Chapter 12 - apsubiology.org
... 10% of people Most right-hemisphere-dominant people are lefthanded and male Equal hemispheric function may result in ambidexterity and/or dyslexia Beware of the many “pop psychology” interpretations of the significance and meaning of ...
... 10% of people Most right-hemisphere-dominant people are lefthanded and male Equal hemispheric function may result in ambidexterity and/or dyslexia Beware of the many “pop psychology” interpretations of the significance and meaning of ...
News Release - האוניברסיטה העברית
... Jerusalem, November 25, 2009 – How does our biological system know that it is supposed to operate on a 24-hour cycle? Scientists at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have discovered that a tiny molecule holds the clue to the mystery. Human as well as most living organisms on earth possess circadian ...
... Jerusalem, November 25, 2009 – How does our biological system know that it is supposed to operate on a 24-hour cycle? Scientists at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have discovered that a tiny molecule holds the clue to the mystery. Human as well as most living organisms on earth possess circadian ...
The Functional Organization of the Barrel Cortex
... • Recordings from the first-order sensory neurons in the trigeminal ganglion of awake rodents • in the absence of whisker movement - no spontaneous action potential firing in the trigeminal ganglion. • ‘‘whisking in air,’’- a low level of spiking activity in the sensory neurons. • phase-locked signa ...
... • Recordings from the first-order sensory neurons in the trigeminal ganglion of awake rodents • in the absence of whisker movement - no spontaneous action potential firing in the trigeminal ganglion. • ‘‘whisking in air,’’- a low level of spiking activity in the sensory neurons. • phase-locked signa ...
Robin Balbernie
... of brain metabolic energy level and the maturation of the cortex and limbic systems. This also triggers the birth of new neurons, protein synthesis and neural growth. Thus caregiving activates the growth of the brain through emotional availability and reciprocal interactions. ...
... of brain metabolic energy level and the maturation of the cortex and limbic systems. This also triggers the birth of new neurons, protein synthesis and neural growth. Thus caregiving activates the growth of the brain through emotional availability and reciprocal interactions. ...
Chapter 1 - Illinois State University Websites
... impairments – Disorder due to abnormal development of the basal ganglia – Basal ganglia modulates the procedural memory system. ...
... impairments – Disorder due to abnormal development of the basal ganglia – Basal ganglia modulates the procedural memory system. ...
Your Body Is Nothing Without A Brain
... most important organ of our body. If that is true, why are so many young children, teenagers, and adults constantly placing themselves at risk of compromising their quality of life with a brain injury whose effects could be temporary, permanent, or delayed into the future? This author was able to so ...
... most important organ of our body. If that is true, why are so many young children, teenagers, and adults constantly placing themselves at risk of compromising their quality of life with a brain injury whose effects could be temporary, permanent, or delayed into the future? This author was able to so ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • A) Life satisfaction peaks at age 50 and then declines after 65. • B) Most people over 90 are senile. • C) Most women feel relief after going through menopause. • D) older people become more susceptible to short-term illnesses. ...
... • A) Life satisfaction peaks at age 50 and then declines after 65. • B) Most people over 90 are senile. • C) Most women feel relief after going through menopause. • D) older people become more susceptible to short-term illnesses. ...
Document
... The nervous system receives signals: called stimulus. (this can be from inside or outside your body) When our nervous system reacts to this stimulus it is called a: response. ...
... The nervous system receives signals: called stimulus. (this can be from inside or outside your body) When our nervous system reacts to this stimulus it is called a: response. ...
B6 Brain and Mind
... are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
Central Nervous System
... 2. The circadian clock: it shifts forwards (in the day) during the teenage years. 3. It’s like a car trying to run on an empty tank. 4. Your mood, your ability to think and your ability to perform and react appropriately. 5. Rapid Eye Movement. Dreaming and learning happens during this time. 6. Whet ...
... 2. The circadian clock: it shifts forwards (in the day) during the teenage years. 3. It’s like a car trying to run on an empty tank. 4. Your mood, your ability to think and your ability to perform and react appropriately. 5. Rapid Eye Movement. Dreaming and learning happens during this time. 6. Whet ...
Chapter 13
... Higher mental functions • Skill memory – performing skilled motor activities (i.e. riding a bike) – When a skill is first learned • more areas of the cerebral cortex are involved – Skill memory involved all the motor areas of the cerebrum below the level of consciousness ...
... Higher mental functions • Skill memory – performing skilled motor activities (i.e. riding a bike) – When a skill is first learned • more areas of the cerebral cortex are involved – Skill memory involved all the motor areas of the cerebrum below the level of consciousness ...
2006 natl fx fnd abstract - University of Illinois Archives
... important ideas you can try to put them back. Good luck! Also, do you mind if my name goes before Robert’s? ...
