The All-Seeing, All-Magnifying Eye
... The brightening can be up to about one magnitude -- the star becomes about 3 times brighter. So far, to date, finding this “flash” is the only technique (other than photometric transits or pulsar-timing) by which we can detect terrestrial-type planets around Sunlike stars or close double-star system ...
... The brightening can be up to about one magnitude -- the star becomes about 3 times brighter. So far, to date, finding this “flash” is the only technique (other than photometric transits or pulsar-timing) by which we can detect terrestrial-type planets around Sunlike stars or close double-star system ...
Lecture 2+3 - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... Cluster of bright young stars in center Winds from young massive stars clearing out a hole in center; Outer layers of dust and hot glowing gas. ...
... Cluster of bright young stars in center Winds from young massive stars clearing out a hole in center; Outer layers of dust and hot glowing gas. ...
June 2013 Kepler Space Telescope Update
... On May 25th, Mercury will pass within 1.4° of Venus, then two days later Mercury comes within 2.4° of Jupiter, and finally on the 28th, Jupiter and Venus approach within 1° of one another. If it weren’t for the slight orbital tilt of our solar system’s planetary orbits, these conjunctions would all ...
... On May 25th, Mercury will pass within 1.4° of Venus, then two days later Mercury comes within 2.4° of Jupiter, and finally on the 28th, Jupiter and Venus approach within 1° of one another. If it weren’t for the slight orbital tilt of our solar system’s planetary orbits, these conjunctions would all ...
Final Study Guide
... 33. What is meant by the terms “event horizon” and “Schwarzschild radius” and what is their relation to the mass of a black hole? 34. What is meant by the “period luminosity relation” of the Cepheid variables, and how can this be used as a distance indicator to the stars? 35. How are the spiral arms ...
... 33. What is meant by the terms “event horizon” and “Schwarzschild radius” and what is their relation to the mass of a black hole? 34. What is meant by the “period luminosity relation” of the Cepheid variables, and how can this be used as a distance indicator to the stars? 35. How are the spiral arms ...
Astronomy 10B List of Concepts– by Chapter
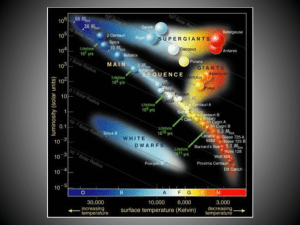
... • The H-R diagram and star formation • Finding the age of star clusters and the H-R diagram • Planetary formation CHAPTER 13: STELLAR EVOLUTION • The main sequence (M.S.) o What are these stars doing? o How long will they be doing this (what fraction of their lives)? o Relation between stellar mass ...
... • The H-R diagram and star formation • Finding the age of star clusters and the H-R diagram • Planetary formation CHAPTER 13: STELLAR EVOLUTION • The main sequence (M.S.) o What are these stars doing? o How long will they be doing this (what fraction of their lives)? o Relation between stellar mass ...
Other Planetary Systems
... This Explains Why… …in many of the planetary systems detected so far, we find big, massive planets quite close to the parent stars (especially with the ‘wobble’ technique; using transits is better able to find smaller planets.) It will take many years, and improving technology, to allow the confirm ...
... This Explains Why… …in many of the planetary systems detected so far, we find big, massive planets quite close to the parent stars (especially with the ‘wobble’ technique; using transits is better able to find smaller planets.) It will take many years, and improving technology, to allow the confirm ...
galaxies
... • has about 200 billion stars, and lots of gas and dust • is a barred-spiral (we think) • about 100,000 light-years wide • our Sun is halfway to the edge, revolving at half a million miles per hour around the center of the Galaxy • takes our Solar System about 200 million years to revolve once aroun ...
... • has about 200 billion stars, and lots of gas and dust • is a barred-spiral (we think) • about 100,000 light-years wide • our Sun is halfway to the edge, revolving at half a million miles per hour around the center of the Galaxy • takes our Solar System about 200 million years to revolve once aroun ...
Cosmology Î Bottom-Up formation of structures
... • Plug into equations for luminosity or angular size distance as needed (Ned Wright’s Cosmology Calculator) ...
... • Plug into equations for luminosity or angular size distance as needed (Ned Wright’s Cosmology Calculator) ...
ppt
... •This picture turns out to be the result of an observational bias inherent with the radial velocity method. (easier to detect massive planets in small orbits) ...
... •This picture turns out to be the result of an observational bias inherent with the radial velocity method. (easier to detect massive planets in small orbits) ...
Introduction to the Earth
... Called main sequence stars Other 10% were once main sequence stars but have changed over time ...
... Called main sequence stars Other 10% were once main sequence stars but have changed over time ...
Tour of the Universe
... ● Some ancient societies used them for religious reasons. ● Today they are used for telescopic study. ● Some of the stars are much closer to Earth than others. Because of proper motion, they will look different in ten thousand years. ● These stars are not held together by gravity. ● Proper mot ...
... ● Some ancient societies used them for religious reasons. ● Today they are used for telescopic study. ● Some of the stars are much closer to Earth than others. Because of proper motion, they will look different in ten thousand years. ● These stars are not held together by gravity. ● Proper mot ...
How Telescopes Changed our Universe
... Big Question 7: Are there other planets? In our own solar system, telescopes found planets our eyes could not see. Are there other planets outside of our solar system? ...
