Characterization of the four new transiting planets KOI
... giant planets. KOI-192b has a similar mass (0.29 MJup ) but a longer orbital period of 10.3 days. This places it in a domain where only a few planets are known. KOI-830b, finally, with a mass of 1.27 MJup and a period of 3.5 days, is a typical hot Jupiter. The four planets have radii of 0.98, 1.09, ...
... giant planets. KOI-192b has a similar mass (0.29 MJup ) but a longer orbital period of 10.3 days. This places it in a domain where only a few planets are known. KOI-830b, finally, with a mass of 1.27 MJup and a period of 3.5 days, is a typical hot Jupiter. The four planets have radii of 0.98, 1.09, ...
oC - geogreenapps
... the book. Thia ..viDI of time aDd repeated explanations to difFereot pupils, wiD be read,ily appreciated by every practical jnatructor~ Again, many of theee draWiDP are ""irel, origiul, and in the opiaion of competeDt jl1da-, better calculated to conyey a correct and permanent idea to the miDd, than ...
... the book. Thia ..viDI of time aDd repeated explanations to difFereot pupils, wiD be read,ily appreciated by every practical jnatructor~ Again, many of theee draWiDP are ""irel, origiul, and in the opiaion of competeDt jl1da-, better calculated to conyey a correct and permanent idea to the miDd, than ...
Moon-Earth-Sun: The oldest three-body problem
... represented by simple arithmetic formulas that lack any insight in terms of geometric models, let alone physical principles. And yet, most physicists are not aware of the important characteristic frequencies in the lunar orbit that were discovered at that time. They can be compared with the masses o ...
... represented by simple arithmetic formulas that lack any insight in terms of geometric models, let alone physical principles. And yet, most physicists are not aware of the important characteristic frequencies in the lunar orbit that were discovered at that time. They can be compared with the masses o ...
Night Sky II Annual Motion Seasons Planetary Motion
... Indeed originally named for their “wandering” movement ...
... Indeed originally named for their “wandering” movement ...
Homework Assignment #7: The Moon
... We have all known, from a very young age, that the moon revolves around Earth and that it takes about a month to do so--hence the word mo(o)nth. But have you ever stopped to wonder which way the moon revolves around Earth? Does it revolve from east to west (clockwise when looking down on Earth's nor ...
... We have all known, from a very young age, that the moon revolves around Earth and that it takes about a month to do so--hence the word mo(o)nth. But have you ever stopped to wonder which way the moon revolves around Earth? Does it revolve from east to west (clockwise when looking down on Earth's nor ...
Abstract - Dept of Maths, NUS
... the Sun. The analemma is the path that the Sun takes if we mark the position of the Sun in the sky at the same time everyday, say sometime around noon. There are two independent reasons why the Sun takes this strange path: 1. The Earth is tilted on its axis 23.5° in relation to the plane of its orbi ...
... the Sun. The analemma is the path that the Sun takes if we mark the position of the Sun in the sky at the same time everyday, say sometime around noon. There are two independent reasons why the Sun takes this strange path: 1. The Earth is tilted on its axis 23.5° in relation to the plane of its orbi ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... (in parsecs) = 1/p (in arcseconds), the method of spectroscopic parallax and the Cepheids method for determining distances in astronomy? Can you define the parsec? Can you state the definitions of apparent brightness, b = L/4πd2 , and apparent and absolute magnitude, b/b0 = 100-m/5 = 2.512-m? ...
... (in parsecs) = 1/p (in arcseconds), the method of spectroscopic parallax and the Cepheids method for determining distances in astronomy? Can you define the parsec? Can you state the definitions of apparent brightness, b = L/4πd2 , and apparent and absolute magnitude, b/b0 = 100-m/5 = 2.512-m? ...
Microsoft Word
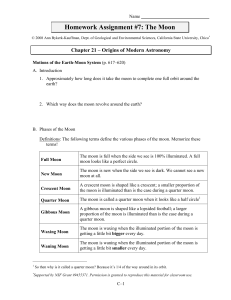
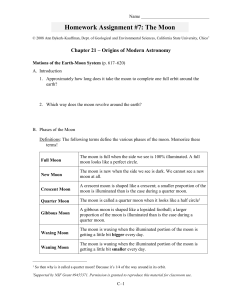
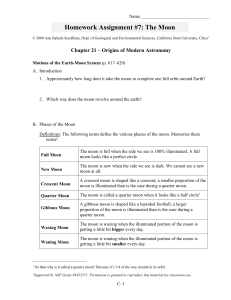
... 1. Demonstrate and illustrate how the relative positions of the sun, earth and moon cause the phases of the moon as seen from earth. 2. Given a drawing or photograph of the moon in any phase, be able to correctly name that phase and draw a diagram showing the relative positions of Earth, the moon an ...
