Early Astronomy
... points of light on the sky, like the stars, but unlike the Sun and Moon. These objects received special attention because they: moved against the background of stars, are always located within several degrees of the ecliptic, periodically undergo retrograde motion with respect to the backgroun ...
... points of light on the sky, like the stars, but unlike the Sun and Moon. These objects received special attention because they: moved against the background of stars, are always located within several degrees of the ecliptic, periodically undergo retrograde motion with respect to the backgroun ...
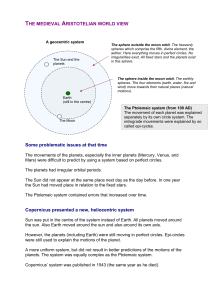
THE MEDIEVAL ARISTOTELIAN WORLD VIEW Some
... spheres which comprise the fifth, divine element, the aether. Here everything moves in perfect circles. No irregularities exist. All fixed stars and the planets exist in this sphere. ...
... spheres which comprise the fifth, divine element, the aether. Here everything moves in perfect circles. No irregularities exist. All fixed stars and the planets exist in this sphere. ...
Astronomy from the ancients to the Renaissance
... The Greeks had a notion that because the planets were located in the heavens, their motions must be “perfect”. Uniform, circular motion was regarded as perfect. So the planets must move through space uniformly on circles. But – the planets do not move uniformly to the east against the stars. Theref ...
... The Greeks had a notion that because the planets were located in the heavens, their motions must be “perfect”. Uniform, circular motion was regarded as perfect. So the planets must move through space uniformly on circles. But – the planets do not move uniformly to the east against the stars. Theref ...
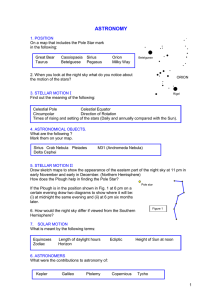
Astronomy work sheet
... If the Plough is in the position shown in Fig. 1 at 6 pm on a certain evening draw two diagrams to show where it will be: (i) at midnight the same evening and (ii) at 6 pm six months later. Figure 1 ...
... If the Plough is in the position shown in Fig. 1 at 6 pm on a certain evening draw two diagrams to show where it will be: (i) at midnight the same evening and (ii) at 6 pm six months later. Figure 1 ...
“The Southern Cross”
... well as calendars for use in religious as well as more general contexts. The ancient Indians used a sidereal system for their astronomical calculations. This uses the stars as a fixed background and times how long it takes an object to make a full orbit relative to them. A year consisted of 360 days ...
... well as calendars for use in religious as well as more general contexts. The ancient Indians used a sidereal system for their astronomical calculations. This uses the stars as a fixed background and times how long it takes an object to make a full orbit relative to them. A year consisted of 360 days ...
History_of_Astronomy
... equator—called it 24 degrees. • Fixed the year at 365 ¼ days. • Postulated the “Great Year”—the number of years when the motion of the Sun and the Moon exactly repeated their motions—59 years. • Oenopides' result leads to a lunar month of 29.53013 days which is remarkably close to the modern value o ...
... equator—called it 24 degrees. • Fixed the year at 365 ¼ days. • Postulated the “Great Year”—the number of years when the motion of the Sun and the Moon exactly repeated their motions—59 years. • Oenopides' result leads to a lunar month of 29.53013 days which is remarkably close to the modern value o ...
History of Astronomy Ancient to 200 A.D.
... equator—called it 24 degrees. • Fixed the year at 365 ¼ days. • Postulated the “Great Year”—the number of years when the motion of the Sun and the Moon exactly repeated their motions—59 years. • Oenopides' result leads to a lunar month of 29.53013 days which is remarkably close to the modern value o ...
... equator—called it 24 degrees. • Fixed the year at 365 ¼ days. • Postulated the “Great Year”—the number of years when the motion of the Sun and the Moon exactly repeated their motions—59 years. • Oenopides' result leads to a lunar month of 29.53013 days which is remarkably close to the modern value o ...
History of Astronomy Ancient to 200 AD
... equator—called it 24 degrees. • Fixed the year at 365 ¼ days. • Postulated the ―Great Year‖—the number of years when the motion of the Sun and the Moon exactly repeated their motions—59 years. • Oenopides' result leads to a lunar month of 29.53013 days which is remarkably close to the modern value o ...
... equator—called it 24 degrees. • Fixed the year at 365 ¼ days. • Postulated the ―Great Year‖—the number of years when the motion of the Sun and the Moon exactly repeated their motions—59 years. • Oenopides' result leads to a lunar month of 29.53013 days which is remarkably close to the modern value o ...
The Dead Guys a.k.a: The development of astronomy
... Egyptian Pyramidal Astronomy Astronomy used for positioning of the pyramids Vents & passageways align with specific stars Pyramids are slightly off Divide the sky into constellations These are known as star clocks “Diagonal calendars” Calendars – 3 seasons ...
... Egyptian Pyramidal Astronomy Astronomy used for positioning of the pyramids Vents & passageways align with specific stars Pyramids are slightly off Divide the sky into constellations These are known as star clocks “Diagonal calendars” Calendars – 3 seasons ...
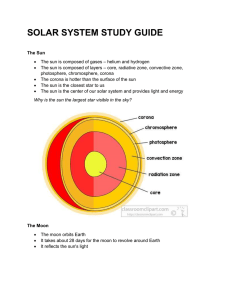
solar system study guide
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
astronomical: (meaning 1)
... Mars Rover Lesson 1 Vocabulary List Teacher Definitions Key Vocabulary apply: use what you have learned in a different way, place or time astronomical: (meaning 1) of or pertaining to the study of stars planets and extraterrestrial matter (meaning 2) a very large number or amount scale: the ratio or ...
