Foods, Nutrition and Health
... Fibre is also an essential component of our diet. The functions of nutrients are given below. Carbohydrates: Starch found in cereals and sugar in sugarcane and fruits are examples of carbohydrates in foods. The chief function of carbohydrates is to provide energy needed by our body. Those not used i ...
... Fibre is also an essential component of our diet. The functions of nutrients are given below. Carbohydrates: Starch found in cereals and sugar in sugarcane and fruits are examples of carbohydrates in foods. The chief function of carbohydrates is to provide energy needed by our body. Those not used i ...
Part 1: Everything is Connected
... Producers: Organisms that use ______________________________________________________________ Mostly ________________________ but also ______________________________, bacteria and plankton Identify the main producers in the following ecosystems: Prairie-Forest-Beach— Consumers: They get the energ ...
... Producers: Organisms that use ______________________________________________________________ Mostly ________________________ but also ______________________________, bacteria and plankton Identify the main producers in the following ecosystems: Prairie-Forest-Beach— Consumers: They get the energ ...
Lesson 3 - Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... A representation of the feeding relationships within a ...
... A representation of the feeding relationships within a ...
Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
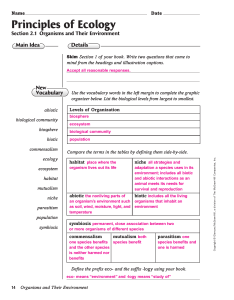
... Levels of Organization in Ecology Need to study more than just an individual to get the whole story Need to study relationships or interactions among organisms of the same and different species ...
... Levels of Organization in Ecology Need to study more than just an individual to get the whole story Need to study relationships or interactions among organisms of the same and different species ...
Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
... Need to study more than just an individual to get the whole story Need to study relationships or interactions among organisms of the same and different species ...
... Need to study more than just an individual to get the whole story Need to study relationships or interactions among organisms of the same and different species ...
Concept Review
... are a result of thousands of years of artificial selection. Humans bred the ancestors of today’s wolves to produce the variety of dogs we have today. Wolves and different kinds of dogs are closely related. 15. Disagree; antibiotics may kill many bacteria, but the bacteria that remain are more resist ...
... are a result of thousands of years of artificial selection. Humans bred the ancestors of today’s wolves to produce the variety of dogs we have today. Wolves and different kinds of dogs are closely related. 15. Disagree; antibiotics may kill many bacteria, but the bacteria that remain are more resist ...
Real Food Web - SD43 Teacher Sites
... of "drift") by abalones, sea urchins, mussels, and barnacles. Many of these animals are then consumed by mid-level predators, such as other sea stars, larger crabs, larger fishes, and octopuses. The sea otter, at the top of the diagram, plays a key role in the community. Because they lack the blubbe ...
... of "drift") by abalones, sea urchins, mussels, and barnacles. Many of these animals are then consumed by mid-level predators, such as other sea stars, larger crabs, larger fishes, and octopuses. The sea otter, at the top of the diagram, plays a key role in the community. Because they lack the blubbe ...
Predation, Mutualism, Commensalism, or Parasitism
... living organism(called its host). The organism which obtains food is called parasite and the organism from whose body food is obtained is called host. Example of parasite –roundworm in animals, Phytophthora infestans ...
... living organism(called its host). The organism which obtains food is called parasite and the organism from whose body food is obtained is called host. Example of parasite –roundworm in animals, Phytophthora infestans ...
Ecology
... interactions of living organisms with one another and with their physical environment (soil, water, climate…) • ECO = house • LOGY = the study of ...
... interactions of living organisms with one another and with their physical environment (soil, water, climate…) • ECO = house • LOGY = the study of ...
Four Winds Nature Institute
... PREDATORS AND PREY: Herbivores and carnivores both must eat, but the challenges these two groups of animals face in getting enough to eat are very different. Plant eaters don't have to stalk their food, but they do need to keep from being eaten while they browse. And carnivores spend lots of time an ...
... PREDATORS AND PREY: Herbivores and carnivores both must eat, but the challenges these two groups of animals face in getting enough to eat are very different. Plant eaters don't have to stalk their food, but they do need to keep from being eaten while they browse. And carnivores spend lots of time an ...
- The University of Liverpool Repository
... cultural, environment and socioeconomic factors) limit generalizability of data to regions other than where studies are conducted (27). Thus research into accessibility of foods remains challenging and, as it stands, the evidence base is not substantial enough to drive government policy intervention ...
... cultural, environment and socioeconomic factors) limit generalizability of data to regions other than where studies are conducted (27). Thus research into accessibility of foods remains challenging and, as it stands, the evidence base is not substantial enough to drive government policy intervention ...
Ecological Pyramids Foldable
... 7. When you are finished, fold the blank flap of your foldable underneath the other three flaps and glue the flaps together to finish your ecological pyramids foldable! ...
... 7. When you are finished, fold the blank flap of your foldable underneath the other three flaps and glue the flaps together to finish your ecological pyramids foldable! ...
