Eve J. Lee - UC Berkeley Astronomy
... • Organizing and leading an annual information/discussion session on choosing research advisors. • Holding mentor-mentee lunch every semester to monitor academic progress and general morale of first and second year graduate students. • Meeting with the head graduate advisor at least once a year to a ...
... • Organizing and leading an annual information/discussion session on choosing research advisors. • Holding mentor-mentee lunch every semester to monitor academic progress and general morale of first and second year graduate students. • Meeting with the head graduate advisor at least once a year to a ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
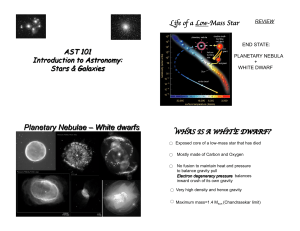
... As the white dwarf cools, the light it gives off will fade through the visible light spectrum, blue to red to back (no light). A black dwarf will continue to generate gravity and low energy transmissions (radio waves). ...
... As the white dwarf cools, the light it gives off will fade through the visible light spectrum, blue to red to back (no light). A black dwarf will continue to generate gravity and low energy transmissions (radio waves). ...
Extra-Solar Planets
... • 1960’s – 1990’s: Numerous claims (and retractions of planet detections via astrometry and spectroscopy • 1991: First extra-solar planetary system (accidentally) found by timing a millisecond pulsar (PSR B1257+12) • 1995: First planet found around a “normal” star (51 Pegasi) ...
... • 1960’s – 1990’s: Numerous claims (and retractions of planet detections via astrometry and spectroscopy • 1991: First extra-solar planetary system (accidentally) found by timing a millisecond pulsar (PSR B1257+12) • 1995: First planet found around a “normal” star (51 Pegasi) ...
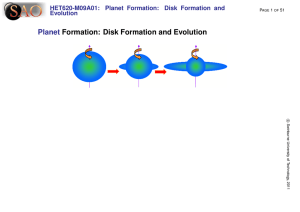
Planet Formation: Disk Formation and Evolution
... (iii) Magnetic support: Magnetic fields only affect charged particles in molecular clouds, making them follow field lines rather than obey gravity (or dragging the field along with them). The fields exert a magnetic force on the charged particles, which acts like a magnetic pressure. The magnetic pr ...
... (iii) Magnetic support: Magnetic fields only affect charged particles in molecular clouds, making them follow field lines rather than obey gravity (or dragging the field along with them). The fields exert a magnetic force on the charged particles, which acts like a magnetic pressure. The magnetic pr ...
1 HoNoRS227 Examination #3 Name
... In accordance with the Big Bang theory of the formation of the universe, which of the following is true? A The Matter Era exists without radiation because it occurred later. B The Vacuum Era occurred after the Matter Era. C The Degenerate Dark Era occurs before the Vacuum Era. *D There were no parti ...
... In accordance with the Big Bang theory of the formation of the universe, which of the following is true? A The Matter Era exists without radiation because it occurred later. B The Vacuum Era occurred after the Matter Era. C The Degenerate Dark Era occurs before the Vacuum Era. *D There were no parti ...
Practice Questions for Final
... Which of the following statements about black holes is NOT true? A. If you fell into a black hole, you would experience time to be running normally as you plunged rapidly across the event horizon. B. A spaceship passing near a 10 solar mass black hole is much more likely to be destroyed than a space ...
... Which of the following statements about black holes is NOT true? A. If you fell into a black hole, you would experience time to be running normally as you plunged rapidly across the event horizon. B. A spaceship passing near a 10 solar mass black hole is much more likely to be destroyed than a space ...
m, a, e
... telescopes with those obtained while combining several such telescopes into an interferometric array (this technique, long practiced by radio astronomers, allows us to achieve very good, low-angular resolution, observations). ...
... telescopes with those obtained while combining several such telescopes into an interferometric array (this technique, long practiced by radio astronomers, allows us to achieve very good, low-angular resolution, observations). ...
Origins of the Universe
... • Grains built up into bigger, rocky lumps – called planetesimals • The planetesimals that survived all the collisions with other objects built up and eventually developed into planets ...
... • Grains built up into bigger, rocky lumps – called planetesimals • The planetesimals that survived all the collisions with other objects built up and eventually developed into planets ...
Lecture 34. Extrasolar Planets.
... Distance between A and b is 20RJup (Jupiter radii - or 5.2 AU) Star: 70% solar mass Planet: 1-42 x MJup (1 Jupiter mass = 318 Earths) First discovered in the 1995 - over 163 are known. ...
... Distance between A and b is 20RJup (Jupiter radii - or 5.2 AU) Star: 70% solar mass Planet: 1-42 x MJup (1 Jupiter mass = 318 Earths) First discovered in the 1995 - over 163 are known. ...
etlife - University of Glasgow
... The Kepler mission (launch 2007?) will detect transits of Earth-type planets, by observing the brightness dip of stars (already done in 2000 with Keck for a 0.5 x Jupiter-mass planet) There was a (rare) transit of Mercury on May 7th 2003, and a (very rare) transit of Venus on June 8th 2004 ...
... The Kepler mission (launch 2007?) will detect transits of Earth-type planets, by observing the brightness dip of stars (already done in 2000 with Keck for a 0.5 x Jupiter-mass planet) There was a (rare) transit of Mercury on May 7th 2003, and a (very rare) transit of Venus on June 8th 2004 ...
The Solar System Sections 16.1-16.8
... Formation of the Solar System • Began with a large, swirling volume of cold gases and dust – a rotating solar nebula • Contracted under the influence of its own gravity – into a flattened, rotating disk • Further contraction produced the protosun and eventually accreted the planets • As particles m ...
... Formation of the Solar System • Began with a large, swirling volume of cold gases and dust – a rotating solar nebula • Contracted under the influence of its own gravity – into a flattened, rotating disk • Further contraction produced the protosun and eventually accreted the planets • As particles m ...
3 - MrFuglestad
... White Dwarf – Earth sized star that is stable with no nuclear reactions and is made of helium or carbon depending on the mass. Less massive than our Sun = Helium. There can be other elements present such as Oxygen, etc. Often the White Dwarf stars are surrounded by nebula. Black Dwarf – This star is ...
... White Dwarf – Earth sized star that is stable with no nuclear reactions and is made of helium or carbon depending on the mass. Less massive than our Sun = Helium. There can be other elements present such as Oxygen, etc. Often the White Dwarf stars are surrounded by nebula. Black Dwarf – This star is ...
CVs
... – Amount of accretion necessary depends on mass of WD – Short time scale (~100yrs) could occur for stars near the ...
... – Amount of accretion necessary depends on mass of WD – Short time scale (~100yrs) could occur for stars near the ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
... When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...