Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
... Presented by Dr Graciela Tesan, PhD Tuesday, 19 October, 1-2pm, in E8A room 280 (Biology tearoom) This talk will provide an overview of this state-of-the-art brain imaging technique. MEG is a non-invasive technique to study cognitive functions and their disorders in both adults and children. MEG can ...
... Presented by Dr Graciela Tesan, PhD Tuesday, 19 October, 1-2pm, in E8A room 280 (Biology tearoom) This talk will provide an overview of this state-of-the-art brain imaging technique. MEG is a non-invasive technique to study cognitive functions and their disorders in both adults and children. MEG can ...
Visual Brain
... receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction ...
... receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction ...
Sensation and Perception
... Sensation and Perception Chapter Preview Sensation is the process by which we detect stimulus energy from our environment and transmit it to our brain. Perception is the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Clear evide ...
... Sensation and Perception Chapter Preview Sensation is the process by which we detect stimulus energy from our environment and transmit it to our brain. Perception is the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Clear evide ...
The Cerebral Cortex
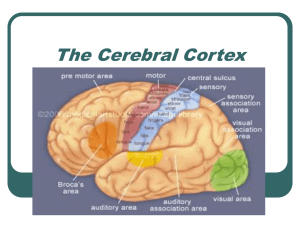
... Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
... Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
The Child’s Growth
... These different analyses occur in parallel. Some cells are analyzing form, while others are analyzing motion, others are analyzing color, and so on. Parallel processing promotes efficiency, interaction between systems. ...
... These different analyses occur in parallel. Some cells are analyzing form, while others are analyzing motion, others are analyzing color, and so on. Parallel processing promotes efficiency, interaction between systems. ...
Chapter 2
... 53. Which of the following is a disadvantage of using fMRI to understand brain function? (p 54) 54. Injecting a participant with a form of radioactive water and then having the participant form various cognitive tasks is using (p 55-56) 55. Using a specialized video camera to measure differences in ...
... 53. Which of the following is a disadvantage of using fMRI to understand brain function? (p 54) 54. Injecting a participant with a form of radioactive water and then having the participant form various cognitive tasks is using (p 55-56) 55. Using a specialized video camera to measure differences in ...
Milestone
... • Always hypothesize a difference. • Hypothesis must be testable. • You should include directionality in the hypothesis • Viewing more TV will increase anxiety. ...
... • Always hypothesize a difference. • Hypothesis must be testable. • You should include directionality in the hypothesis • Viewing more TV will increase anxiety. ...
AP Practice unit 3 and 4
... 62. The reticular formation is located in the A) brainstem. B) limbic system. C) sensory cortex. D) motor cortex. E) cerebellum. ...
... 62. The reticular formation is located in the A) brainstem. B) limbic system. C) sensory cortex. D) motor cortex. E) cerebellum. ...
MS Word - GEOCITIES.ws
... Coding – conversion of an item’s physical features into specific pattern of _________ activity, which represents those features in the brain ...
... Coding – conversion of an item’s physical features into specific pattern of _________ activity, which represents those features in the brain ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... The cerebellum, responsible for organizing thoughts and cognition, changes the most during adolescence. The cerebellum is not fully developed until a person is 21 years old. This lack of development can account for adolescents not always hearing or understanding what their parents or teachers are tr ...
... The cerebellum, responsible for organizing thoughts and cognition, changes the most during adolescence. The cerebellum is not fully developed until a person is 21 years old. This lack of development can account for adolescents not always hearing or understanding what their parents or teachers are tr ...
Academic Misconduct/ Cheating policy
... Less impediment from other cells & blood vessels One to one communication with bipolar cells & ganglion cells You really do have a blind spot ...
... Less impediment from other cells & blood vessels One to one communication with bipolar cells & ganglion cells You really do have a blind spot ...
Methods in Cognitive Neuroscience I
... – Advantages: better experimental control in some situations, e.g., temporary lesions can be very focal and reversible – Disadvantages: all subjects in these subjects are undergoing these procedures because they have a neurological disorder, therefore it is not clear how generalizable the results ar ...
... – Advantages: better experimental control in some situations, e.g., temporary lesions can be very focal and reversible – Disadvantages: all subjects in these subjects are undergoing these procedures because they have a neurological disorder, therefore it is not clear how generalizable the results ar ...
Biology and Psychology - Austin Community College
... produce myelin nourish & insulate neuron direct growth, remove waste ...
... produce myelin nourish & insulate neuron direct growth, remove waste ...
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... to have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and is unable to signal to the speech center, which generally is found in the left side of the brain. Remarkably, if a split-brain patient is asked to pick up a specifi ...
... to have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and is unable to signal to the speech center, which generally is found in the left side of the brain. Remarkably, if a split-brain patient is asked to pick up a specifi ...
Pharmacology - The reward pathway
... crosses the emotional centre of the brain and connects to the decision-making part of the brain-will reinforce a behaviour. It does so because it produces a pleasurable feeling. Dopamine is a monoamine. Our mood is affected by the monoamines. There's an association between the altered function of mo ...
... crosses the emotional centre of the brain and connects to the decision-making part of the brain-will reinforce a behaviour. It does so because it produces a pleasurable feeling. Dopamine is a monoamine. Our mood is affected by the monoamines. There's an association between the altered function of mo ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Hippocampus – forms memories Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
... Hippocampus – forms memories Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
Pituitary malfunctions
... 1. This is a diagram of the left side of the brain. Left side functions: The left hemisphere controls touch and movement of the right side of the body, vision in the right half of the visual field, comprehension and production of speech, reading ability, mathematical reasoning, and a host of other a ...
... 1. This is a diagram of the left side of the brain. Left side functions: The left hemisphere controls touch and movement of the right side of the body, vision in the right half of the visual field, comprehension and production of speech, reading ability, mathematical reasoning, and a host of other a ...
Brain Teasers - Dartmouth Math Home
... suggesting that there is not much truth to the claim that cognitive performance is negatively affected by time constraints. On the other hand, no one was really invested in our little task, so who really knows what would happen under real pressure. ...
... suggesting that there is not much truth to the claim that cognitive performance is negatively affected by time constraints. On the other hand, no one was really invested in our little task, so who really knows what would happen under real pressure. ...
The CNS - Mr. Lesiuk
... The Cerebellum – “little brain” The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes, ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input from the cerebral cortex. It integrates this information to maintain posture, coordination and ...
... The Cerebellum – “little brain” The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes, ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input from the cerebral cortex. It integrates this information to maintain posture, coordination and ...
Study Guide 3
... 1. What is light? How can light be characterized in physical terms? 2. What is the difference between white light and colored light? 3. What is the difference between mixing wavelengths of light and pigments in terms of what colors we perceive? 4. What happens to light when it impinges upon objects ...
... 1. What is light? How can light be characterized in physical terms? 2. What is the difference between white light and colored light? 3. What is the difference between mixing wavelengths of light and pigments in terms of what colors we perceive? 4. What happens to light when it impinges upon objects ...
The Nervous System
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
psych mod 4 terms
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 10. _____________________ refers to the fact that a neuron either fires completely or does not fire at all. 11. The _____________ _____________ are sack-like structures found inside the synaptic knob containing chemicals. 12. __________________________ are chemicals found in the synaptic vesicles wh ...
... 10. _____________________ refers to the fact that a neuron either fires completely or does not fire at all. 11. The _____________ _____________ are sack-like structures found inside the synaptic knob containing chemicals. 12. __________________________ are chemicals found in the synaptic vesicles wh ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.