MCDB 3650 Take Home Quiz 1 50 points (6) Describe how an
... 2. (6) Describe how the neurons in your visual system create a representation of the real world. Include how cells in the retina take in information, process it, and deliver it to the parts of your brain that can actually consciously interpret your visual input. As a follow up, describe why do some ...
... 2. (6) Describe how the neurons in your visual system create a representation of the real world. Include how cells in the retina take in information, process it, and deliver it to the parts of your brain that can actually consciously interpret your visual input. As a follow up, describe why do some ...
Nervous System
... Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region in the center called the cel ...
... Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region in the center called the cel ...
The Brain and the Nervous System
... Convoluted (folded, wrinkled) structure enables more tissue to fit The cortex provides flexibility in behavior Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
... Convoluted (folded, wrinkled) structure enables more tissue to fit The cortex provides flexibility in behavior Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
Study Guide
... Study Guide Biol 2121 Test #5 The following study guide is exactly that, a guide. Use it to direct your studies for the first exam. The text should be used to clarify any questions you have. You are still responsible for all class notes covered or not covered in my lectures. Good luck to you all. CH ...
... Study Guide Biol 2121 Test #5 The following study guide is exactly that, a guide. Use it to direct your studies for the first exam. The text should be used to clarify any questions you have. You are still responsible for all class notes covered or not covered in my lectures. Good luck to you all. CH ...
What” and ”where” – dynamic parallel processing of sound
... modulation of STRFs at lower auditory system structures, MGB, IC, even cochlea! • Animal data suggest that the lower one goes, the longer time it takes to see such changes • AC as the ”initiator” of modulatory effects? ...
... modulation of STRFs at lower auditory system structures, MGB, IC, even cochlea! • Animal data suggest that the lower one goes, the longer time it takes to see such changes • AC as the ”initiator” of modulatory effects? ...
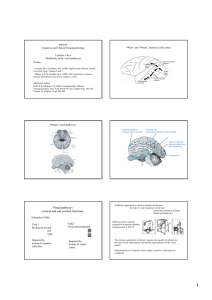
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... Electrophysiological studies in monkeys 1970s Mountcastle & Hyvarinen electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
... Electrophysiological studies in monkeys 1970s Mountcastle & Hyvarinen electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
Unit 4A: Sensation
... ◦ Cocktail Party Effect: The ability to attend to only one voice among many. For example, at a party, if another voice speaks your name at a party, your cognitive radar, operating on the mind’s other track, will instantly bring that voice into consciousness. You may tune in long enough to decide to ...
... ◦ Cocktail Party Effect: The ability to attend to only one voice among many. For example, at a party, if another voice speaks your name at a party, your cognitive radar, operating on the mind’s other track, will instantly bring that voice into consciousness. You may tune in long enough to decide to ...
File
... Scientists can map which parts of the brain control various parts of the body. The mapping is done by stimulating the sensory or motor cortex with a weak electric current. The stimulation often produces tingling or movement in part of the body. Humans put great emphasis on speech and manipulation of ...
... Scientists can map which parts of the brain control various parts of the body. The mapping is done by stimulating the sensory or motor cortex with a weak electric current. The stimulation often produces tingling or movement in part of the body. Humans put great emphasis on speech and manipulation of ...
Chapter 8
... Building the Brain: Get 2 pictures: The first one of a newborn networks in the brain. The second one of the networks of a 2 year old brain. ...
... Building the Brain: Get 2 pictures: The first one of a newborn networks in the brain. The second one of the networks of a 2 year old brain. ...
Phenomenology without conscious access is a form of
... must be a concern that this might affect sensory processing, and hence that phenomenal experience of the stimulus is affected along with cognitive access. We know, for example, that attention affects visual sensitivity (Solomon 2004). Changes in the response gain of neurons in sensory areas of corte ...
... must be a concern that this might affect sensory processing, and hence that phenomenal experience of the stimulus is affected along with cognitive access. We know, for example, that attention affects visual sensitivity (Solomon 2004). Changes in the response gain of neurons in sensory areas of corte ...