... Big Question 7: Are there other planets? In our own solar system, telescopes found planets our eyes could not see. Are there other planets outside of our solar system? ...
E1 a-d
... are many more than cannot be seen without a telescope. Stars have ____________________ sizes, colors, and patterns. The ___________ of a star tells us the star’s temperature. ____________ can be red, yellow, or blue. Red Dwarf stars are smaller than other stars and have the ____________ ...
... are many more than cannot be seen without a telescope. Stars have ____________________ sizes, colors, and patterns. The ___________ of a star tells us the star’s temperature. ____________ can be red, yellow, or blue. Red Dwarf stars are smaller than other stars and have the ____________ ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... These stars are aging stars. They lie in a region of the HR diagram called the Instability Strip. A star becomes a Cepheid variable star (unstable to oscillations) several times before it dies. These stars are more massive than the sun. ...
... These stars are aging stars. They lie in a region of the HR diagram called the Instability Strip. A star becomes a Cepheid variable star (unstable to oscillations) several times before it dies. These stars are more massive than the sun. ...
Answer titese questions on a piece of loose leaf paper.
... 15. What force pulls gas and dust together to begin forming stais? 16. A star is "bom** when what process begins? 17. - Stars with less mass "live" than stars witli more mass. 18. When a star begins to run out of fiicl, its outer layers 19. Name the stages in the "h'fe** of a low/medium mass star 20 ...
... 15. What force pulls gas and dust together to begin forming stais? 16. A star is "bom** when what process begins? 17. - Stars with less mass "live" than stars witli more mass. 18. When a star begins to run out of fiicl, its outer layers 19. Name the stages in the "h'fe** of a low/medium mass star 20 ...
Oceanography Chapter 1 – “Origins”
... temperature. • Over 14 billion years, gravity magnified these small differences into clusters of galaxies today. ...
... temperature. • Over 14 billion years, gravity magnified these small differences into clusters of galaxies today. ...
The Drake Equation
... Did they all destroy themselves with nuclear weapons long ago? Worlds smashed by comets or gamma ray bursts? Perhaps they survive a long time if they can travel to other habitable worlds Can ET’s communicate with us via sub-space transmission, inter-dimensional transmission or using optical ...
... Did they all destroy themselves with nuclear weapons long ago? Worlds smashed by comets or gamma ray bursts? Perhaps they survive a long time if they can travel to other habitable worlds Can ET’s communicate with us via sub-space transmission, inter-dimensional transmission or using optical ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... A second evidence that supports the Big Bang theory is the overall chemical composition of the Universe. Calculations predict that the composition of the Universe should be about three fourths hydrogen and one fourth helium by mass, being a closed match to the overall chemical composition of the uni ...
... A second evidence that supports the Big Bang theory is the overall chemical composition of the Universe. Calculations predict that the composition of the Universe should be about three fourths hydrogen and one fourth helium by mass, being a closed match to the overall chemical composition of the uni ...
STUDY QUESTIONS #10 The MILKY WAY GALAXY diameter face
... 9. Using the rotation curve above, astronomers have calculated a mass for the whole Galaxy, out to about 50,000 light-year radius where there are no more stars, to be about 2 × 1011 M , yet by measuring light at all wavelengths, they only measure one sixth of that mass (3 × 1010 M ). Using the orbit ...
... 9. Using the rotation curve above, astronomers have calculated a mass for the whole Galaxy, out to about 50,000 light-year radius where there are no more stars, to be about 2 × 1011 M , yet by measuring light at all wavelengths, they only measure one sixth of that mass (3 × 1010 M ). Using the orbit ...
Astrophysics Presentation
... easily (radar guns don’t reach that far, besides which... ?) However we can use the same technique: Radar guns measure the shift in frequency of the microwaves bounced off a moving vehicle. If the moving object is itself emitting waves we also have a shift in frequency. This is known as the ... ...
... easily (radar guns don’t reach that far, besides which... ?) However we can use the same technique: Radar guns measure the shift in frequency of the microwaves bounced off a moving vehicle. If the moving object is itself emitting waves we also have a shift in frequency. This is known as the ... ...
Galaxies
... concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
... concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
Teaching Text Structure with Understanding the Scale of the Universe
... Harvard College Observatory found a way to calculate the distance to a certain type of star in our galaxy by looking at astronomical photographs and studying how these stars regularly change in brightness. The data she collected and the techniques she developed became standard tools for astronomers ...
... Harvard College Observatory found a way to calculate the distance to a certain type of star in our galaxy by looking at astronomical photographs and studying how these stars regularly change in brightness. The data she collected and the techniques she developed became standard tools for astronomers ...
hubble_refurb
... space by the cluster’s gravitational field distorts the light from galaxies lying far behind it. This is manifested as arcs and streaks in the picture, which are the stretched images of background galaxies. Gravitational lensing proves a vital tool for astronomers when measuring the dark matter dist ...
... space by the cluster’s gravitational field distorts the light from galaxies lying far behind it. This is manifested as arcs and streaks in the picture, which are the stretched images of background galaxies. Gravitational lensing proves a vital tool for astronomers when measuring the dark matter dist ...
Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy
... Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy The ______________ _________ Galaxy ...
... Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy The ______________ _________ Galaxy ...
Space Interferometry Mission

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars.The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM's case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected ""no earlier"" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. In 2009 the project continued its risk reduction work while waiting for the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, which would determine the project's future.On 13 August 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on 24 September 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.