Was Northern Italy an ideal place for the start of the Renaissance?
... Nobles, they firmly believed that a person’s achievements are more important than the status of birth Social- the merchant class in the Italian city states enjoyed a luxurious lifestyle and began to compete with the church in becoming patrons of arts ...
... Nobles, they firmly believed that a person’s achievements are more important than the status of birth Social- the merchant class in the Italian city states enjoyed a luxurious lifestyle and began to compete with the church in becoming patrons of arts ...
Georgetown University Liberal Studies Graduate Program Spring
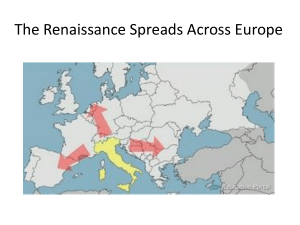
... ended. We will consider the interface among the Italian city-states and between Italy and the larger world during those centuries. We will ask where not only mainstream Christians but those considered heretical together with non-Christians (specifically, Jews and Muslims) fit into this reshaped worl ...
... ended. We will consider the interface among the Italian city-states and between Italy and the larger world during those centuries. We will ask where not only mainstream Christians but those considered heretical together with non-Christians (specifically, Jews and Muslims) fit into this reshaped worl ...
study guide for the
... First, there is the idea that the Middle Ages had few cultural accomplishments to their credit. Second, there is the idea that, sometime around 1350, a sudden rebirth of literature, art, and scholarship began in Italy. These views overlook the accomplishments of medieval European civilization, espec ...
... First, there is the idea that the Middle Ages had few cultural accomplishments to their credit. Second, there is the idea that, sometime around 1350, a sudden rebirth of literature, art, and scholarship began in Italy. These views overlook the accomplishments of medieval European civilization, espec ...
File
... passed the Elizabethan Settlement, which controlled outward conformity towards the English Church but didn’t push inward conformity. Her reign also saw the defeat of the Spanish Armada (1588), marking the end of Spain’s golden era. Louis XI (1423-1483) Louis XI began to move France towards absolut ...
... passed the Elizabethan Settlement, which controlled outward conformity towards the English Church but didn’t push inward conformity. Her reign also saw the defeat of the Spanish Armada (1588), marking the end of Spain’s golden era. Louis XI (1423-1483) Louis XI began to move France towards absolut ...
The Renaissance Study Guide Be able to identify the following
... emotion) and prose (writing – the ordinary form of spoken or written language) Who had the most power in Italy? The Pope and the Catholic Church, The Medici What are patrons? People who give money to artists and sponsor their work What is Humanism? Rebirth/renewed interest in human – centered classi ...
... emotion) and prose (writing – the ordinary form of spoken or written language) Who had the most power in Italy? The Pope and the Catholic Church, The Medici What are patrons? People who give money to artists and sponsor their work What is Humanism? Rebirth/renewed interest in human – centered classi ...
Renaissance Art - Great Neck Public Schools
... Focused on human beings Use of perspective and shading Blended religious themes with natural settings Also used classical mythology as a theme ...
... Focused on human beings Use of perspective and shading Blended religious themes with natural settings Also used classical mythology as a theme ...
the renaissance
... Characteristics of Renaissance Art: 1. Influenced by the artistic achievements of Classical Greece and Rome. Particularly in sculpture and architecture---Renaissance artists often imitated classical works. 2. Renaissance painting emphasized realism, attention to detail, and a desire for perfection. ...
... Characteristics of Renaissance Art: 1. Influenced by the artistic achievements of Classical Greece and Rome. Particularly in sculpture and architecture---Renaissance artists often imitated classical works. 2. Renaissance painting emphasized realism, attention to detail, and a desire for perfection. ...
sg1 west civ - Grants Pass School District 7
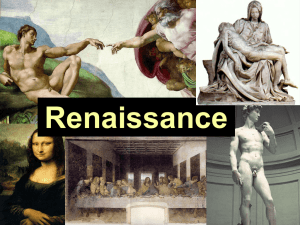
... artists, who became more famous. Renaissance art was based on classical styles and used new techniques like geometric perspective. They also painted using models and themes from their own everyday life. Michelangelo Sistine Chapel, David Raphael The School of Athens Leonardo daVinci Last Supper, Mon ...
... artists, who became more famous. Renaissance art was based on classical styles and used new techniques like geometric perspective. They also painted using models and themes from their own everyday life. Michelangelo Sistine Chapel, David Raphael The School of Athens Leonardo daVinci Last Supper, Mon ...
Chapter 12 Student PowerPoint Answers on Renaissance Topics
... 1.The pyramidal structure of Italian society in the Renaissance consisted of clergy, nobility, the Third Estate, and slaves. The clergy were ranking members of the Church and their importance was grounded in the belief that people should be guided to spiritual ends. The nobility had privileges based ...
... 1.The pyramidal structure of Italian society in the Renaissance consisted of clergy, nobility, the Third Estate, and slaves. The clergy were ranking members of the Church and their importance was grounded in the belief that people should be guided to spiritual ends. The nobility had privileges based ...
Renaissance notes
... which had been neglected during the Middle Ages. 2. It emphasized reason, a questioning attitude, experimentation, and free inquiry. This is contrasted with the medieval concern with faith, authority, and tradition. 3. It glorified the individual and approved worldly pleasures, viewing life as worth ...
... which had been neglected during the Middle Ages. 2. It emphasized reason, a questioning attitude, experimentation, and free inquiry. This is contrasted with the medieval concern with faith, authority, and tradition. 3. It glorified the individual and approved worldly pleasures, viewing life as worth ...
