Intro to Supply & Demand
... • The quantity of goods or services that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices ...
... • The quantity of goods or services that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices ...
Theory of Markets
... results in an inward shift of the supply curve. • Subsidies - reduce costs and cause outward shift in supply curve Prices of other Goods- ...
... results in an inward shift of the supply curve. • Subsidies - reduce costs and cause outward shift in supply curve Prices of other Goods- ...
Marginalist Hall of Fame
... • Léon Walras, Elements of Pure Economics,1874,1877 • General Equilibrium: Cantillon/Quesnay interdependencies • Tâtonnement: “Groping” for equilibrium » “Auctioneer” announces and revises prices until markets clear » Quantities demanded and supplied equate relative marginal utilities to relative pr ...
... • Léon Walras, Elements of Pure Economics,1874,1877 • General Equilibrium: Cantillon/Quesnay interdependencies • Tâtonnement: “Groping” for equilibrium » “Auctioneer” announces and revises prices until markets clear » Quantities demanded and supplied equate relative marginal utilities to relative pr ...
Problem Set 2 Solutions
... people don’t understand how the EITC is phased in or phased out, so they don’t know that they should reduce hours to maximize utility. c) How would the effect on hours of labor differ if the individual initially did not work? For someone who initially chose zero hours of labor, the EITC could only h ...
... people don’t understand how the EITC is phased in or phased out, so they don’t know that they should reduce hours to maximize utility. c) How would the effect on hours of labor differ if the individual initially did not work? For someone who initially chose zero hours of labor, the EITC could only h ...
DISBURSEMENTS RECOVERY POLICY Category 1
... In the event that the Officeholder is authorised to charge fees on a time costs basis, the current hourly rates, subject to periodic review, and chargeable in six minutes units are as ...
... In the event that the Officeholder is authorised to charge fees on a time costs basis, the current hourly rates, subject to periodic review, and chargeable in six minutes units are as ...
Monopolistic Competition
... many producers. Hence, product differentiation is the only way monopolistically competitive firms can acquire some market power. ...
... many producers. Hence, product differentiation is the only way monopolistically competitive firms can acquire some market power. ...
a. Calculate the price elasticity of demand when the
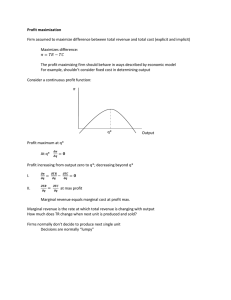
... different ways. Verify that the two are numerically equivalent. The graph below illustrates the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve. The average cost curve hits the marginal cost curve at a quantity of approximately 7, and is increasing thereafter (this is not shown in the ...
... different ways. Verify that the two are numerically equivalent. The graph below illustrates the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve. The average cost curve hits the marginal cost curve at a quantity of approximately 7, and is increasing thereafter (this is not shown in the ...
Solutions to Problems
... 5a. The profit-maximizing output is 150 newspapers a day. Profit is maximized when the firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue which is at 150 newspapers a day in figure 3. 5b. The price charged is 70 cents a paper. The highest price that the publisher can sell 150 ne ...
... 5a. The profit-maximizing output is 150 newspapers a day. Profit is maximized when the firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue which is at 150 newspapers a day in figure 3. 5b. The price charged is 70 cents a paper. The highest price that the publisher can sell 150 ne ...
Koç University
... You are required to attend classes by university policy. There will be weekly problem sessions, time schedule and place for those will be announced by the registrar. There will be one midterm exam and a final exam. The midterm will count for 35% of your grade. The final exam will count for 50% of yo ...
... You are required to attend classes by university policy. There will be weekly problem sessions, time schedule and place for those will be announced by the registrar. There will be one midterm exam and a final exam. The midterm will count for 35% of your grade. The final exam will count for 50% of yo ...
Module 10 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... Long-Run Profit Maximization o If a monopoly is insulated from competition by high barriers that block new entry, economic profit can persist in the long run. Price Discrimination o Increasing profits by charging different groups of consumers different prices when the price differences are not justi ...
... Long-Run Profit Maximization o If a monopoly is insulated from competition by high barriers that block new entry, economic profit can persist in the long run. Price Discrimination o Increasing profits by charging different groups of consumers different prices when the price differences are not justi ...
1) The supply curve for a good shows (for each quantity) the sellers`
... 40. If we internalize this externality and have producers pay for it, the new supply curve for the producers will be: A. P = 4 + QS. B. P = 2 + (1/2)QS. C. P = 6 + QS. D. P = 2 + 2QS. E. P = 10 - 2QS. 41. Suppose government officials have set an emissions tax to reduce pollution. Further suppose tha ...
... 40. If we internalize this externality and have producers pay for it, the new supply curve for the producers will be: A. P = 4 + QS. B. P = 2 + (1/2)QS. C. P = 6 + QS. D. P = 2 + 2QS. E. P = 10 - 2QS. 41. Suppose government officials have set an emissions tax to reduce pollution. Further suppose tha ...
Choice with Certainty Part II File
... 1. Use $ for prices so you keep your units clear! 2. Check your answer by substituting your answer into the budget constraint! ...
... 1. Use $ for prices so you keep your units clear! 2. Check your answer by substituting your answer into the budget constraint! ...
Econ 105 Section 8 Take-home Homework 1 Due Date: Wednesday
... d. Assume Japan is consuming 400 bolts of cloth and 300 tons of wheat, and the United States is consuming 400 bolts of cloth and 200 tons of wheat BEFORE trade. If both produce the goods for which they have a comparative advantage and trade half, what will be the new production, consumption, and ga ...
... d. Assume Japan is consuming 400 bolts of cloth and 300 tons of wheat, and the United States is consuming 400 bolts of cloth and 200 tons of wheat BEFORE trade. If both produce the goods for which they have a comparative advantage and trade half, what will be the new production, consumption, and ga ...
ECON 2010-100 Principles of Microeconomics
... the Problem Set which show evidence of effort (your answer need not be correct). If you are present and if your answer shows evidence of effort, you will receive a score of 1 for that week. If you are not present at the recitation and do not hand in an answer, you will receive a score of zero for th ...
... the Problem Set which show evidence of effort (your answer need not be correct). If you are present and if your answer shows evidence of effort, you will receive a score of 1 for that week. If you are not present at the recitation and do not hand in an answer, you will receive a score of zero for th ...
15 - Cengage Learning
... Figure 6 The Monopolist’s Profit Costs and revenue Marginal cost Monopoly E price ...
... Figure 6 The Monopolist’s Profit Costs and revenue Marginal cost Monopoly E price ...
2008D-MC-Non-Math - Mid
... When a farmer borrows money to purchase land, he usually must offer the title to the property as security until the debt has been repaid. This credit instrument is commonly referred to as a A. B. C. D. E. ...
... When a farmer borrows money to purchase land, he usually must offer the title to the property as security until the debt has been repaid. This credit instrument is commonly referred to as a A. B. C. D. E. ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.