File
... Cycle: Autotrophs then extract these materials from the soil and use them to manufacture food. Thus the process of decomposition recycles chemical nutrients, making them available to the producers again. This cycle is repeated over and over in the same ecosystem. 3. Energy flow: Food chains. Lindema ...
... Cycle: Autotrophs then extract these materials from the soil and use them to manufacture food. Thus the process of decomposition recycles chemical nutrients, making them available to the producers again. This cycle is repeated over and over in the same ecosystem. 3. Energy flow: Food chains. Lindema ...
ExamView Pro - Chapter 16 TeamStudyWorksheet.tst
... 20. What are omnivores? 21. Explain the difference between detritivores and decomposers. 22. What is a food web? 23. What happens to the amount of energy as it is transferred from one trophic level to another? Why? 24. What is an ecological pyramid? 25. Explain why food chains do not normally exceed ...
... 20. What are omnivores? 21. Explain the difference between detritivores and decomposers. 22. What is a food web? 23. What happens to the amount of energy as it is transferred from one trophic level to another? Why? 24. What is an ecological pyramid? 25. Explain why food chains do not normally exceed ...
Assessment of Energy Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the
... Energy use in food production, processing, transport, and consumption has long been a topic of study. Some of the most widely cited work on the topic originated with Pimentel and Pimentel (1979, updated 1996; also Pimentel 1980), who used an input/output model to quantify energy requirements of indu ...
... Energy use in food production, processing, transport, and consumption has long been a topic of study. Some of the most widely cited work on the topic originated with Pimentel and Pimentel (1979, updated 1996; also Pimentel 1980), who used an input/output model to quantify energy requirements of indu ...
Food Labeling: Allergy Information Summary Donna V. Porter Specialist in Life Sciences
... Observations on Food Allergy Labeling For food allergy sufferers, providing ingredient information that will facilitate their selection of foods that do not contain allergens should be useful. Easy identification, by use of a well-recognized symbol and/or specific terms or phrases on packages, as fr ...
... Observations on Food Allergy Labeling For food allergy sufferers, providing ingredient information that will facilitate their selection of foods that do not contain allergens should be useful. Easy identification, by use of a well-recognized symbol and/or specific terms or phrases on packages, as fr ...
Food Chains - Montgomery County Schools
... area, as well as the non-living parts of their environment, is called an ecosystem. Example: deer + rabbits + bears + water + temperature + sunlight + soil + air ...
... area, as well as the non-living parts of their environment, is called an ecosystem. Example: deer + rabbits + bears + water + temperature + sunlight + soil + air ...
Lecture 6 - life.illinois.edu
... 13. What is the function of the locust descending contralateral movement detectors (DCMDs)? a. they detect the presence of the horizon b. they detect impending collisions c. they detect the presence of an overhead swarm d. they detect approaching predators 14. True or false: Locusts can eat their o ...
... 13. What is the function of the locust descending contralateral movement detectors (DCMDs)? a. they detect the presence of the horizon b. they detect impending collisions c. they detect the presence of an overhead swarm d. they detect approaching predators 14. True or false: Locusts can eat their o ...
topics covered – 7th grade ecology district test
... Be able to give examples of populations living in a typical New Jersey forest Know the difference between an ecosystem and a community Be able to give specific examples of commensalism, mutualism and parasitism in a typical New Jersey forest Tell why predators are necessary for maintaining b ...
... Be able to give examples of populations living in a typical New Jersey forest Know the difference between an ecosystem and a community Be able to give specific examples of commensalism, mutualism and parasitism in a typical New Jersey forest Tell why predators are necessary for maintaining b ...
Nitrogen cycle review - North Penn School District
... The Mute Swan is a species of bird with an orange-reddish bill and white feathers. It is naturally found in Europe and Asia but can sometimes be found in the United States as a result of the importation of these non-native birds. 10. Mute Swans are one of the heaviest flying birds and consume up to ...
... The Mute Swan is a species of bird with an orange-reddish bill and white feathers. It is naturally found in Europe and Asia but can sometimes be found in the United States as a result of the importation of these non-native birds. 10. Mute Swans are one of the heaviest flying birds and consume up to ...
Science Notebook Chapter 2 - Answer Key
... Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
... Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
Trophic level
... Trophic position – trophic height of species. Considers diet and energy flow pathways. Species can fall between trophic levels. Omnivory – feeding on more than one trophic level ...
... Trophic position – trophic height of species. Considers diet and energy flow pathways. Species can fall between trophic levels. Omnivory – feeding on more than one trophic level ...
Local food

Local food or the local food movement is a movement which aims to connect food producers and food consumers in the same geographic region; in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks, improve local economies, or for health, environmental, community, or social impact in a particular place. The term has also been extended to include not only geographic location of supplier and consumer but can also be ""defined in terms of social and supply chain characteristics."" For example, local food initiatives often promote sustainable and organic farming practices, although these are not explicitly related to the geographic proximity of the producer and consumer.Local food represents an alternative to the global food model, a model which often sees food travelling long distances before it reaches the consumer. A local food network involves relationships between food producers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a particular place where they work together to increase food security and ensure economic, ecological and social sustainability of a community