... 1. Demonstrate and illustrate how the relative positions of the sun, earth and moon cause the phases of the moon as seen from earth. 2. Given a drawing or photograph of the moon in any phase, be able to correctly name that phase and draw a diagram showing the relative positions of Earth, the moon an ...
Section 1.2 Astrometric Data
... parsec is given by 1000 / π , where π is expressed in mas. The common reference epoch used throughout the catalogue is T0 = J1991.25(TT) (see Section 1.2.6). The standard astrometric model, using the five astrometric parameters, was found to be adequate for the majority of the stars, including the c ...
... parsec is given by 1000 / π , where π is expressed in mas. The common reference epoch used throughout the catalogue is T0 = J1991.25(TT) (see Section 1.2.6). The standard astrometric model, using the five astrometric parameters, was found to be adequate for the majority of the stars, including the c ...
PLANETS
... solar system. Only a minority of the nearby stars are so young. Even for them, planets— and particularly those in the terrestrial planet/asteroidal region—are faint and are lost in the glare of their central stars. However, when bodies in this zone collide, they initiate cascades of further collisio ...
... solar system. Only a minority of the nearby stars are so young. Even for them, planets— and particularly those in the terrestrial planet/asteroidal region—are faint and are lost in the glare of their central stars. However, when bodies in this zone collide, they initiate cascades of further collisio ...
the strange case of claudius ptolemy
... given the name 'E Mathematike Syntaxis in English transliterations of the Greek. Since the names now given to many ancient works were assigned by later editors or commentators, I do not know whether this is a title that Ptolemy himself chose or not. It is an old title in any event. The work is divid ...
... given the name 'E Mathematike Syntaxis in English transliterations of the Greek. Since the names now given to many ancient works were assigned by later editors or commentators, I do not know whether this is a title that Ptolemy himself chose or not. It is an old title in any event. The work is divid ...
Hariprasad comes from well known Jyotish family in Andhrapradesh
... Sun’s entry into Makara (Capricorn) = ‘Varuna’. ‘Vishuvath chalanam’ = ‘Agastya chara’ In Vishnupurana, it was stated that Dhruva did penance (Tapas). Lord Vishnu was pleased and rewarded his penance stating that ‘Saptarishi Mandalam’ would revolve around Dhruva once every 26,000 years. (Source: ‘N ...
... Sun’s entry into Makara (Capricorn) = ‘Varuna’. ‘Vishuvath chalanam’ = ‘Agastya chara’ In Vishnupurana, it was stated that Dhruva did penance (Tapas). Lord Vishnu was pleased and rewarded his penance stating that ‘Saptarishi Mandalam’ would revolve around Dhruva once every 26,000 years. (Source: ‘N ...
A Reminder of the Policy on Collaboration: We allow and expect you
... A. The Days of the Week: The reason we have 7-day weeks is because our ancestors noticed seven heavenly bodies “wandering” among the stars on the celestial sphere. These seven heavenly bodies were the sun, the moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. The outermost planets (Nept ...
... A. The Days of the Week: The reason we have 7-day weeks is because our ancestors noticed seven heavenly bodies “wandering” among the stars on the celestial sphere. These seven heavenly bodies were the sun, the moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. The outermost planets (Nept ...
Magnitudes - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... We measure the brightness of a star by its magnitude. There are two types of magnitude: Apparent magnitude is how bright an object is to us on Earth. Absolute magnitude is how bright a star would appear in space from a certain distance. ...
... We measure the brightness of a star by its magnitude. There are two types of magnitude: Apparent magnitude is how bright an object is to us on Earth. Absolute magnitude is how bright a star would appear in space from a certain distance. ...
Habitable Zone Lifetimes of Exoplanets around Main Sequence Stars
... surface, experiencing high rates of evaporation and increasing humidity. The resulting increase in temperature serves to further accelerate evaporation, eventually resulting in the irreversible evaporation of the ocean into the atmosphere (Kasting, 1988; Goldblatt and Watson, 2012). The outer bounda ...