Chapter 14: Renaissance & Reformation
... how to gain and maintain power - looks at real rulers - the ends justifies the means; do not have to keep promises ...
... how to gain and maintain power - looks at real rulers - the ends justifies the means; do not have to keep promises ...
The Renaissance Chapter 17 Section 1 What was the Renaissance
... o He died of a fever at the age of 37 years old o He was supported by the Medici family o He was known for painting cherubs or angels, The School of Athens o Donatello o Born in Florence, Italy in 1386 o His first sculpture was of the Three Prophets o One of his best pieces was made by stone and was ...
... o He died of a fever at the age of 37 years old o He was supported by the Medici family o He was known for painting cherubs or angels, The School of Athens o Donatello o Born in Florence, Italy in 1386 o His first sculpture was of the Three Prophets o One of his best pieces was made by stone and was ...
Renaissance Begins - Oxford School District
... Even without the approval of his father, Petrarch continued to study the writings of ancient Rome which can be seen in his famous poems. ...
... Even without the approval of his father, Petrarch continued to study the writings of ancient Rome which can be seen in his famous poems. ...
Renaissance Contributions - Dolgeville Central School
... Shift in focus from religious (sacred) matters to worldly (secular) People start thinking about “What can I do with my life in the world right now?” instead of “What do I need to do to get into heaven when I die?” Leads to a questioning of church authority & more faith in human reasoning ...
... Shift in focus from religious (sacred) matters to worldly (secular) People start thinking about “What can I do with my life in the world right now?” instead of “What do I need to do to get into heaven when I die?” Leads to a questioning of church authority & more faith in human reasoning ...
View Presentation
... • Florence the leader in Renaissance art esp. in quattrocento (1400s). • The wealth of Florence meant that it had many patrons who would pay for art projects of artists such as... • Leon Battista Alberti (1404-1472), architect of cathedrals. • Masaccio (1401-1428) painter: nude human figures • Giova ...
... • Florence the leader in Renaissance art esp. in quattrocento (1400s). • The wealth of Florence meant that it had many patrons who would pay for art projects of artists such as... • Leon Battista Alberti (1404-1472), architect of cathedrals. • Masaccio (1401-1428) painter: nude human figures • Giova ...
Medieval Theater
... Depicted Christ’s life through resurrection Passion play in Oberammergau, Germany Residents of Bavarian village vowed that to be spared from the Black Plague, they would put on a passion play every 10 years Village was spared, began performances in ...
... Depicted Christ’s life through resurrection Passion play in Oberammergau, Germany Residents of Bavarian village vowed that to be spared from the Black Plague, they would put on a passion play every 10 years Village was spared, began performances in ...
Period 1 AP European History Key Terms
... Catherine de’ Medici St. Barholomew’s Day Massacre War of the Three Henry IV Habsburg rulers’ role in Religion Ferdinand and Isabella Spanish Inquisition Charles IV Philip II Philip III Philip IV State Exploitation of Religious Conflicts (explain these examples) Catholic Spain and Protestant England ...
... Catherine de’ Medici St. Barholomew’s Day Massacre War of the Three Henry IV Habsburg rulers’ role in Religion Ferdinand and Isabella Spanish Inquisition Charles IV Philip II Philip III Philip IV State Exploitation of Religious Conflicts (explain these examples) Catholic Spain and Protestant England ...
Chapter 13 Part 2
... Chiaroscuro: The use of dark and light colors to give the impression of depth ...
... Chiaroscuro: The use of dark and light colors to give the impression of depth ...
Spanish Golden Age

The Spanish Golden Age (Spanish: Siglo de Oro, Golden Century) is a period of flourishing in arts and literature in Spain, coinciding with the political rise and decline of the Spanish Habsburg dynasty. El Siglo de Oro does not imply precise dates and is usually considered to have lasted longer than an actual century. It begins no earlier than 1492, with the end of the Reconquista (Reconquest), the sea voyages of Christopher Columbus to the New World, and the publication of Antonio de Nebrija's Gramática de la lengua castellana (Grammar of the Castilian Language). Politically, it ends no later than 1659, with the Treaty of the Pyrenees, ratified between France and Habsburg Spain. The last great writer of the period, Pedro Calderón de la Barca, died in 1681, and his death usually is considered the end of El Siglo de Oro in the arts and literature.The Habsburgs, both in Spain and Austria, were great patrons of art in their countries. El Escorial, the great royal monastery built by King Philip II, invited the attention of some of Europe's greatest architects and painters. Diego Velázquez, regarded as one of the most influential painters of European history and a greatly respected artist in his own time, cultivated a relationship with King Philip IV and his chief minister, the Count-Duke of Olivares, leaving us several portraits that demonstrate his style and skill. El Greco, another respected artist from the period, infused Spanish art with the styles of the Italian renaissance and helped create a uniquely Spanish style of painting. Some of Spain's greatest music is regarded as having been written in the period. Such composers as Tomás Luis de Victoria, Cristóbal de Morales, Francisco Guerrero, Luis de Milán and Alonso Lobo helped to shape Renaissance music and the styles of counterpoint and polychoral music, and their influence lasted far into the Baroque period which resulted in a revolution of music. Spanish literature blossomed as well, most famously demonstrated in the work of Miguel de Cervantes, the author of Don Quixote de la Mancha. Spain's most prolific playwright, Lope de Vega, wrote possibly as many as one thousand plays during his lifetime, of which over four hundred survive to the present day.