... important ideas you can try to put them back. Good luck! Also, do you mind if my name goes before Robert’s? ...
biological bases of behavior
... Speak about information received exclusively in their right hemisphere. Speak about information received exclusively in their left hemisphere. Solve abstract problems involving integrating logical (left-hemisphere) and spatial ...
... Speak about information received exclusively in their right hemisphere. Speak about information received exclusively in their left hemisphere. Solve abstract problems involving integrating logical (left-hemisphere) and spatial ...
SKZ Hx Ebefrenia Catatonia Demenza paranoide Demenza precox
... Thus → check more in delay period and representation, check other parts of the brain ...
... Thus → check more in delay period and representation, check other parts of the brain ...
Infancy: Physical Development
... Development of Coordination of the Senses • Young infants recognize that objects experienced by one sense are the same as those experienced through another sense. • Five-month-old infants look at novel stimulation longer than familiar sources of stimulation. – Infants looked at unfamiliar objects l ...
... Development of Coordination of the Senses • Young infants recognize that objects experienced by one sense are the same as those experienced through another sense. • Five-month-old infants look at novel stimulation longer than familiar sources of stimulation. – Infants looked at unfamiliar objects l ...
This newsletter is for your information only and is not a substitute for
... on. Experiences greatly influence how all this gets refined (developed). We begin with and form trillions more connections than we can ever possibly use. Based on our experiences, millions of nerve cell connections are eliminated, kept, downgraded, or reinforced. As an example, let's take the visual ...
... on. Experiences greatly influence how all this gets refined (developed). We begin with and form trillions more connections than we can ever possibly use. Based on our experiences, millions of nerve cell connections are eliminated, kept, downgraded, or reinforced. As an example, let's take the visual ...
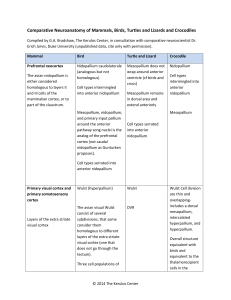
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... Wulst Cell division are thin and overlappingincludes a dorsal mesopallium, intercalated hyperpallium, and hyperpallium. Overall structure equivalent with birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
... Wulst Cell division are thin and overlappingincludes a dorsal mesopallium, intercalated hyperpallium, and hyperpallium. Overall structure equivalent with birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
Central Nervous System
... Warm Up 1/28/11 • HAPPY FRIDAY!! • Pick up a worksheet from the counter • Please write “quiz” for the block day warm up • Warm ups are due today (no sheet = no credit) Warm Up: 1. A cerebrovascular accident is also referred to as a…..? 2. What are the 2 main causes of a CVA? 3. If there is damage ...
... Warm Up 1/28/11 • HAPPY FRIDAY!! • Pick up a worksheet from the counter • Please write “quiz” for the block day warm up • Warm ups are due today (no sheet = no credit) Warm Up: 1. A cerebrovascular accident is also referred to as a…..? 2. What are the 2 main causes of a CVA? 3. If there is damage ...
Nervous System (1)
... 1. Stimulus - a change in an organism’s internal or external environment that initiates a response. 2. Receptors - structures specialized in detecting stimuli Ex. sense organs - eye, ear, nose, tongue, skin. 3. Effectors - organs that produce responses to stimuli Ex. muscles or glands ...
... 1. Stimulus - a change in an organism’s internal or external environment that initiates a response. 2. Receptors - structures specialized in detecting stimuli Ex. sense organs - eye, ear, nose, tongue, skin. 3. Effectors - organs that produce responses to stimuli Ex. muscles or glands ...
Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity
... • Tumors – these can be small to large cyst-like tumors or sticky, tentacle-like tumors • Toxins – heavy metals such as lead cause damage. Lead replaces the oxygen molecule, causing widespread damage (sources: lead paint, leaded gasoline fumes) • Anoxia – loss of oxygen causes diffuse damage • Disea ...
... • Tumors – these can be small to large cyst-like tumors or sticky, tentacle-like tumors • Toxins – heavy metals such as lead cause damage. Lead replaces the oxygen molecule, causing widespread damage (sources: lead paint, leaded gasoline fumes) • Anoxia – loss of oxygen causes diffuse damage • Disea ...
Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form
... N vISIoN,AS IN orHERmental oPerations, we exPerrence the world as a whole. Independent attributesmotion, depth, form, and color-are coordinated into a single visual image. In the two Previous chapters we began to consider how two parallel Pathways-the magnocellular and parvocellular pathways, that e ...
... N vISIoN,AS IN orHERmental oPerations, we exPerrence the world as a whole. Independent attributesmotion, depth, form, and color-are coordinated into a single visual image. In the two Previous chapters we began to consider how two parallel Pathways-the magnocellular and parvocellular pathways, that e ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.