... surface, experiencing high rates of evaporation and increasing humidity. The resulting increase in temperature serves to further accelerate evaporation, eventually resulting in the irreversible evaporation of the ocean into the atmosphere (Kasting, 1988; Goldblatt and Watson, 2012). The outer bounda ...
Space, Earth and Celestial Objects Test Prep
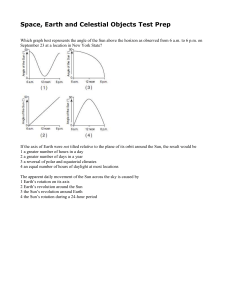
... and Jupiter, in a vast ring known as the Asteroid Belt. Occasionally, though, an asteroid leaves this orbit belt and moves into a more eccentric orbit that brings it into the inner solar system. This sudden change may be caused by an impact with another asteroid or by the gravitational pull of Jupit ...
... and Jupiter, in a vast ring known as the Asteroid Belt. Occasionally, though, an asteroid leaves this orbit belt and moves into a more eccentric orbit that brings it into the inner solar system. This sudden change may be caused by an impact with another asteroid or by the gravitational pull of Jupit ...
Unit 1 test review and answer key 16
... 112. How was the model of the universe proposed by Copernicus different than the one proposed by Ptolemy? 113. a) How are the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars classified? b) Identify two features that these planets have in common. 114. a) What is a dwarf planet? In your answer make sure you e ...
... 112. How was the model of the universe proposed by Copernicus different than the one proposed by Ptolemy? 113. a) How are the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars classified? b) Identify two features that these planets have in common. 114. a) What is a dwarf planet? In your answer make sure you e ...
solar system
... and demonstrated that ordinary observers could see things that the great Aristotle had not dreamed of. It therefore helped shift authority in the observation of nature from men to instruments. In short, it was the prototype of modern scienti c instruments. But the telescope was not the invention of ...
... and demonstrated that ordinary observers could see things that the great Aristotle had not dreamed of. It therefore helped shift authority in the observation of nature from men to instruments. In short, it was the prototype of modern scienti c instruments. But the telescope was not the invention of ...
DIO 15 - DIO, The International Journal of Scientific History
... The next candidate was another fixed star Galileo plotted five days later. This turned out to be SAO 119234. Finally, I found the Holy Grail on the drawing for January 28, 1613. On that night Galileo drew two stars near Jupiter. Star ‘A’ was SAO 119234 again. Star ‘B’ was Neptune! Galileo made a sep ...
... The next candidate was another fixed star Galileo plotted five days later. This turned out to be SAO 119234. Finally, I found the Holy Grail on the drawing for January 28, 1613. On that night Galileo drew two stars near Jupiter. Star ‘A’ was SAO 119234 again. Star ‘B’ was Neptune! Galileo made a sep ...
DIO vol. 15 - DIO, The International Journal of Scientific History
... done originally in Greco-Roman times or later in India seems impossible to say in the absence of any further evidence. ...
... done originally in Greco-Roman times or later in India seems impossible to say in the absence of any further evidence. ...
Howard 2013 Observed properties of exoplanets
... Observational surveys for extrasolar planets probe the diverse outcomes of planet formation and evolution. These surveys measure the frequency of planets with different masses, sizes, orbital characteristics, and host star properties. Small planets between the sizes of Earth and Neptune substantiall ...
... Observational surveys for extrasolar planets probe the diverse outcomes of planet formation and evolution. These surveys measure the frequency of planets with different masses, sizes, orbital characteristics, and host star properties. Small planets between the sizes of Earth and Neptune substantiall ...
Kepler Mission Workshop Presentation
... lava and much too hot for life as we know it • All five of the exoplanets orbit stars hotter and larger than Earth's sun. ...
... lava and much too hot for life as we know it • All five of the exoplanets orbit stars hotter and larger than Earth's sun. ...
2Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... Way appears somewhat wider in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, because that is the direction in which we are looking toward the galaxy’s central bulge. We have a clear view to the distant universe only when we look away from the galactic plane, along directions that have relatively fe ...
... Way appears somewhat wider in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, because that is the direction in which we are looking toward the galaxy’s central bulge. We have a clear view to the distant universe only when we look away from the galactic plane, along directions that have relatively fe ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