7-1-10 - Food Chain
... This simulation related a lot more to Boohan’s article than Millar’s article. As far as Boohan’s ideas about simulations we think this simulation is a good simulation because it takes something big like an ecosystem and looks at a simple interaction that occurs in every ecosystem. The food chain is ...
... This simulation related a lot more to Boohan’s article than Millar’s article. As far as Boohan’s ideas about simulations we think this simulation is a good simulation because it takes something big like an ecosystem and looks at a simple interaction that occurs in every ecosystem. The food chain is ...
Study Guide KEY - Kawameeh Middle School
... When predator population size increases – prey will decrease When predator population size decrease – prey will over populate 20. Define producer: an organism that creates its own energy from sunlight; first organism in food chain 21. Define decomposer: organism that breaks down dead organisms and r ...
... When predator population size increases – prey will decrease When predator population size decrease – prey will over populate 20. Define producer: an organism that creates its own energy from sunlight; first organism in food chain 21. Define decomposer: organism that breaks down dead organisms and r ...
Chapter 11. Diversification of the Eukaryotes: Animals
... then consume the primary producers, the herbivores are consumed by carnivores, and the carnivores, in turn, may be consumed by top carnivores. ...
... then consume the primary producers, the herbivores are consumed by carnivores, and the carnivores, in turn, may be consumed by top carnivores. ...
“Sunergy - THE BASIC FIVE” Sunrider`s
... For a weak system eat extra system-specific food: 10 capsules a day, for 10 days or longer, for dramatic results; then 2-4 capsules/day for ongoing maintenance. Most people have Quinary – 3 to 10 capsules daily. ...
... For a weak system eat extra system-specific food: 10 capsules a day, for 10 days or longer, for dramatic results; then 2-4 capsules/day for ongoing maintenance. Most people have Quinary – 3 to 10 capsules daily. ...
Food webs and trophic levels in a grassland ecosystem
... already discussed. Pose the following questions to the students. What are producers? Where do they get their energy from? Producers are plants, algae, phytoplankton and some types of bacteria. Producers are also known as autotrophs. They make their own food ...
... already discussed. Pose the following questions to the students. What are producers? Where do they get their energy from? Producers are plants, algae, phytoplankton and some types of bacteria. Producers are also known as autotrophs. They make their own food ...
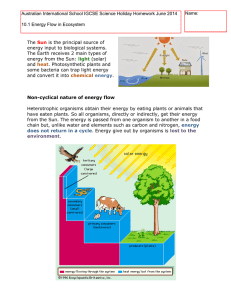
14 Ecosystem #138 Energy flow, energy loss The Sun
... plants) capture some of this energy and transfer it to organic substances such as carbohydrates. Consumers (animals and fungi) gets their energy by eating producers or other consumers. ...
... plants) capture some of this energy and transfer it to organic substances such as carbohydrates. Consumers (animals and fungi) gets their energy by eating producers or other consumers. ...
Ecology Core and Ecology Option
... • Explain that energy enters and leaves ecosystems, but nutrients must be recycled. ...
... • Explain that energy enters and leaves ecosystems, but nutrients must be recycled. ...
Ecology Note packet
... 1) Construct a food web using the animals listed below in the box. This ecosystem represents a farm area. The corn is the main source of food for many of the herbivores in the area. You do not have to draw pictures; you can just use the animal names and draw arrows between them. o CORN o SNAKE (eats ...
... 1) Construct a food web using the animals listed below in the box. This ecosystem represents a farm area. The corn is the main source of food for many of the herbivores in the area. You do not have to draw pictures; you can just use the animal names and draw arrows between them. o CORN o SNAKE (eats ...
Food webs and networks: the architecture of biodiversity
... • Lawton and Pimm: short chains were more stable than long chains (quicker return times), but re-analysis suggests that this may be a consequence of greater frequency of density-dependent selfregulation not food chain length ...
