
... Fiber – the part of fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans that your body cannot digest. ...
... Fiber – the part of fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans that your body cannot digest. ...
8 th Grade Health Unit 3 Study Guide
... Fiber – the part of fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans that your body cannot digest. ...
... Fiber – the part of fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans that your body cannot digest. ...
The Biosphere – Ch
... Studying Our Living Planet Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. Earth’s organisms live in the biosphere. The biosphere consists of the parts of the planet in which all life exists. Ecologists may study different levels of ecolog ...
... Studying Our Living Planet Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. Earth’s organisms live in the biosphere. The biosphere consists of the parts of the planet in which all life exists. Ecologists may study different levels of ecolog ...
Food Webs
... This loss of energy is one reason there are more primary consumers (herbivores) than secondary consumers (carnivores) – and so-on-and-soforth. Predators are rare compared to their prey. ...
... This loss of energy is one reason there are more primary consumers (herbivores) than secondary consumers (carnivores) – and so-on-and-soforth. Predators are rare compared to their prey. ...
Ecology Biomes - Peterson Science
... all the living and nonliving things that interact in an area the place where an organism lives and that provides the things the organism needs living parts of an ecosystem nonliving parts of an ecosystem all the members of one species in a particular area all the different populations that live toge ...
... all the living and nonliving things that interact in an area the place where an organism lives and that provides the things the organism needs living parts of an ecosystem nonliving parts of an ecosystem all the members of one species in a particular area all the different populations that live toge ...
Chapter 3 Notes - Prof-desk
... Community – all the living organisms found in an area. Ecosystem – all the organisms that live in a place, along with their environment. Biome – group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. Biosphere – the combined portions on Earth where living things are found. ...
... Community – all the living organisms found in an area. Ecosystem – all the organisms that live in a place, along with their environment. Biome – group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. Biosphere – the combined portions on Earth where living things are found. ...
Organisms and Environment Ecosystems
... Changes in environmental conditions can affect the survival of individual organisms and entire species Long- term environmental changes, like climate change, can permanently alter an ecosystem, but over time the change, may cause genetic variations to become more favorable or less favorable in the n ...
... Changes in environmental conditions can affect the survival of individual organisms and entire species Long- term environmental changes, like climate change, can permanently alter an ecosystem, but over time the change, may cause genetic variations to become more favorable or less favorable in the n ...
Food groups - Excellence Gateway
... maintain their own health and the health of their families. Other learners may have specific conditions such as heart disease, diabetes and high blood pressure where a healthy approach to eating is essential. Healthy eating can be tasty and interesting. The key is to eat a variety of different foods ...
... maintain their own health and the health of their families. Other learners may have specific conditions such as heart disease, diabetes and high blood pressure where a healthy approach to eating is essential. Healthy eating can be tasty and interesting. The key is to eat a variety of different foods ...
Symbiosis
... The bird does not harm the tree by preparing a nest in the tree branches. But, the bird needs the tree to make a nest that is high up, and protected from predators. ...
... The bird does not harm the tree by preparing a nest in the tree branches. But, the bird needs the tree to make a nest that is high up, and protected from predators. ...
Symbiotic Relationships
... The bird does not harm the tree by preparing a nest in the tree branches. But, the bird needs the tree to make a nest that is high up, and protected from predators. ...
... The bird does not harm the tree by preparing a nest in the tree branches. But, the bird needs the tree to make a nest that is high up, and protected from predators. ...
Ecology Review Draw a diagram of a marine food chain and label
... Habitat Destruction, Sea Level Rise, Marine Invasive Species 32. What are some affects that solid waste can have on ocean organisms? Animals can get tangled up in debris and drown, sea turtles and other animals eat plastic, mistaking it for food 33. How does runoff affect coral reef systems? Nitroge ...
... Habitat Destruction, Sea Level Rise, Marine Invasive Species 32. What are some affects that solid waste can have on ocean organisms? Animals can get tangled up in debris and drown, sea turtles and other animals eat plastic, mistaking it for food 33. How does runoff affect coral reef systems? Nitroge ...
Ecology Review 1. Draw a diagram of a marine food chain and label
... Habitat Destruction, Sea Level Rise, Marine Invasive Species 32. What are some affects that solid waste can have on ocean organisms? Animals can get tangled up in debris and drown, sea turtles and other animals eat plastic, mistaking it for food 33. How does runoff affect coral reef systems? Nitroge ...
... Habitat Destruction, Sea Level Rise, Marine Invasive Species 32. What are some affects that solid waste can have on ocean organisms? Animals can get tangled up in debris and drown, sea turtles and other animals eat plastic, mistaking it for food 33. How does runoff affect coral reef systems? Nitroge ...
Examining the Stages in Ecological Succession
... The relationship is that of predation. One primary consumer feeding on the producer and a secondary consumer(carnivore) feeding on the primary consumer(herbivore). Q3. Which organisms are producers, and which are consumers? Nitella is the aquatic producer. Snails are primary consumers and minnows ar ...
... The relationship is that of predation. One primary consumer feeding on the producer and a secondary consumer(carnivore) feeding on the primary consumer(herbivore). Q3. Which organisms are producers, and which are consumers? Nitella is the aquatic producer. Snails are primary consumers and minnows ar ...
Local food

Local food or the local food movement is a movement which aims to connect food producers and food consumers in the same geographic region; in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks, improve local economies, or for health, environmental, community, or social impact in a particular place. The term has also been extended to include not only geographic location of supplier and consumer but can also be ""defined in terms of social and supply chain characteristics."" For example, local food initiatives often promote sustainable and organic farming practices, although these are not explicitly related to the geographic proximity of the producer and consumer.Local food represents an alternative to the global food model, a model which often sees food travelling long distances before it reaches the consumer. A local food network involves relationships between food producers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a particular place where they work together to increase food security and ensure economic, ecological and social sustainability of a community