Class 1 notes
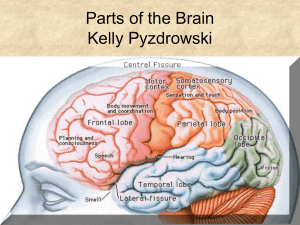
... The parietal lobes are imp for perception and interpretation of sensory info especially somato-sensory info. Non-dominant parietal lobe = imp for visual/spatial function. Dom parietal lobe is imp for praxis or the formation of the idea of a complex purposeful motor act. Frontal lobes by contrast are ...
... The parietal lobes are imp for perception and interpretation of sensory info especially somato-sensory info. Non-dominant parietal lobe = imp for visual/spatial function. Dom parietal lobe is imp for praxis or the formation of the idea of a complex purposeful motor act. Frontal lobes by contrast are ...
The Human Brain
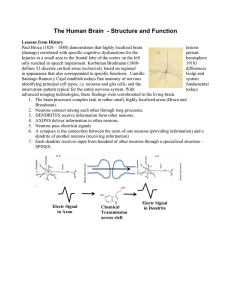
... a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
... a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
the central nervous system
... coverings called the meninges and are bathed in cerebrospinal fluids. ...
... coverings called the meninges and are bathed in cerebrospinal fluids. ...
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... The Cerebrum is the largest and “newest” part of the human brain and is made up of the cortex. Major regions of the cortext are responsible for the processing of our sensations, how we receive the world. The Frontal Lobe is implicated in motor control, complex thoughts, associations, and social thin ...
... The Cerebrum is the largest and “newest” part of the human brain and is made up of the cortex. Major regions of the cortext are responsible for the processing of our sensations, how we receive the world. The Frontal Lobe is implicated in motor control, complex thoughts, associations, and social thin ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... The electrical component of neural communication is captured in the action potential ...
... The electrical component of neural communication is captured in the action potential ...
SRCD Abstract 01 - University of Illinois Archives
... environment. By looking at this process in the brain and behavior, we can see how genes and experience interact. The initial development of the basic pattern of organization of the brain, positioning cells and forming initial connections, occurs under substantial control of orchestrated patterns of ...
... environment. By looking at this process in the brain and behavior, we can see how genes and experience interact. The initial development of the basic pattern of organization of the brain, positioning cells and forming initial connections, occurs under substantial control of orchestrated patterns of ...
Physical Development in Infancy & Early Childhood
... Brain has some plasticity Neurons can reorganize and change function Plasticity may also express itself through unique neuronal connection density due to experience • Adult exposed to music/athletics at an early age ...
... Brain has some plasticity Neurons can reorganize and change function Plasticity may also express itself through unique neuronal connection density due to experience • Adult exposed to music/athletics at an early age ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... Perceptual constancy is our tendency to perceive objects as unchanging in the face of changes in sensory stimulation. Once we have formed a stable perception of an object, we can recognize it from almost any angle ...
... Perceptual constancy is our tendency to perceive objects as unchanging in the face of changes in sensory stimulation. Once we have formed a stable perception of an object, we can recognize it from almost any angle ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. ...
... The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. ...
NOTE
... White matter. The white matter is made up of dendrites and axons, which create the network by which neurons send their signals. Gray and white. Your brain is 60% white matter and 40% gray matter. Water. The brain is made up of about 75% water. ...
... White matter. The white matter is made up of dendrites and axons, which create the network by which neurons send their signals. Gray and white. Your brain is 60% white matter and 40% gray matter. Water. The brain is made up of about 75% water. ...
sensation - LackeyLand
... • Thus, if you add 10 grams to a 100-gram weight, you will notice the difference; add 10 grams to a 1 kilogram weight and you will not. ...
... • Thus, if you add 10 grams to a 100-gram weight, you will notice the difference; add 10 grams to a 1 kilogram weight and you will not. ...
File
... learning and converting information to memory (if damaged or removed can not remember anything afterward) 2. The Amygdala- plays an important role in emotions and regulates interactions with environment (attack, escape, mate, or eat) These parts of the brain work together to ensure that we remember ...
... learning and converting information to memory (if damaged or removed can not remember anything afterward) 2. The Amygdala- plays an important role in emotions and regulates interactions with environment (attack, escape, mate, or eat) These parts of the brain work together to ensure that we remember ...
Neuroscience insights on variations by age v2
... nerve cells and biological processes that guide the construction provided by DNA we inherit from our parents (this encoding is like blueprints for a building). The human body and brain are composed of cells. Each cell contains membranes, a cytoskeleton, organelles, mitochondria, and a nucleus that c ...
... nerve cells and biological processes that guide the construction provided by DNA we inherit from our parents (this encoding is like blueprints for a building). The human body and brain are composed of cells. Each cell contains membranes, a cytoskeleton, organelles, mitochondria, and a nucleus that c ...
Document
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 51.1 Normal and pathological brain
... FIGURE 51.1 Normal and pathological brain states can be situated in a two-dimensional graph. Increasing levels of behaviorally determined arousal are plotted on the x-axis and the “richness” or “representational capacity of consciousness” is plotted on the y-axis. Increasing arousal can be measured ...
... FIGURE 51.1 Normal and pathological brain states can be situated in a two-dimensional graph. Increasing levels of behaviorally determined arousal are plotted on the x-axis and the “richness” or “representational capacity of consciousness” is plotted on the y-axis. Increasing arousal can be measured ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ 1. The self-examination of one's own emotional and mental processes is called: a) introspection. b) humanism. c) cognitive neuroscience. d) behaviorism. 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for ...
... Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ 1. The self-examination of one's own emotional and mental processes is called: a) introspection. b) humanism. c) cognitive neuroscience. d) behaviorism. 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for ...
(with Perception 6
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
romistalk - Marieke Rohde
... Bodies do not produce sensations, but complexes of sensations (complexes of elements) make up bodies. If, to the physicist, bodies appear the real, abiding existences, whilst sensations are regarded merely as their evanescent, transitory show, the physicist forgets, in the assumption of such a view ...
... Bodies do not produce sensations, but complexes of sensations (complexes of elements) make up bodies. If, to the physicist, bodies appear the real, abiding existences, whilst sensations are regarded merely as their evanescent, transitory show, the physicist forgets, in the assumption of such a view ...
Brain Anatomy and Function p. 95
... Damage to the medulla can stop spontaneous breathing.The fact that motor fibers cross at the medulla explains why a stroke affects the movement of the opposite side of the body from where the brain damage occurred. ...
... Damage to the medulla can stop spontaneous breathing.The fact that motor fibers cross at the medulla explains why a stroke affects the movement of the opposite side of the body from where the brain damage occurred. ...
True or False: Write “True” or “False”
... organized and represented in the brain. Marshall showed that even though the different systems carry different types of information and end up in different regions of the cerebral cortex, they share a common logic in their organization: all sensory information is organized topographically in the bra ...
... organized and represented in the brain. Marshall showed that even though the different systems carry different types of information and end up in different regions of the cerebral cortex, they share a common logic in their organization: all sensory information is organized topographically in the bra ...
Sensation2011
... Specialized neurons that are activated by stimulation and transduce (convert) it into a nerve impulse Sensory pathway – Bundles of neurons that carry information from the sense organs to the brain ...
... Specialized neurons that are activated by stimulation and transduce (convert) it into a nerve impulse Sensory pathway – Bundles of neurons that carry information from the sense organs to the brain ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.