... • Lawton and Pimm: short chains were more stable than long chains (quicker return times), but re-analysis suggests that this may be a consequence of greater frequency of density-dependent selfregulation not food chain length ...
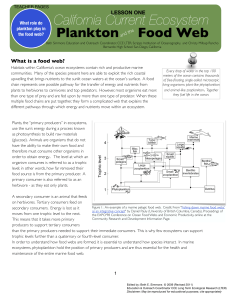
L3_fnl_Plankton Food Web_TEACHER
... Figure 1: An example of a marine pelagic food web. Credit: From "Fishing down marine food webs' secondary consumers. Energy is lost as it as an integrative concept" by Daniel Pauly (University of British Columbia, Canada), Proceedings of moves from one trophic level to the next. the EXPO'98 Conferen ...
... Figure 1: An example of a marine pelagic food web. Credit: From "Fishing down marine food webs' secondary consumers. Energy is lost as it as an integrative concept" by Daniel Pauly (University of British Columbia, Canada), Proceedings of moves from one trophic level to the next. the EXPO'98 Conferen ...
Insect populations—locusts
... 5. What prevents most populations from reaching their biotic potenetial? What is “biotic potential”? environmental resistance biotic potential is full reproductive potential without limits 6. Carrying capacity is (choose a or b): a. the number of viable eggs or embryos that a particular female can c ...
... 5. What prevents most populations from reaching their biotic potenetial? What is “biotic potential”? environmental resistance biotic potential is full reproductive potential without limits 6. Carrying capacity is (choose a or b): a. the number of viable eggs or embryos that a particular female can c ...
Version o1 o2
... First, label the pyramid levels (producers, primary consumers…). Next, using the food web on the left, put the hawk, snake, shrew, frog, marsh grass, grasshopper, cricket, and cattail into the food pyramid to the ...
... First, label the pyramid levels (producers, primary consumers…). Next, using the food web on the left, put the hawk, snake, shrew, frog, marsh grass, grasshopper, cricket, and cattail into the food pyramid to the ...
Ecology 1 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
... 2. Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters). 3. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). 4. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. 5. Qua ...
... 2. Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters). 3. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). 4. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. 5. Qua ...
Aquatic Ecology And The Food Web
... animals) -Insects - Blue gill Largemouth Bass -Turtle –Bacteria ...
... animals) -Insects - Blue gill Largemouth Bass -Turtle –Bacteria ...
Chapter 10 Biological Productivity in the Ocean
... • Most fish production is equally divided between areas of upwelling and coastal waters. • Calculations suggest that the annual fish production is about 240 million tons/yr. ...
... • Most fish production is equally divided between areas of upwelling and coastal waters. • Calculations suggest that the annual fish production is about 240 million tons/yr. ...
CHAPTER 18 - Southern Local Schools
... • Find the fox and the rabbit in figure 5, page 440. Notice that the arrow goes from the rabbit to the fox, showing that the rabbit is food for the fox. The rabbit is also food for the owl. Neither the fox nor the owl is ever food for the rabbit. Energy moves from one organism to the next in a one-w ...
... • Find the fox and the rabbit in figure 5, page 440. Notice that the arrow goes from the rabbit to the fox, showing that the rabbit is food for the fox. The rabbit is also food for the owl. Neither the fox nor the owl is ever food for the rabbit. Energy moves from one organism to the next in a one-w ...
ppt
... Blepharisma increases more rapidly and has higher mean abundance when feeding as omnivore; max population was the same Population dynamics of bacterivores vary more in longer food chains except in one case Omnivore abundance varies less than that of nonomnivores at third trophic level Blepharisma sh ...
... Blepharisma increases more rapidly and has higher mean abundance when feeding as omnivore; max population was the same Population dynamics of bacterivores vary more in longer food chains except in one case Omnivore abundance varies less than that of nonomnivores at third trophic level Blepharisma sh ...
Bioloģija angliski
... provide everything that is neede. Foods are often grouped into six main groups: 3. … , vegetables, animal products, fruits, fats. It is also important to keep the overall 4. … of energy intake. A balanced diet will not be healthy if you are eating too much or too little to provide energy you use for ...
