Day 9 - Ch. 4 -
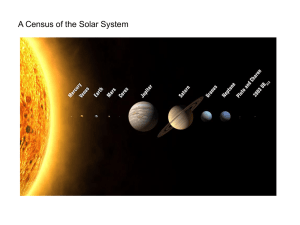
... Each planet is relatively isolated in space. The orbits of the planets are nearly circular. The orbits of the planets all lie in nearly the same plane. Direction of planet’s movement in orbit is same as sun’s rotation. Direction of planet’s rotation is same as sun’s rotation. (*usually*) Direction o ...
... Each planet is relatively isolated in space. The orbits of the planets are nearly circular. The orbits of the planets all lie in nearly the same plane. Direction of planet’s movement in orbit is same as sun’s rotation. Direction of planet’s rotation is same as sun’s rotation. (*usually*) Direction o ...
Ch. 3 Sec. 5 Notes
... -Called the asteroid belt *More than 100,000 asteroids have been discovered *The largest asteroid, Ceres, was recently classified as a dwarf planet *Some asteroids have an extremely elliptical orbit that crosses paths with Earth -Someday, one of these asteroids could hit Earth and wipe out our entir ...
... -Called the asteroid belt *More than 100,000 asteroids have been discovered *The largest asteroid, Ceres, was recently classified as a dwarf planet *Some asteroids have an extremely elliptical orbit that crosses paths with Earth -Someday, one of these asteroids could hit Earth and wipe out our entir ...
ppt-file 2.4 MB
... have a better chance." The 47 UMa system intrigues experts because the star has roughly the same mass, age and spectrum as the Sun. Moreover, it hosts two giant gas planets, analogous to Jupiter and Saturn. It is thought that such large planets help to shelter Earth from bombardment by comets and as ...
... have a better chance." The 47 UMa system intrigues experts because the star has roughly the same mass, age and spectrum as the Sun. Moreover, it hosts two giant gas planets, analogous to Jupiter and Saturn. It is thought that such large planets help to shelter Earth from bombardment by comets and as ...
Big Bang
... A planet of the red dwarf star Gliese 581, appeared to be the best known example of a possibly terrestrial exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone that surrounds its star. The number of Earth-like planets increase all the time. ...
... A planet of the red dwarf star Gliese 581, appeared to be the best known example of a possibly terrestrial exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone that surrounds its star. The number of Earth-like planets increase all the time. ...
Solar System
... Universe: all of space and ________________________________________________ Galaxy: A large group of __________________________________, solar systems, and associated gas and dust in space that is bound by _____________________________ Solar System: Composed of one or more ____________________ ...
... Universe: all of space and ________________________________________________ Galaxy: A large group of __________________________________, solar systems, and associated gas and dust in space that is bound by _____________________________ Solar System: Composed of one or more ____________________ ...
25drake3s
... ne = Average number of suitable planets per star fl = Fraction of suitable planets on which life ...
... ne = Average number of suitable planets per star fl = Fraction of suitable planets on which life ...
Life on Billions of Planets
... tens of billions of Goldilocks planets are peppered throughout the Milky Way, with a hundred or so just in our solar system's immediate neighborhood. For planet hunters, that's an especially tantalizing prospect. Ground- and space-based telescopes have discovered many hundreds of worlds orbiting sta ...
... tens of billions of Goldilocks planets are peppered throughout the Milky Way, with a hundred or so just in our solar system's immediate neighborhood. For planet hunters, that's an especially tantalizing prospect. Ground- and space-based telescopes have discovered many hundreds of worlds orbiting sta ...
Other Planetary Systems
... … the possibility that some things may have significantly changed (either in the SS, or in other systems) since the formative stages. Some important evidence may have been eradicated; or the ‘final’ arrangement may have slowly evolved over billions of years ...
... … the possibility that some things may have significantly changed (either in the SS, or in other systems) since the formative stages. Some important evidence may have been eradicated; or the ‘final’ arrangement may have slowly evolved over billions of years ...
Lecture 1 Review Sheet
... List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean when astronomers speak of a planet having “cleared all of its orbit”? Why is there an asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter? What are the three original sources of most meteorites? Why can meteorites most ...
... List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean when astronomers speak of a planet having “cleared all of its orbit”? Why is there an asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter? What are the three original sources of most meteorites? Why can meteorites most ...
Earth Science Chapter Two: What Makes Up the Solar System
... 2. How many planets are there in our solar system? 3. Ashley makes a model of the solar system. Which planet should she space between Earth and Mercury in her model? 4. Name the order of the planets in our solar system. 5. What planets make up the four inner planets? 6. How did the inner planets get ...
