Electrophysiology & fMRI
... Neurons spend more energy on “listening” than “talking” Dogma: Neural output (firing rate) is the interesting part. ...
... Neurons spend more energy on “listening” than “talking” Dogma: Neural output (firing rate) is the interesting part. ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... 1. Sensory Input: Conduction of signals from sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, skin, etc.) to information processing centers (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signa ...
... 1. Sensory Input: Conduction of signals from sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, skin, etc.) to information processing centers (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signa ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... a) Single main dendrite and axon b) Is found in the brain and spinal cord c) Has several dendrites and a single axon d) Has a single process that extends from the cell body e) Found in the peripheral nervous system. 3) Which of the option is true? Serotonin: a) Is used by the brain and autonomic neu ...
... a) Single main dendrite and axon b) Is found in the brain and spinal cord c) Has several dendrites and a single axon d) Has a single process that extends from the cell body e) Found in the peripheral nervous system. 3) Which of the option is true? Serotonin: a) Is used by the brain and autonomic neu ...
Slide ()
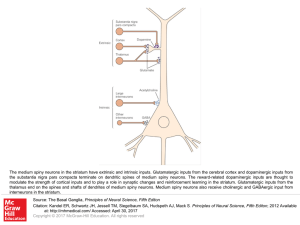
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
Session 2. Synaptic Plasticity (Chair, H. Kamiguchi)
... subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is tyrosine-phosphorylated in the brain, with Tyr-1472 its major phosphorylation site. We have generated mutant mice with a knockin mutation of the Tyr-1472 site to phenylalanine (Y1472F). These mutant mice (YF/YF mice) show that Tyr-1472 phosphory ...
... subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is tyrosine-phosphorylated in the brain, with Tyr-1472 its major phosphorylation site. We have generated mutant mice with a knockin mutation of the Tyr-1472 site to phenylalanine (Y1472F). These mutant mice (YF/YF mice) show that Tyr-1472 phosphory ...
Ch3
... Tell whether the following statement is true or false: If you get a paper cut, epithelial tissue will be replaced with connective tissue. ...
... Tell whether the following statement is true or false: If you get a paper cut, epithelial tissue will be replaced with connective tissue. ...
Biosychology_Intro Reading
... branches: the sympathetic system regulates the flight-or-fight responses, while the parasympathetic system helps maintain normal body functions and conserves physical resources. The Brain The outermost part of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex. This portion of the brain is responsible for fu ...
... branches: the sympathetic system regulates the flight-or-fight responses, while the parasympathetic system helps maintain normal body functions and conserves physical resources. The Brain The outermost part of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex. This portion of the brain is responsible for fu ...
Tongue: Herpes Simplex Glossitis
... Brain section stained with antibody against herpes simplex Even at this magnification, it is easy to pick out cells that are positive for the virus (arrows). ...
... Brain section stained with antibody against herpes simplex Even at this magnification, it is easy to pick out cells that are positive for the virus (arrows). ...
Invertebrate nervous systems:
... Briefly, the modifications were these:1.The hindbrain became divided into a ventral portion, called the medulla oblongata, a dorsal portion, the cerebellum, and the anterior pons. The medulla became specialized as a control center for some autonomic and somatic pathways concerned with vital function ...
... Briefly, the modifications were these:1.The hindbrain became divided into a ventral portion, called the medulla oblongata, a dorsal portion, the cerebellum, and the anterior pons. The medulla became specialized as a control center for some autonomic and somatic pathways concerned with vital function ...
Design of Intelligent Machines Heidi 2005
... They are significantly bigger than minicolumns, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm and have 4000-8000 neurons ...
... They are significantly bigger than minicolumns, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm and have 4000-8000 neurons ...
File - Mr. Jacobson`s Site
... which an action potential travels down an axon • The diameter of the axon, the larger the diameter the faster the action potential • The presence of myelin around the axon, myelin insulates the axon and allows the action potential to travel quicker ...
... which an action potential travels down an axon • The diameter of the axon, the larger the diameter the faster the action potential • The presence of myelin around the axon, myelin insulates the axon and allows the action potential to travel quicker ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... Afferent (sensory): neurons that transmit information into the CNS from sensory cells or sensory receptors outside the nervous system (dorsal root ganglion cell and neurons in the sensory nucleus of the fifth cranial nerve). Interneurons: relay or association neurons Efferent (motor): neurons that t ...