... provide everything that is neede. Foods are often grouped into six main groups: 3. … , vegetables, animal products, fruits, fats. It is also important to keep the overall 4. … of energy intake. A balanced diet will not be healthy if you are eating too much or too little to provide energy you use for ...
An Overview of Organismal Interactions in Ecosystems in
... Fig. 1. Whittaker's (1969) five-Kingdomclassificationof life on earth, altered slightly,to emphasize that the Kingdomsact as buildingblocksin food-webdevelopment.The alteration broadens the base of the fungi,to illustrate their essential role in the radiation of plants and many animal groups. mycorr ...
... Fig. 1. Whittaker's (1969) five-Kingdomclassificationof life on earth, altered slightly,to emphasize that the Kingdomsact as buildingblocksin food-webdevelopment.The alteration broadens the base of the fungi,to illustrate their essential role in the radiation of plants and many animal groups. mycorr ...
Lion King - Cloudfront.net
... • (b) list the reasons why pride rock is failing (not balanced) – Nila and Simba’s mom give really good reasons. ...
... • (b) list the reasons why pride rock is failing (not balanced) – Nila and Simba’s mom give really good reasons. ...
ch05_sec1
... An Exception to the Rule • Deep-ocean communities of worms, clams, crabs, mussels, and barnacles, exist in total darkness on the ocean floor, where photosynthesis cannot occur. • The producers in this environment are bacteria that use hydrogen sulfide present in the water. • Other underwater organis ...
... An Exception to the Rule • Deep-ocean communities of worms, clams, crabs, mussels, and barnacles, exist in total darkness on the ocean floor, where photosynthesis cannot occur. • The producers in this environment are bacteria that use hydrogen sulfide present in the water. • Other underwater organis ...
Lecture #10 – Animal Nutrition and Digestion
... • Feces are stored in the rectum • When the “time” comes, feces are eliminated through the anus Sphincter muscles control elimination One is voluntary, one involuntary Some, but not complete control over defecation ...
... • Feces are stored in the rectum • When the “time” comes, feces are eliminated through the anus Sphincter muscles control elimination One is voluntary, one involuntary Some, but not complete control over defecation ...
State Indicator Report Fruits Vegetables 2013
... In 2011‚ two updates occurred in the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) that will affect estimation of fruit and vegetable intake. First, there was an overall change in the BRFSS methodology to adjust sample weighting procedures and accommodate cell phone usage. Second, there were ...
... In 2011‚ two updates occurred in the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) that will affect estimation of fruit and vegetable intake. First, there was an overall change in the BRFSS methodology to adjust sample weighting procedures and accommodate cell phone usage. Second, there were ...
A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY TO ASSESS THE KNOWEDGE OF HIGH
... An experimental study on factors related to top 10 Junk foods consumption at 8 to 16 years of age in Haidian district of Beijing. The purpose of the study was to study the current situation of ten types of Junk food consumption among children and adolescent. The study selected 1019 children. A ques ...
... An experimental study on factors related to top 10 Junk foods consumption at 8 to 16 years of age in Haidian district of Beijing. The purpose of the study was to study the current situation of ten types of Junk food consumption among children and adolescent. The study selected 1019 children. A ques ...
Local food

Local food or the local food movement is a movement which aims to connect food producers and food consumers in the same geographic region; in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks, improve local economies, or for health, environmental, community, or social impact in a particular place. The term has also been extended to include not only geographic location of supplier and consumer but can also be ""defined in terms of social and supply chain characteristics."" For example, local food initiatives often promote sustainable and organic farming practices, although these are not explicitly related to the geographic proximity of the producer and consumer.Local food represents an alternative to the global food model, a model which often sees food travelling long distances before it reaches the consumer. A local food network involves relationships between food producers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a particular place where they work together to increase food security and ensure economic, ecological and social sustainability of a community