Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
Acetylcholinesterase in Neuron Survival and
... Each year 10,000 new spinal cord injury occurs in USA ...
... Each year 10,000 new spinal cord injury occurs in USA ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Cell Body or Soma The control center of the neuron. Function: Directs impulses from the dendrites to the axon. Nucleus Control center of the Soma. Function: Tells the soma what to do. Axon Pathway for the nerve impulse (electrical message) from the soma to the opposite end of the neuron. My ...
... Cell Body or Soma The control center of the neuron. Function: Directs impulses from the dendrites to the axon. Nucleus Control center of the Soma. Function: Tells the soma what to do. Axon Pathway for the nerve impulse (electrical message) from the soma to the opposite end of the neuron. My ...
HISTOLOGY REVISIT: NEURONS AND NEUROGLIA LEARNING
... Interfacicular oligodendrocyes are found in the white mater lying between the nerve fibers. Perineural oligodendrocyes are present adjacent to perikaryon of neuron (in the gray mater) Perivascular oligodendrocytes found around the blood vessels In perivascular and interfacicular location the oligode ...
... Interfacicular oligodendrocyes are found in the white mater lying between the nerve fibers. Perineural oligodendrocyes are present adjacent to perikaryon of neuron (in the gray mater) Perivascular oligodendrocytes found around the blood vessels In perivascular and interfacicular location the oligode ...
Nervous_System
... lipid and protein sheath covering neuron axons (not all axons are myelinated) Electrically insulates axon and increases conduction speed (Ex. Leaky garden hose) Multiple Sclerosis: Autoimmune disease that breaks down the myelin sheath in the CNS. Tremors: Unregulated electrical impulses ...
... lipid and protein sheath covering neuron axons (not all axons are myelinated) Electrically insulates axon and increases conduction speed (Ex. Leaky garden hose) Multiple Sclerosis: Autoimmune disease that breaks down the myelin sheath in the CNS. Tremors: Unregulated electrical impulses ...
Central nervous system
... 3 kinds of synapses with different modes of action • Excitatory cholinergic synapse • Inhibitory GABA-ergic synapse • Excitatory adrenergic synapse Synaptic delay (.5 msec) – time from arrival of nerve signal at synapse to start of AP in postsynaptic cell ...
... 3 kinds of synapses with different modes of action • Excitatory cholinergic synapse • Inhibitory GABA-ergic synapse • Excitatory adrenergic synapse Synaptic delay (.5 msec) – time from arrival of nerve signal at synapse to start of AP in postsynaptic cell ...
Chapter 7 Part 1 Nervous Tissue
... • The nuclei of the white matter are involved in the relay of sensory information from the rest of the body to the cerebral cortex, as well as in the regulation of autonomic (unconscious) functions such as body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure. ...
... • The nuclei of the white matter are involved in the relay of sensory information from the rest of the body to the cerebral cortex, as well as in the regulation of autonomic (unconscious) functions such as body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure. ...
HBNervous
... terminus; the location of the synapse. Action potential develops in the axon. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter In humans, neurons can grow up to a meter long. All the functions of the nervous system involve neurons co ...
... terminus; the location of the synapse. Action potential develops in the axon. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter In humans, neurons can grow up to a meter long. All the functions of the nervous system involve neurons co ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... • Oligodendrocytes: They coat axons in the CNS with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate more ...
... • Oligodendrocytes: They coat axons in the CNS with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate more ...
The Nervous System - Riverside Preparatory High School
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into ...
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into ...
base text pdf
... cellular mapping of neurons. These studies allow a better insight into the communication of neurons and demonstrate the high potential for the analysis of neural networks. Promising research is going on for the recovery of vision by transfection of different cell types such as ganglion and bipolar c ...
... cellular mapping of neurons. These studies allow a better insight into the communication of neurons and demonstrate the high potential for the analysis of neural networks. Promising research is going on for the recovery of vision by transfection of different cell types such as ganglion and bipolar c ...
Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]
... • One person holds the yard stick up • Second person is being tested at how fast they can respond to the yard stick falling • The first person will release the yard stick and the second person will catch it. They will record where their hand grabs the yard stick. • Using this formula: t = √2y/g , y ...
... • One person holds the yard stick up • Second person is being tested at how fast they can respond to the yard stick falling • The first person will release the yard stick and the second person will catch it. They will record where their hand grabs the yard stick. • Using this formula: t = √2y/g , y ...
The Nervous System Ch. 12 & 13
... closer to 0 mV and will continue to +30 mV. Means we now have more + ions in the cell than outside of the cell. Voltage-gated Na+ channels only stay open for about 1 millisecond before they close. Action potentials are all-or-none, either they will occur or not at all. Once the peak of the action po ...
