Fixed mindset
... Learning helps our neurons GROW. The more we learn, the more connections they make. ...
... Learning helps our neurons GROW. The more we learn, the more connections they make. ...
Neural Correlates Underlying Action-intention and Aim-intention Mauro Adenzato () Cristina Becchio
... Decety (2001) asked participants to imagine actions from different perspectives. In the first-person perspective, participants were told to imagine that they are executing a given action. In the third-person perspective, the instruction was to imagine that they were watching somebody else doing that ...
... Decety (2001) asked participants to imagine actions from different perspectives. In the first-person perspective, participants were told to imagine that they are executing a given action. In the third-person perspective, the instruction was to imagine that they were watching somebody else doing that ...
The Deferred Event Model for Hardware-Oriented Spiking
... ∼1-0.1%, will be active at any time, with 10% a reasonable upper limit. For a “typical” neuron containing 5000 dendritic connections with 1% activity, spiking at 10 Hz, we therefore expect an average input rate of 500 events (input spikes) per second, requiring an update rate of only 2ms. A worst-ca ...
... ∼1-0.1%, will be active at any time, with 10% a reasonable upper limit. For a “typical” neuron containing 5000 dendritic connections with 1% activity, spiking at 10 Hz, we therefore expect an average input rate of 500 events (input spikes) per second, requiring an update rate of only 2ms. A worst-ca ...
HEAD/NECK: Cranial Nerves
... • Parasympathetic to most of gut • Taste to back posterior pharynx XI: (Spinal) • Motor to traps, Accesory sternocleidomastoid IX: Glosso- • Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal • Taste to posterior tongue • Sensory to ear opening/middle ear • Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus ...
... • Parasympathetic to most of gut • Taste to back posterior pharynx XI: (Spinal) • Motor to traps, Accesory sternocleidomastoid IX: Glosso- • Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal • Taste to posterior tongue • Sensory to ear opening/middle ear • Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus ...
Physiology of the Striate Cortex
... • Analysis of fine objects • Small receptive fields, sustained ...
... • Analysis of fine objects • Small receptive fields, sustained ...
Fact vs fiction—how paratextual information
... in such processes. The FPC has been found activated in tasks which require constructive mental processes like mind-wandering (Gilbert et al., 2005; Dumontheil et al., 2010), simulation of the future (Schacter et al., 2008) and complex imagery of hypothetical events (Addis et al., 2009). In addition ...
... in such processes. The FPC has been found activated in tasks which require constructive mental processes like mind-wandering (Gilbert et al., 2005; Dumontheil et al., 2010), simulation of the future (Schacter et al., 2008) and complex imagery of hypothetical events (Addis et al., 2009). In addition ...
Position Selectivity in Scene- and Object-Responsive
... within each block ranged from two and six, and spots appeared in 25% of stimuli on average. (Note that this percentage applied to the total number of stimuli, of which there were 12 per block, and not the number of unique images, which was either two or four per block. Also, the appearance of a blur ...
... within each block ranged from two and six, and spots appeared in 25% of stimuli on average. (Note that this percentage applied to the total number of stimuli, of which there were 12 per block, and not the number of unique images, which was either two or four per block. Also, the appearance of a blur ...
Document
... a clap in a single dream concurred with Galen’s prescient theory that one pneuma acts for each sense organ. This dream suggests an association of two sensory inputs or crossmodal processing: the ability to use one sense–vision–to learn something in another sense–sound. ...
... a clap in a single dream concurred with Galen’s prescient theory that one pneuma acts for each sense organ. This dream suggests an association of two sensory inputs or crossmodal processing: the ability to use one sense–vision–to learn something in another sense–sound. ...
Word`s - Semiosis Evolution Energy
... aspects of biological sign-exchange - lacks even one generally accepted, much less fully explanatory, theory of the very principles by which the emergence of mental ...
... aspects of biological sign-exchange - lacks even one generally accepted, much less fully explanatory, theory of the very principles by which the emergence of mental ...
Auditory Precedence Effect
... second click as a separate event and then begin to localize it with increasing accuracy; see Blauert 1997). For more “natural” sounds, like speech or music, the precedence effect persists for tens of ms. Many researchers argue that the precedence effect has a longer time course for ongoing signals b ...
... second click as a separate event and then begin to localize it with increasing accuracy; see Blauert 1997). For more “natural” sounds, like speech or music, the precedence effect persists for tens of ms. Many researchers argue that the precedence effect has a longer time course for ongoing signals b ...
Hemispheric Differences in the Activation of
... Language comprehension, like most cognitive abilities, involves the coordination of multiple distinct processes that occur in both cerebral hemispheres. Comprehension requires the decoding of words and propositions in a sentence as well as the use of world knowledge retrieved from long-term memory. ...
... Language comprehension, like most cognitive abilities, involves the coordination of multiple distinct processes that occur in both cerebral hemispheres. Comprehension requires the decoding of words and propositions in a sentence as well as the use of world knowledge retrieved from long-term memory. ...
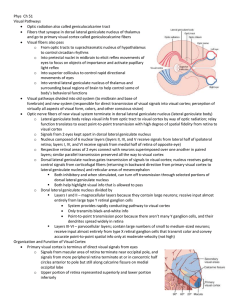
Stimulus-Specific Adaptation in Auditory Cortex Is an NMDA
... and the MMN is found. – First, during an oddball paradigm with frequency deviants, neuronal responses showed clear SSA but failed to encode novelty in a manner analogous to the human MMN. – Second, oddball paradigms using intensity or duration deviants revealed a pattern of unit responses that showe ...
