Attending to Contrast
... basis of the psychological phenomena of visual attention. Desimone and colleagues have suggested that attention may increase the efficiency with which attended stimuli are encoded, while Maunsell and colleagues have argued that attention boosts the overall strength of neural signals without altering ...
... basis of the psychological phenomena of visual attention. Desimone and colleagues have suggested that attention may increase the efficiency with which attended stimuli are encoded, while Maunsell and colleagues have argued that attention boosts the overall strength of neural signals without altering ...
Where does breathing start?
... It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which are located in the lower brainstem. The medulla oblongata contains the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) and the Dorsal Respiratory Group and the pons contains the Pneumotaxic (PNG) and the Apneustic centres (APN). The f ...
... It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which are located in the lower brainstem. The medulla oblongata contains the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) and the Dorsal Respiratory Group and the pons contains the Pneumotaxic (PNG) and the Apneustic centres (APN). The f ...
Posterior Parietal Cortex: Space…and Beyond
... require different responses at home (answer the phone) than when dining in a restaurant (let the host or hostess get it). If we were unable to take such contextual cues into account when planning voluntary actions, every stimulus would lead to a highly predictable reflex-like response that could be ...
... require different responses at home (answer the phone) than when dining in a restaurant (let the host or hostess get it). If we were unable to take such contextual cues into account when planning voluntary actions, every stimulus would lead to a highly predictable reflex-like response that could be ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions. The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cortex that carries the functions out have been identified) but it is i ...
... brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions. The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cortex that carries the functions out have been identified) but it is i ...
Scientific priorities for the BRAIN Initiative
... Current technologies are starting to make it possible to record from most of the neurons in the small brain of the zebrafish larva7, but substantial technical breakthroughs will be required to record all of the neural activity in an animal as large as a mouse. There was a consensus that brain activi ...
... Current technologies are starting to make it possible to record from most of the neurons in the small brain of the zebrafish larva7, but substantial technical breakthroughs will be required to record all of the neural activity in an animal as large as a mouse. There was a consensus that brain activi ...
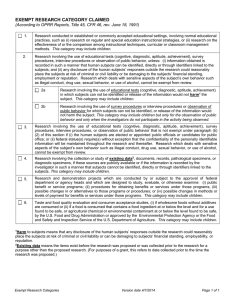
EXEMPT CATEGORY CLAIMED
... procedures, interview procedures or observation of public behavior, unless: (i) information obtained is recorded in such a manner that human subjects can be identified, directly or through identifiers linked to the subjects; and (ii) any disclosure of the human subjects’ responses outside the resear ...
... procedures, interview procedures or observation of public behavior, unless: (i) information obtained is recorded in such a manner that human subjects can be identified, directly or through identifiers linked to the subjects; and (ii) any disclosure of the human subjects’ responses outside the resear ...
Dispatch Vision: How to Train Visual Cortex to Predict Reward Time
... The basal forebrain contains a neurochemically heterogeneous population of projection neurons, not only cholinergic ones. Therefore, Liu et al. [4] repeated this experiment, this time using cholinergic-specific optogenetic stimulation within visual cortex, and found that it was indeed sufficient to ...
... The basal forebrain contains a neurochemically heterogeneous population of projection neurons, not only cholinergic ones. Therefore, Liu et al. [4] repeated this experiment, this time using cholinergic-specific optogenetic stimulation within visual cortex, and found that it was indeed sufficient to ...
Slide 1
... Motor areas – continued Broca’s area (44): specialized motor speech area Base of precentral gyrus just above lateral sulcus in only one hemisphere, usually left Word articulation: the movements necessary for speech Damage: can understand but can’t speak; or if can still speak, words are rig ...
... Motor areas – continued Broca’s area (44): specialized motor speech area Base of precentral gyrus just above lateral sulcus in only one hemisphere, usually left Word articulation: the movements necessary for speech Damage: can understand but can’t speak; or if can still speak, words are rig ...
No Slide Title
... What acts as a relay station for information going to the cerebrum (sensory information) is the __________. ...
... What acts as a relay station for information going to the cerebrum (sensory information) is the __________. ...
The Brain - Misty Cherie
... • This was sometimes knows as “split brain” surgery, because patients experienced a dissociation of the left and right sides of their brains • This created peculiar problems for some patients in which one side of the brain seemed not to know what the other side of the brain was doing ...
... • This was sometimes knows as “split brain” surgery, because patients experienced a dissociation of the left and right sides of their brains • This created peculiar problems for some patients in which one side of the brain seemed not to know what the other side of the brain was doing ...
“Conscious” Dorsal Stream
... subdivides the posterior parietal lobe into two main sectors: the superior parietal lobule (SPL) and the inferior parietal lobule (IPL). These two sectors receive different cortical inputs and have different connections with the motor cortex and frontal lobe. Early experiments in monkeys showed that ...
... subdivides the posterior parietal lobe into two main sectors: the superior parietal lobule (SPL) and the inferior parietal lobule (IPL). These two sectors receive different cortical inputs and have different connections with the motor cortex and frontal lobe. Early experiments in monkeys showed that ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ...
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ...
Perception of three-dimensional structure from motion
... MT, involves the reconstruction of surfaces. The large re- ...
... MT, involves the reconstruction of surfaces. The large re- ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... The more neurons are exercised, the thicker the myelin tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
... The more neurons are exercised, the thicker the myelin tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
In your journal, take notes by writing the name of
... the brain. The human thalamus can be divided into two pear-shaped halves. The thalamus is often referred to as the "relay station" of the brain. This is because the thalamus has a primary function of relaying information to other parts of the body. The thalamus is a very important part of the brain ...
... the brain. The human thalamus can be divided into two pear-shaped halves. The thalamus is often referred to as the "relay station" of the brain. This is because the thalamus has a primary function of relaying information to other parts of the body. The thalamus is a very important part of the brain ...
Forebrain
... sensory systems in that it receives direct input from secondary sensory neurons without an intervening thalamic relay. ...
... sensory systems in that it receives direct input from secondary sensory neurons without an intervening thalamic relay. ...
The Brain, Biology, and Behavior
... The corpus callosum is the major “cable system” through which the right and left cerebral hemispheres communicate. A recent study found that the corpus callosum is larger in classically trained musicians than it is in nonmusicians. When a person plays a violin or piano, the two hemispheres must comm ...
... The corpus callosum is the major “cable system” through which the right and left cerebral hemispheres communicate. A recent study found that the corpus callosum is larger in classically trained musicians than it is in nonmusicians. When a person plays a violin or piano, the two hemispheres must comm ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The Somatic Nervous System – contains all the nerves that serve the musculo-skeletal system and the sensory organs. The actions are generally conscious and deliberate. The Autonomic Nervous System – contains all the nerves that serve the internal organs. The actions are unconscious and automatic. Th ...
... The Somatic Nervous System – contains all the nerves that serve the musculo-skeletal system and the sensory organs. The actions are generally conscious and deliberate. The Autonomic Nervous System – contains all the nerves that serve the internal organs. The actions are unconscious and automatic. Th ...
Psychology as a Science
... The Cerebral Cortex (“new brain”): Approx 6” thick covers most of the brain and related to higher mental abilities such as thinking, language, problem solving. The two sides (left-right) are connected by the corpus callosum. Cortex subdivided into lobes that have different functions: 1) Occipital: v ...
... The Cerebral Cortex (“new brain”): Approx 6” thick covers most of the brain and related to higher mental abilities such as thinking, language, problem solving. The two sides (left-right) are connected by the corpus callosum. Cortex subdivided into lobes that have different functions: 1) Occipital: v ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.