... closer to 0 mV and will continue to +30 mV. Means we now have more + ions in the cell than outside of the cell. Voltage-gated Na+ channels only stay open for about 1 millisecond before they close. Action potentials are all-or-none, either they will occur or not at all. Once the peak of the action po ...
Brain and Behaviour
... For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the threshold or they don’t . If the Threshold is reached then the neuron transmits an electrical impu ...
... For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the threshold or they don’t . If the Threshold is reached then the neuron transmits an electrical impu ...
THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... Stage 1: The neuron is at rest A neuron is resting when its membrane forms a partial barrier between the inside and outside of the neuron. The solution contains electrically charged particles called ions. When the neuron is at rest, there are more negative ions on the outside which is called the res ...
... Stage 1: The neuron is at rest A neuron is resting when its membrane forms a partial barrier between the inside and outside of the neuron. The solution contains electrically charged particles called ions. When the neuron is at rest, there are more negative ions on the outside which is called the res ...
Message Transmission
... Resting potential • This is a nerve cell that is ready to work. • The cell membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+, so more positives are leaving than entering. Add the Na+ K+ pump ( a mechanism in the cell membrane that shunts the Na+ back out) and the inside is decidedly negative and the out ...
... Resting potential • This is a nerve cell that is ready to work. • The cell membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+, so more positives are leaving than entering. Add the Na+ K+ pump ( a mechanism in the cell membrane that shunts the Na+ back out) and the inside is decidedly negative and the out ...
notes as
... Idealized neurons • To model things we have to idealize them (e.g. atoms) – Idealization removes complicated details that are not essential for understanding the main principles – Allows us to apply mathematics and to make analogies to other, familiar systems. – Once we understand the basic princip ...
... Idealized neurons • To model things we have to idealize them (e.g. atoms) – Idealization removes complicated details that are not essential for understanding the main principles – Allows us to apply mathematics and to make analogies to other, familiar systems. – Once we understand the basic princip ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... • Neural crest cells transplanted to a new part of the neural crest migrate to the destination that is appropriate for cells in the new location; thus the migration routes must be encoded in the medium through which they travel rather than in the cells themselves; many different types of chemical si ...
... • Neural crest cells transplanted to a new part of the neural crest migrate to the destination that is appropriate for cells in the new location; thus the migration routes must be encoded in the medium through which they travel rather than in the cells themselves; many different types of chemical si ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... 6. Because the Na & K ions have different voltages, an electrical differential exists between the inside & outside of the cell membrane. 7. The Resting Potential of a “charged” or Polarized axon is –70 mV. (The inside is negative relative to the outside) C. The Acton Potential 1. The transmission of ...
... 6. Because the Na & K ions have different voltages, an electrical differential exists between the inside & outside of the cell membrane. 7. The Resting Potential of a “charged” or Polarized axon is –70 mV. (The inside is negative relative to the outside) C. The Acton Potential 1. The transmission of ...
Neurons - WordPress.com
... the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal buttons, through which messages are sent to other neurons or to muscles or glands transmit an electro-chemical signal to other neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. ...
... the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal buttons, through which messages are sent to other neurons or to muscles or glands transmit an electro-chemical signal to other neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. ...
Emergence of Sense-Making Behavior by the Stimulus Avoidance
... higher spatio-temporal resolution. The number of electrodes in conventional MEAs is small, usually about 64, and the locations of the recording electrodes are predetermined with an inter-electrode distance of about 200 m; thus, it is difficult to identify signals from an individual cell. In contrast ...
... higher spatio-temporal resolution. The number of electrodes in conventional MEAs is small, usually about 64, and the locations of the recording electrodes are predetermined with an inter-electrode distance of about 200 m; thus, it is difficult to identify signals from an individual cell. In contrast ...
brain - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... This is what musicians, athletes and others often refer to as being “in the zone.” Spreng’s findings involve the whole brain. However, those changes actually reflect what’s happening at the level of individual cells. How neurons function The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells, called neuron ...
... This is what musicians, athletes and others often refer to as being “in the zone.” Spreng’s findings involve the whole brain. However, those changes actually reflect what’s happening at the level of individual cells. How neurons function The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells, called neuron ...
Slide ()
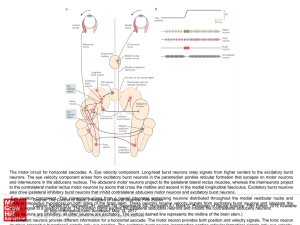
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...












![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)