... Afferent (sensory): neurons that transmit information into the CNS from sensory cells or sensory receptors outside the nervous system (dorsal root ganglion cell and neurons in the sensory nucleus of the fifth cranial nerve). Interneurons: relay or association neurons Efferent (motor): neurons that t ...
Neuroanatomy Handout #1: The Motor Neuron
... unmyelinated sections called nodes of Ranvier. • At each node of Ranvier, the action potential is regenerated by a chain of positively charged ions pushed along by the previous segment. ...
... unmyelinated sections called nodes of Ranvier. • At each node of Ranvier, the action potential is regenerated by a chain of positively charged ions pushed along by the previous segment. ...
Journal Paper 1 - Information Services and Technology
... most recent work shows that glia also communicate among themselves, in a separate but parallel network to the neural network, influencing how well the brain performs. Neuroscientists are cautious about assigning new prominence to glia too quickly, yet they are excited by the prospect that more than ...
... most recent work shows that glia also communicate among themselves, in a separate but parallel network to the neural network, influencing how well the brain performs. Neuroscientists are cautious about assigning new prominence to glia too quickly, yet they are excited by the prospect that more than ...
Principles of neural ensemble physiology underlying the operation
... neural redundancy in that different combinations of single neurons belonging to a neural circuit can produce different spatiotemporal firing patterns that end up encoding the same motor outputs166. Degenerate coding has been demonstrated in several neural circuits, including the pyloric network of t ...
... neural redundancy in that different combinations of single neurons belonging to a neural circuit can produce different spatiotemporal firing patterns that end up encoding the same motor outputs166. Degenerate coding has been demonstrated in several neural circuits, including the pyloric network of t ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue
... between smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and some neurons of the CNS. Provide fast, synchronized, and two-way transmission of information. 2. Chemical Synapses: Communication via chemical neurotransmitters that diffuse across a synaptic cleft. Provides slow one-way information flow ...
... between smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and some neurons of the CNS. Provide fast, synchronized, and two-way transmission of information. 2. Chemical Synapses: Communication via chemical neurotransmitters that diffuse across a synaptic cleft. Provides slow one-way information flow ...
Modeling and interpretation of extracellular potentials
... Current source density • Neural tissue is a spaghettilike mix of dendrites, axons, glial branches at micrometer scale • In general, the extracellular potential will get contributions from a mix of all these ...
... Current source density • Neural tissue is a spaghettilike mix of dendrites, axons, glial branches at micrometer scale • In general, the extracellular potential will get contributions from a mix of all these ...
the structure of the nervous system
... • Axon Hillock- the conical area of origin of the axon from the nerve cell body • Telodendria- structures at the terminal branches of axon that contain neurotransmitters • Synaptic terminal- a bulb at the end of the axon in which the neurotransmitter molecules are stored and released ...
... • Axon Hillock- the conical area of origin of the axon from the nerve cell body • Telodendria- structures at the terminal branches of axon that contain neurotransmitters • Synaptic terminal- a bulb at the end of the axon in which the neurotransmitter molecules are stored and released ...
PDF
... Therefore, it is likely that these excitatory effects were mediated indirectly, through higher auditory centers, and re¯ected a long-lasting multisynaptic activity triggered by sounds. The discrepancy between our ®ndings and previously observed shortlatency excitation of CN neurons [15] could have t ...
... Therefore, it is likely that these excitatory effects were mediated indirectly, through higher auditory centers, and re¯ected a long-lasting multisynaptic activity triggered by sounds. The discrepancy between our ®ndings and previously observed shortlatency excitation of CN neurons [15] could have t ...
Slide 1
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
Current concepts in central nervous system regeneration
... Aguayo has shown that Muller cells engineered to produce BDNF may temporarily rescue injured retinal ganglion cells.40 Fibroblasts engineered to express BDNF have also been shown to promote long-tract regeneration in the spinal cord.41 Various studies have only shown adequate regeneration in the mil ...
... Aguayo has shown that Muller cells engineered to produce BDNF may temporarily rescue injured retinal ganglion cells.40 Fibroblasts engineered to express BDNF have also been shown to promote long-tract regeneration in the spinal cord.41 Various studies have only shown adequate regeneration in the mil ...
Slide ()
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
autonomic nervous system
... Sympathetic Division • Fight or Flight response • Increases activity under conditions of physical or physiological stress • All resources for physical exertion are activated ...
... Sympathetic Division • Fight or Flight response • Increases activity under conditions of physical or physiological stress • All resources for physical exertion are activated ...