... 2. How many planets are there in our solar system? 3. Ashley makes a model of the solar system. Which planet should she space between Earth and Mercury in her model? 4. Name the order of the planets in our solar system. 5. What planets make up the four inner planets? 6. How did the inner planets get ...
Lecture 27 (pdf from the powerpoint)
... •fp = the fraction of those stars which have planets •Estimated by Drake as 0.5. It is now known from modern planet searches that at least 10% of sunlike stars have planets, and the true proportion may be much higher, since only planets gas-giant size and larger can be detected with current technolo ...
... •fp = the fraction of those stars which have planets •Estimated by Drake as 0.5. It is now known from modern planet searches that at least 10% of sunlike stars have planets, and the true proportion may be much higher, since only planets gas-giant size and larger can be detected with current technolo ...
The Solar System
... Grouping Planets Planets divided into 2 groups Inner: Mercury, Venus, Earth, & Mars Outer: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto * Separated by asteroid belt ...
... Grouping Planets Planets divided into 2 groups Inner: Mercury, Venus, Earth, & Mars Outer: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto * Separated by asteroid belt ...
25drake6s
... A planet of moderate mass in the habitable zone Organic compounds reacting to form simple life Life evolving over billions of years with no ...
... A planet of moderate mass in the habitable zone Organic compounds reacting to form simple life Life evolving over billions of years with no ...
Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015
... • Describe the Sun’s internal structure using stellar structure equations, the nuclear generation of energy in the Sun and how this energy is transported to the surface • Understand and use the concepts of hydrostatic equilibrium and the Schwarzschild convective stability criterion in stellar interi ...
... • Describe the Sun’s internal structure using stellar structure equations, the nuclear generation of energy in the Sun and how this energy is transported to the surface • Understand and use the concepts of hydrostatic equilibrium and the Schwarzschild convective stability criterion in stellar interi ...
Lecture 22 - Star Formation from Molecular Clouds
... • We understand the physics of these processes (at least partially) • We believe the Sun formed like this. • What characteristic of the solar system can we see that is an indicator of the processes of contraction, jet formation, accretion disk formation, etc? ...
... • We understand the physics of these processes (at least partially) • We believe the Sun formed like this. • What characteristic of the solar system can we see that is an indicator of the processes of contraction, jet formation, accretion disk formation, etc? ...
The Solar System
... Sun estimated age is based on all the circumstantial evidence ~ 4.5 - 5 billion years. It has about a 10 billion-year life. ...
... Sun estimated age is based on all the circumstantial evidence ~ 4.5 - 5 billion years. It has about a 10 billion-year life. ...
Lecture 1 Review Sheet
... List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean when astronomers speak of a planet having “cleared all of its orbit”? Why is there an asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter? What are the three original sources of most meteorites? Why can meteorites most ...
... List all the planets and dwarf planets from closest to farthest from the sun What does it mean when astronomers speak of a planet having “cleared all of its orbit”? Why is there an asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter? What are the three original sources of most meteorites? Why can meteorites most ...
Unit: Southern Europe
... GLE 0507.6.2: I can use charts to locate and identify star patterns. This means I can use a star chart to identify constellations in the night’s sky throughout the year. I can explain why it is important to know the time of night, the time of year, and the latitude to correctly identify the constell ...
... GLE 0507.6.2: I can use charts to locate and identify star patterns. This means I can use a star chart to identify constellations in the night’s sky throughout the year. I can explain why it is important to know the time of night, the time of year, and the latitude to correctly identify the constell ...
Is there anybody out there?
... ne = planets in a stars habitable zone --> 1 ng = stars in a galactic habitable zone fi = fraction of habitable planets where life does arise ...
... ne = planets in a stars habitable zone --> 1 ng = stars in a galactic habitable zone fi = fraction of habitable planets where life does arise ...
Formation of the Solar System Target 1 Notes
... __________________. Surrounding the sun was a rotating disc of space dust and gas. Over millions of years these particles of dust and gas began to collide with each other and increase in size and mass, forming the planets and many other bodies such as comets and asteroids which continue to orbit the ...
... __________________. Surrounding the sun was a rotating disc of space dust and gas. Over millions of years these particles of dust and gas began to collide with each other and increase in size and mass, forming the planets and many other bodies such as comets and asteroids which continue to orbit the ...
5-SolarSystem
... Fundamental Properties of the solar System 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun an ...
... Fundamental Properties of the solar System 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun an ...















![Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007097773_1-15996a23762c2249db404131f50612f3-300x300.png)