... and the MMN is found. – First, during an oddball paradigm with frequency deviants, neuronal responses showed clear SSA but failed to encode novelty in a manner analogous to the human MMN. – Second, oddball paradigms using intensity or duration deviants revealed a pattern of unit responses that showe ...
The speed of learning instructed stimulus
... Keywords: Rapid instructed task learning, Pre-frontal cortex, Inferior-temporal Cortex, Hippocampus, synaptic learning Abstract Humans can learn associations between visual stimuli and motor responses from just a single instruction. This is known to be a fast process, but how fast is it? To answer t ...
... Keywords: Rapid instructed task learning, Pre-frontal cortex, Inferior-temporal Cortex, Hippocampus, synaptic learning Abstract Humans can learn associations between visual stimuli and motor responses from just a single instruction. This is known to be a fast process, but how fast is it? To answer t ...
Brainwaves ("40 Hz") Research
... background even though different and widely-separated cortical areas detect its shape, color, movement, etc.. And the same areas also detect the features of the background. All this information then can be linked efficiently to the motor system to allow us to catch the Frisbee. A more plausible idea ...
... background even though different and widely-separated cortical areas detect its shape, color, movement, etc.. And the same areas also detect the features of the background. All this information then can be linked efficiently to the motor system to allow us to catch the Frisbee. A more plausible idea ...
Short-Term and Long-Term Memory in Early
... has been reported to produce deficits traditionally associated with prefrontal dysfunction, whereas the same damage later in life does not. Bachevalier (1994) has reported that early, bilateral medial temporal damage in monkeys produces emotional and social dysfunction as well as deficits in learnin ...
... has been reported to produce deficits traditionally associated with prefrontal dysfunction, whereas the same damage later in life does not. Bachevalier (1994) has reported that early, bilateral medial temporal damage in monkeys produces emotional and social dysfunction as well as deficits in learnin ...
Sensory receptors - E
... • Bats use sonar to detect their prey. • Moths, a common prey for bats, can detect the bat’s sonar and attempt to flee. • Both organisms have complex sensory systems that facilitate survival. • These systems include diverse mechanisms that sense stimuli and generate appropriate movement. Copyrig ...
... • Bats use sonar to detect their prey. • Moths, a common prey for bats, can detect the bat’s sonar and attempt to flee. • Both organisms have complex sensory systems that facilitate survival. • These systems include diverse mechanisms that sense stimuli and generate appropriate movement. Copyrig ...
Biological Perspective Studies
... themselves by pressing the lever. The results indicate that various places exist in the brain "where electrical stimulation is rewarding in the sense that the experimental animal will stimulate itself in these places frequently and regularly for long periods of time if permitted to do so." The rewar ...
... themselves by pressing the lever. The results indicate that various places exist in the brain "where electrical stimulation is rewarding in the sense that the experimental animal will stimulate itself in these places frequently and regularly for long periods of time if permitted to do so." The rewar ...
No Slide Title - people.vcu.edu
... FROM THE MOTOR CORTEX CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY CORTICOBULBAR PATHWAY PYRAMIDAL TRACT LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT ...
... FROM THE MOTOR CORTEX CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY CORTICOBULBAR PATHWAY PYRAMIDAL TRACT LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT ...
Document
... primary motor cortex • When stimulated, muscles on the opposite side of the body contract. • Has complete representation of body’s musculature. • Greater space for fine motor control than for less precise motor control • Very focal stimulation --> organized movement (excitation and inhibition) Wed. ...
... primary motor cortex • When stimulated, muscles on the opposite side of the body contract. • Has complete representation of body’s musculature. • Greater space for fine motor control than for less precise motor control • Very focal stimulation --> organized movement (excitation and inhibition) Wed. ...
Amsterdam Brn Adapt View P3
... be brought about by experience. It also suggests that multiple forms of plasticity may occur at the synapse. In short, while memory researchers largely focus on naturallyand artificially-induced changes in synaptic connectivity, the brains of real animals (and presumably people) in realworld situati ...
... be brought about by experience. It also suggests that multiple forms of plasticity may occur at the synapse. In short, while memory researchers largely focus on naturallyand artificially-induced changes in synaptic connectivity, the brains of real animals (and presumably people) in realworld situati ...
Chapter 9 powerpoint file
... Primary somatic sensory cortex- found on the postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe) Skin, musculoskeletal system, and visceracomponents that send information to this region when a stimulus activates a sensory receptor Somatosensory pathways – carry information of senses in conscious awareness of ge ...
... Primary somatic sensory cortex- found on the postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe) Skin, musculoskeletal system, and visceracomponents that send information to this region when a stimulus activates a sensory receptor Somatosensory pathways – carry information of senses in conscious awareness of ge ...
BIOL 218 F 2012 MTX 4 Q NS 121121
... ………about how you are kinda sure that you are never ever ever ever going to be a Nurse, let alone an MD and now you will probably have to settle for orderly or bank clerk or waitress but you are only monolingual and even those jobs require you to speak at least two languages and you have trouble writ ...
... ………about how you are kinda sure that you are never ever ever ever going to be a Nurse, let alone an MD and now you will probably have to settle for orderly or bank clerk or waitress but you are only monolingual and even those jobs require you to speak at least two languages and you have trouble writ ...
phys chapter 51 [3-20
... o Initiated details of color contrast detected by simple cells; more complex contrasts detected by complex and hypercomplex cells Removal of primary visual cortex causes loss of conscious vision (blindness); blind people can still at times react subconsciously to changes in light intensity, moveme ...
... o Initiated details of color contrast detected by simple cells; more complex contrasts detected by complex and hypercomplex cells Removal of primary visual cortex causes loss of conscious vision (blindness); blind people can still at times react subconsciously to changes in light intensity, moveme ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.