Sermon Presentation
... enter retina detected and transduced into neural signals. The light passes through the pupil, and cornea. Rods and cones send signals to the brain by activating bipolar and ganglion cells. The Signal exits eye through optic nerve to brain for further processing. ...
... enter retina detected and transduced into neural signals. The light passes through the pupil, and cornea. Rods and cones send signals to the brain by activating bipolar and ganglion cells. The Signal exits eye through optic nerve to brain for further processing. ...
The Brain
... information much faster than other neurons Axon terminal – at the end of the neuron and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons (through synapses) ...
... information much faster than other neurons Axon terminal – at the end of the neuron and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons (through synapses) ...
Your Brain and What It Does
... THALAMUS: Located at the top of the brain stem, the thalamus acts as a two-way relay station, sorting, processing, and directing signals from the spinal cord and mid-brain structures up to the cerebrum, and, conversely, from the cerebrum These two halves are connected by long neuron branches called ...
... THALAMUS: Located at the top of the brain stem, the thalamus acts as a two-way relay station, sorting, processing, and directing signals from the spinal cord and mid-brain structures up to the cerebrum, and, conversely, from the cerebrum These two halves are connected by long neuron branches called ...
study notes quiz 1
... (a) White matter has myelin sheath: the axons of neurons – where information is communicated (b) Gray matter is cell bodies: where information is processed. ...
... (a) White matter has myelin sheath: the axons of neurons – where information is communicated (b) Gray matter is cell bodies: where information is processed. ...
Chapter 7 part two
... First, given the limits on our ability to process several stimuli at once, visual objects compete for representational resources, and only one or a small number of stimuli can be represented at one time. As the neural representations of visual stimuli are highly distributed, competitive processing o ...
... First, given the limits on our ability to process several stimuli at once, visual objects compete for representational resources, and only one or a small number of stimuli can be represented at one time. As the neural representations of visual stimuli are highly distributed, competitive processing o ...
Vision
... Bipolar cells – collect impulses from photo receptors and shuttle them on to the ganglion cells Ganglion cells – collect neural impulses from bipolar cells and shuttle them through the brain via the optic nerve ...
... Bipolar cells – collect impulses from photo receptors and shuttle them on to the ganglion cells Ganglion cells – collect neural impulses from bipolar cells and shuttle them through the brain via the optic nerve ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
node of action heroin
... has failed to fully comply with any of his doctor’s orders. This includes complete detoxification (controlled withdrawal from drugs) which also involves counseling sessions. ...
... has failed to fully comply with any of his doctor’s orders. This includes complete detoxification (controlled withdrawal from drugs) which also involves counseling sessions. ...
consciousness
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
File chapter 2 vocab pp
... above the kidneys. They secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (nonadrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress. ...
... above the kidneys. They secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (nonadrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress. ...
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378
... 4) Cerebral Cortex and Central White Matter Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts ...
... 4) Cerebral Cortex and Central White Matter Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts ...
Second-Order Patterns in Human Visual Cortex`` on ``Orientation
... effects were of comparable magnitude across visual occipitotemporal areas for first-order patterns, whereas orientationselective adaptation for second-order patterns was larger in several higher extrastriate areas than in V1. What are the implications of these fMRI adaptation effects for understandi ...
... effects were of comparable magnitude across visual occipitotemporal areas for first-order patterns, whereas orientationselective adaptation for second-order patterns was larger in several higher extrastriate areas than in V1. What are the implications of these fMRI adaptation effects for understandi ...
Brain PowerPoints - Raleigh Charter High School
... Located on the top and rear of head Contains the sensory cortex (part of brain that registers and processes tactile information (phantom limb) Contains the angular gyrus (left hemisphere only) which is involved in converting written words into sound ...
... Located on the top and rear of head Contains the sensory cortex (part of brain that registers and processes tactile information (phantom limb) Contains the angular gyrus (left hemisphere only) which is involved in converting written words into sound ...
Nervous Systems (ch. 48 & 49) Sum13
... Diagram a basic neuron – for sensory, motor, and interneurons explain the location of each region with respect to peripheral or central nervous system. ...
... Diagram a basic neuron – for sensory, motor, and interneurons explain the location of each region with respect to peripheral or central nervous system. ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.