... Mars Rover Lesson 1 Vocabulary List Teacher Definitions Key Vocabulary apply: use what you have learned in a different way, place or time astronomical: (meaning 1) of or pertaining to the study of stars planets and extraterrestrial matter (meaning 2) a very large number or amount scale: the ratio or ...
Astronomy - AG Web Services
... 4. Explain what is meant by light-year. Give the distance in light-years to the nearest star and the estimated distance to the farthest galaxy. 5. Explain the difference between an asterism and a constellation. 6. Do ONE of the following: a. Find a total of at least five asterisms and/or constellati ...
... 4. Explain what is meant by light-year. Give the distance in light-years to the nearest star and the estimated distance to the farthest galaxy. 5. Explain the difference between an asterism and a constellation. 6. Do ONE of the following: a. Find a total of at least five asterisms and/or constellati ...
Astronomy and Humanism by Ray Thompson A. EARLY
... that the spectra of very distant stars were much redder than they should be when the spectral class of the star was taken into account. In addition, the further away the objects were, the more pronounced was the move into the red end of the spectrum. Only one thing could explain this. The objects we ...
... that the spectra of very distant stars were much redder than they should be when the spectral class of the star was taken into account. In addition, the further away the objects were, the more pronounced was the move into the red end of the spectrum. Only one thing could explain this. The objects we ...
Astronomy Review Sheet
... - Astronomy- study of out space (planets, stars, moons) - Solar System- the Sun, the planets, and their moons - Spherical- round shaped like a ball - Atmosphere- layer of gas found around some planets (including Earth) - Inertia- a moving object will keep moving in a straight line until another forc ...
... - Astronomy- study of out space (planets, stars, moons) - Solar System- the Sun, the planets, and their moons - Spherical- round shaped like a ball - Atmosphere- layer of gas found around some planets (including Earth) - Inertia- a moving object will keep moving in a straight line until another forc ...
Astronomy Study Guide axis - A real or imaginary line through the
... The earth has seasons because the Earth is slightly tilted as it travels around the sun. We live in the Milky Way galaxy. Stars are hot, distant, and made of gas. Comets, Asteroids and Meteoroids are all found within our Solar System. The planets in our solar system orbit around the sun. The moon or ...
... The earth has seasons because the Earth is slightly tilted as it travels around the sun. We live in the Milky Way galaxy. Stars are hot, distant, and made of gas. Comets, Asteroids and Meteoroids are all found within our Solar System. The planets in our solar system orbit around the sun. The moon or ...
22 Jan: The Sky Tonight and Overview of the Solar System
... Where are the other planets you learned about in school? Where do they fall on our “map”? ...
... Where are the other planets you learned about in school? Where do they fall on our “map”? ...
Lecture notes -
... Where are the other planets you learned about in school? Where do they fall on our “map”? ...
... Where are the other planets you learned about in school? Where do they fall on our “map”? ...
File Space Test (March 11th) - Bonus Points
... frozen gases begin to melt. The tail always points away from the sun due to its solar winds. ...
... frozen gases begin to melt. The tail always points away from the sun due to its solar winds. ...
Topic 4 Guided Notes
... bodies that independently orbit the sun. •Range from 100 to 1000km in diameter. Asteroid belt- most asteroids are in orbits between ...
... bodies that independently orbit the sun. •Range from 100 to 1000km in diameter. Asteroid belt- most asteroids are in orbits between ...
Universe Game - Science
... Q. What’s the scientific name for the constellation of The Southern Cross? A. Crucis Q. Name the 9 planets. Q. Between which planets in our A. Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, solar system are asteroids found? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto A. Mars and Jupiter Q. Which planets have rings? Q. Wh ...
... Q. What’s the scientific name for the constellation of The Southern Cross? A. Crucis Q. Name the 9 planets. Q. Between which planets in our A. Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, solar system are asteroids found? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto A. Mars and Jupiter Q. Which planets have rings? Q. Wh ...
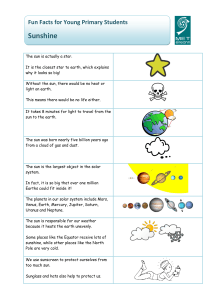
Fun Facts: Sunshine
... The sun is the largest object in the solar system. In fact, it is so big that over one million Earths could fit inside it! The planets in our solar system include Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The sun is responsible for our weather because it heats the earth uneve ...
... The sun is the largest object in the solar system. In fact, it is so big that over one million Earths could fit inside it! The planets in our solar system include Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The sun is responsible for our weather because it heats the earth uneve ...
Space Jeopardy 2
... The Outer Planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) are also known by this name ...
... The Outer Planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) are also known by this name ...
ch. 5 study guide
... o Why do we see different stars during different seasons? As Earth revolves around the Sun, it passes different groups of stars. o What is one constellation from our science book? The constellations in our science book include the Big Dipper, the Little Dipper, Orion, Cassiopeia, and Scorpius. Know ...
... o Why do we see different stars during different seasons? As Earth revolves around the Sun, it passes different groups of stars. o What is one constellation from our science book? The constellations in our science book include the Big Dipper, the Little Dipper, Orion, Cassiopeia, and Scorpius. Know ...